1,000 AI agents can now predict human behavior with 85% accuracy in social experiments

Researchers from Stanford, Washington University, and Google DeepMind have created AI agents that can closely mimic human behavior in social experiments.
According to the study, such simulations could serve as a laboratory for testing theories in fields such as economics, sociology, organization, and political science. The team built these agents using interview data from more than 1,000 people selected to represent the US population across age, gender, education, and political views.
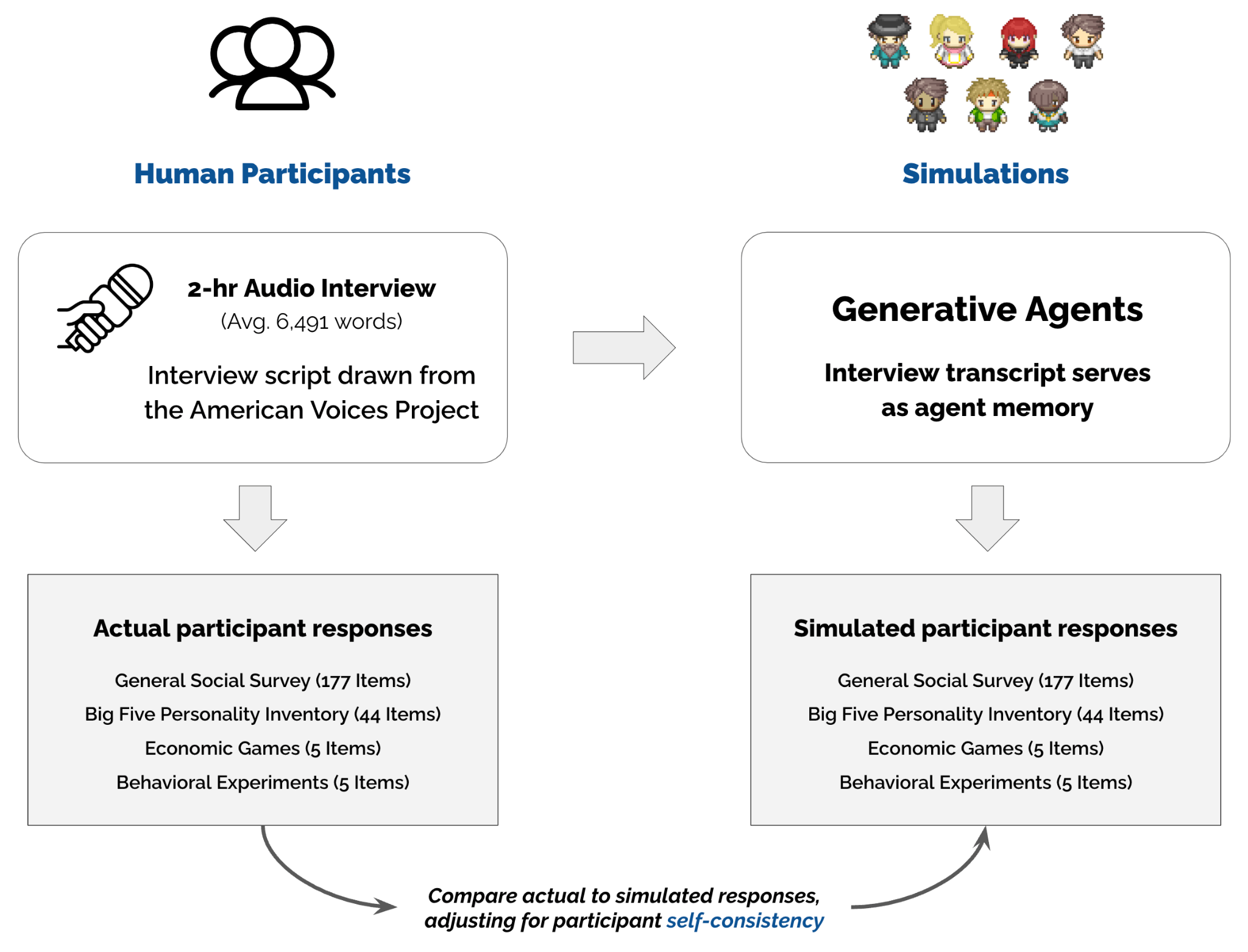
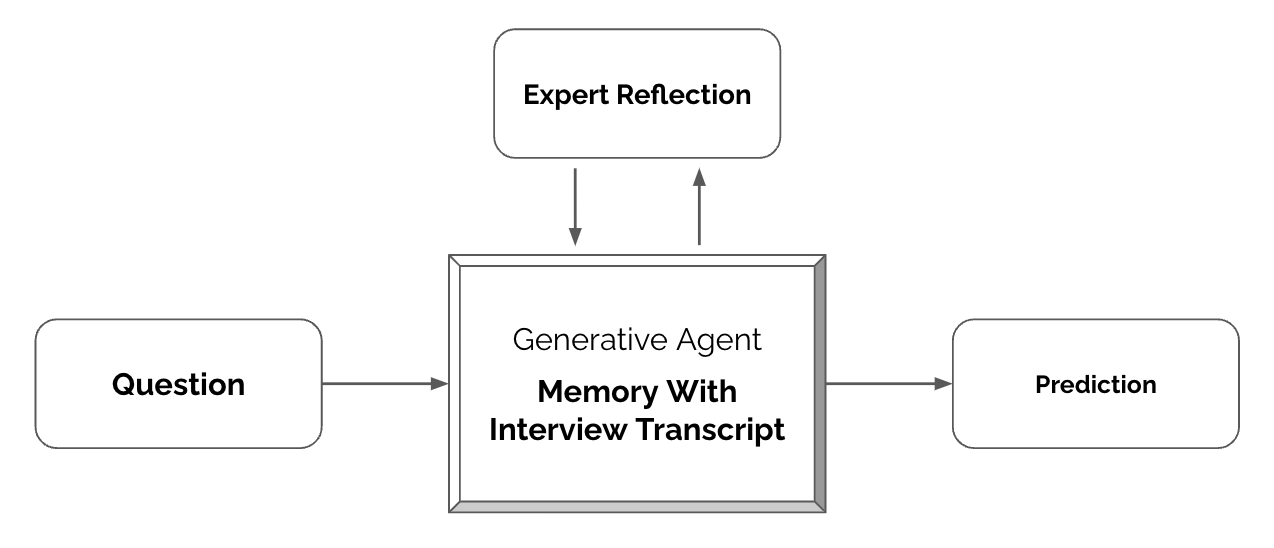
The system works by combining detailed interview transcripts with GPT-4o. When someone queries an agent, it loads the interview transcript into the model and instructs it to imitate the person based on their responses. To create these transcripts, the researchers conducted two-hour interviews with each participant and used OpenAI's Whisper model to convert the conversations to text.
Interview-based agents outperform demographic agents
The research team put these AI agents through several tests to measure their ability to predict human behavior. They used questions from the General Social Survey, Big Five personality assessments, and multiple behavioral economics games.
The AI agents based on interview data predicted human GSS responses with 85% accuracy, performing significantly better than AI agents that only used basic demographic information.
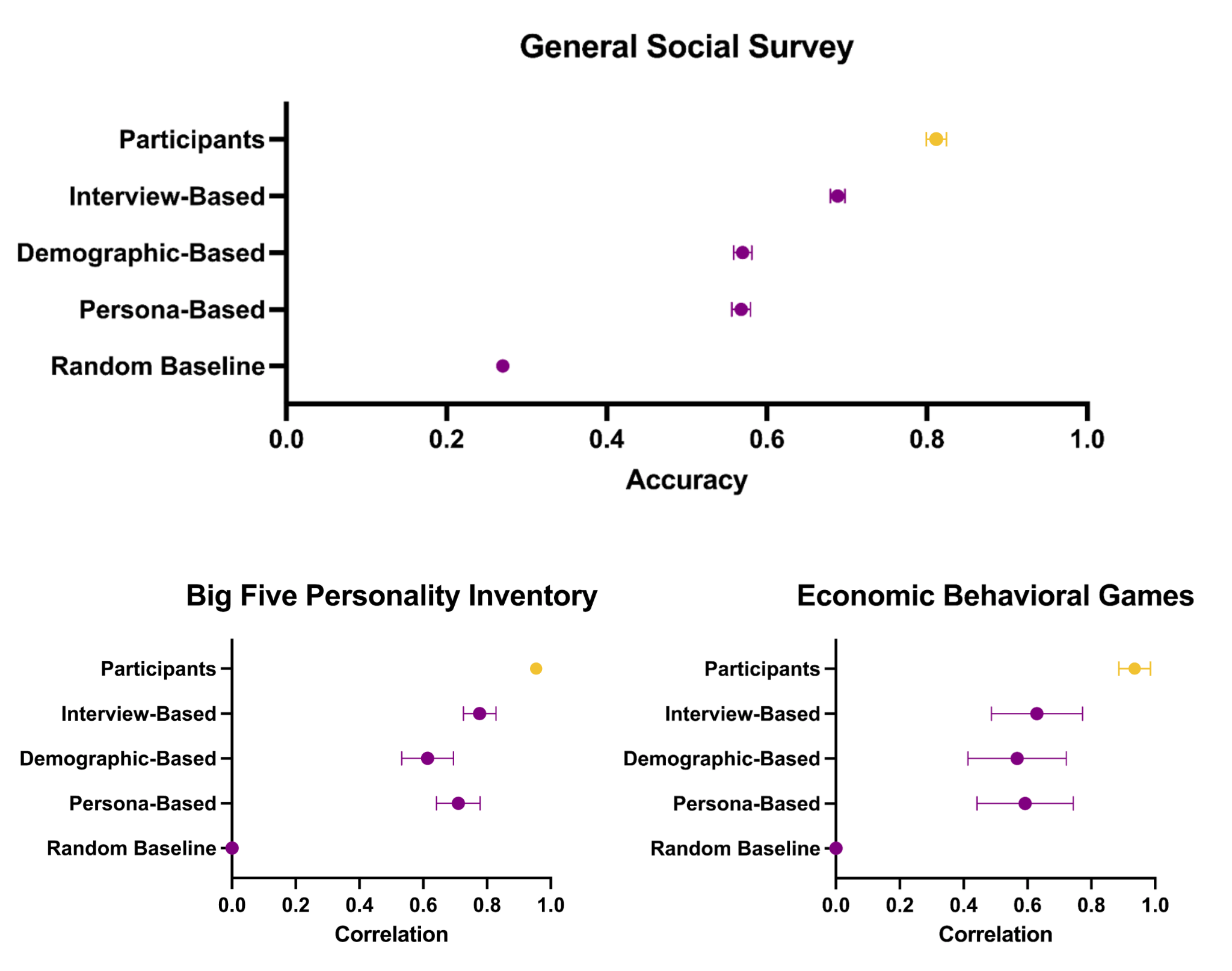
The researchers ran five social science experiments with both human participants and AI agents. In four out of these five studies, the AI agents produced results that closely matched human responses. The statistical measurements showed a strong correlation between AI and human responses, with a correlation coefficient of 0.98.
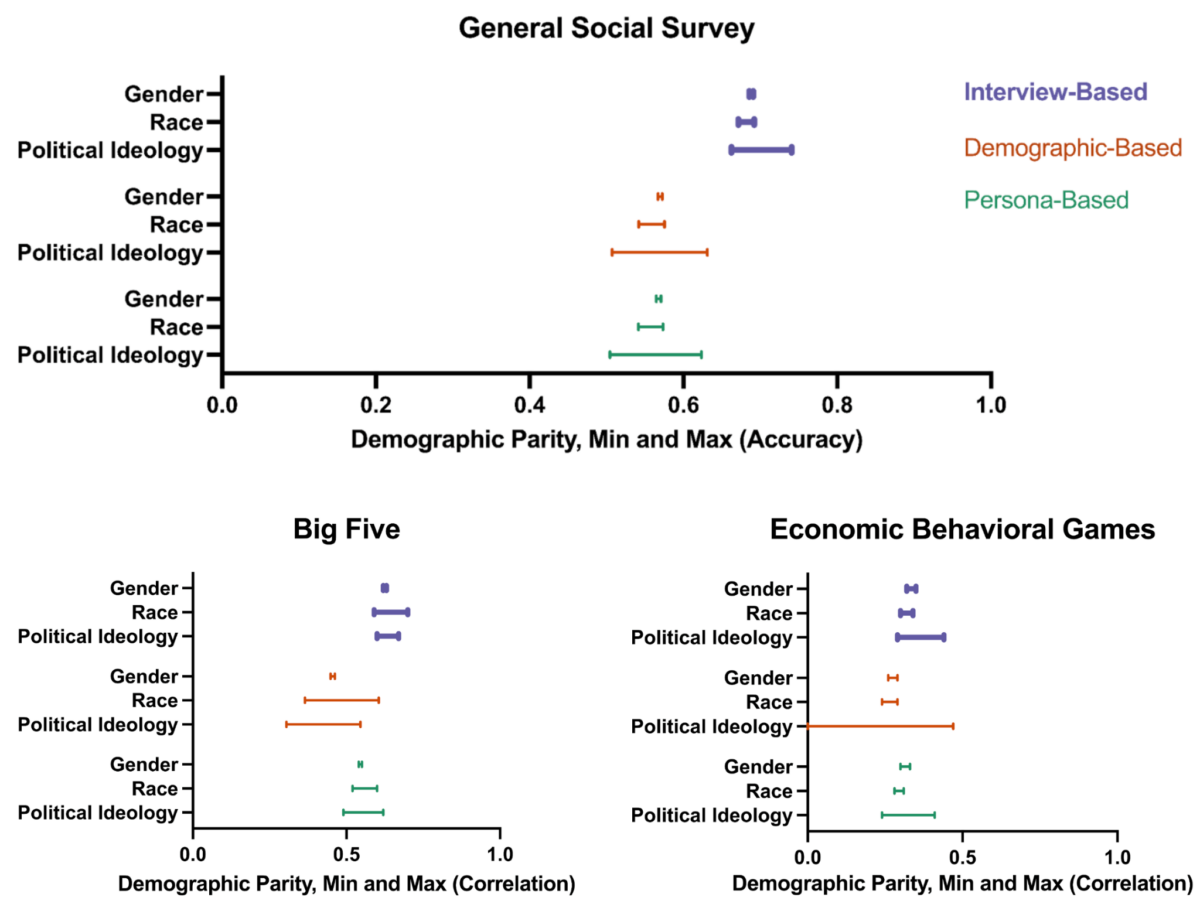
The interview-based approach showed significant improvements in handling bias compared to methods using only demographics. The AI agents made more accurate predictions across different political ideologies and ethnic groups. They also showed more balanced performance when analyzing responses between various demographic categories.
Access to research data
The research team has made their dataset of 1,000 AI agents available to other scientists through GitHub. They created a two-tier access system to protect participant privacy while supporting further research. Scientists can freely access combined response data for specific tasks, while access to individual response data for open-ended research requires special permission.
This system aims to help researchers study human behavior while maintaining strong privacy protections for the original interview participants. The dataset could serve as a testing ground for theories in economics, sociology, and political science.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.