OpenAI says its latest models outperform doctors in medical benchmark
OpenAI has released a new benchmark for testing AI systems in healthcare. Called HealthBench, it's designed to evaluate how well language models handle realistic medical conversations. According to OpenAI, its latest models outperform doctors on the test.
The company says earlier benchmarks fell short—they didn't reflect real-world doctor-patient interactions, lacked input from medical experts, or weren't detailed enough to measure progress in newer models. To fix that, OpenAI collaborated with 262 doctors from 60 countries. Together, they created 5,000 realistic medical scenarios covering 26 specialties and 49 languages.
HealthBench spans seven medical domains, from emergency medicine to global health. Each AI response is rated across five categories: communication quality, instruction-following, accuracy, contextual understanding, and completeness. Altogether, the system applies 48,000 medically grounded evaluation points.
The scoring is handled by GPT-4.1. To check how reliable that is, OpenAI compared the model's evaluations with those of human doctors. The results showed that GPT-4.1's judgments matched human assessments at about the same level of agreement you'd see between different doctors.
GPT-4.1 and o3 outscore doctors—at least on this test
OpenAI says its latest models—GPT-4.1 and o3—outperformed physician responses on the HealthBench benchmark. In early tests from September 2024, doctors could improve older model outputs by editing them, while unaided doctor responses scored the lowest. But by April 2025, the results had shifted: GPT-4.1 and o3 outperformed physicians even without any additional input or refinement.
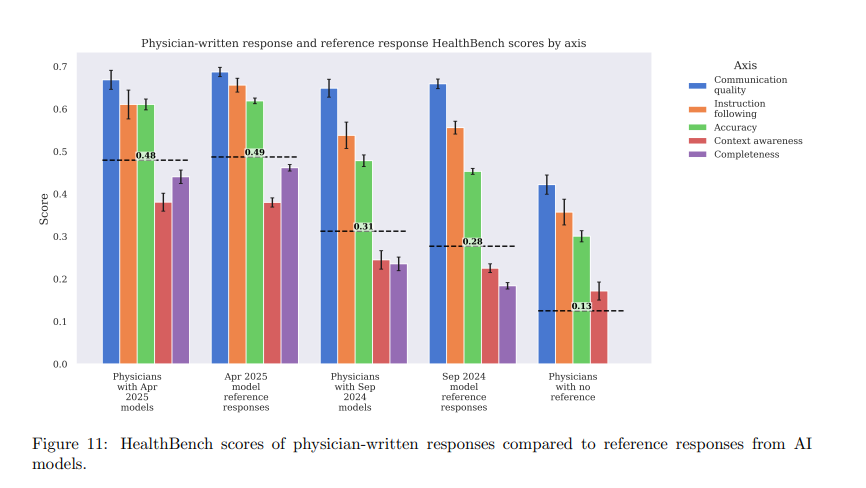
OpenAI notes that the comparison has important limitations. Doctors don't typically write chat-style responses to medical questions, so the benchmark doesn't reflect how clinical care actually works. Instead, it tests how well language models handle a very specific kind of communication—one that may play to AI's strengths more than a physician's.
In terms of raw scores, the o3 model reached 0.60 on the benchmark, nearly twice the 0.32 scored by GPT-4o in August 2024. Only a few competing models came close: xAI's Grok 3 scored 0.54, and Google's Gemini 2.5 hit 0.52.
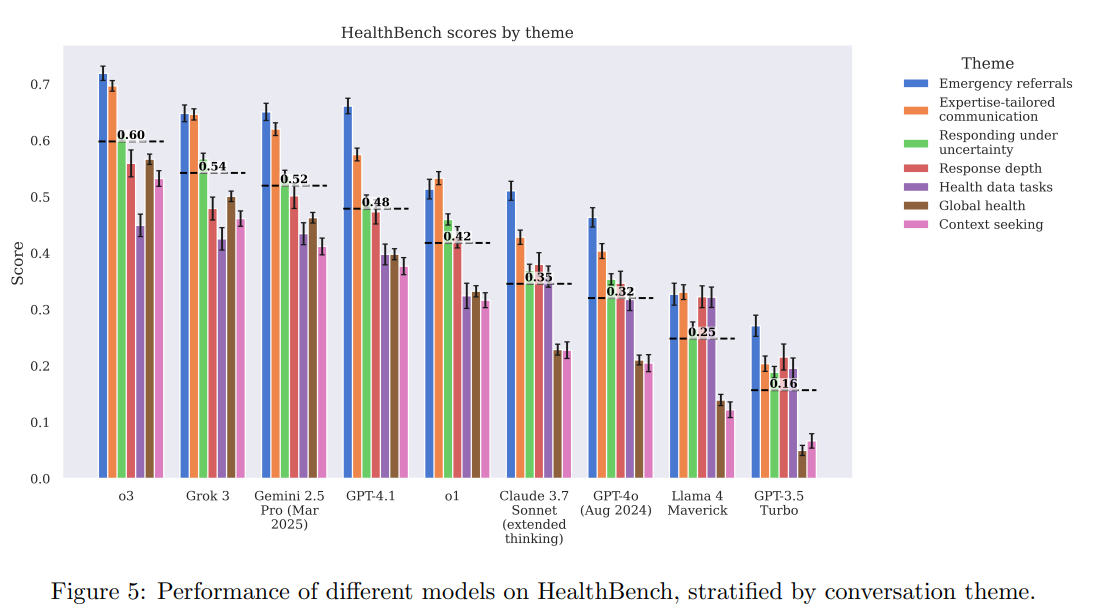
Measuring worst-case reliability
In healthcare, a single wrong answer can outweigh dozens of correct ones. HealthBench includes a stress test to measure worst-case performance: how good is the least helpful response a model gives? OpenAI says its latest models show major improvements here too, but admits there's still work to be done.
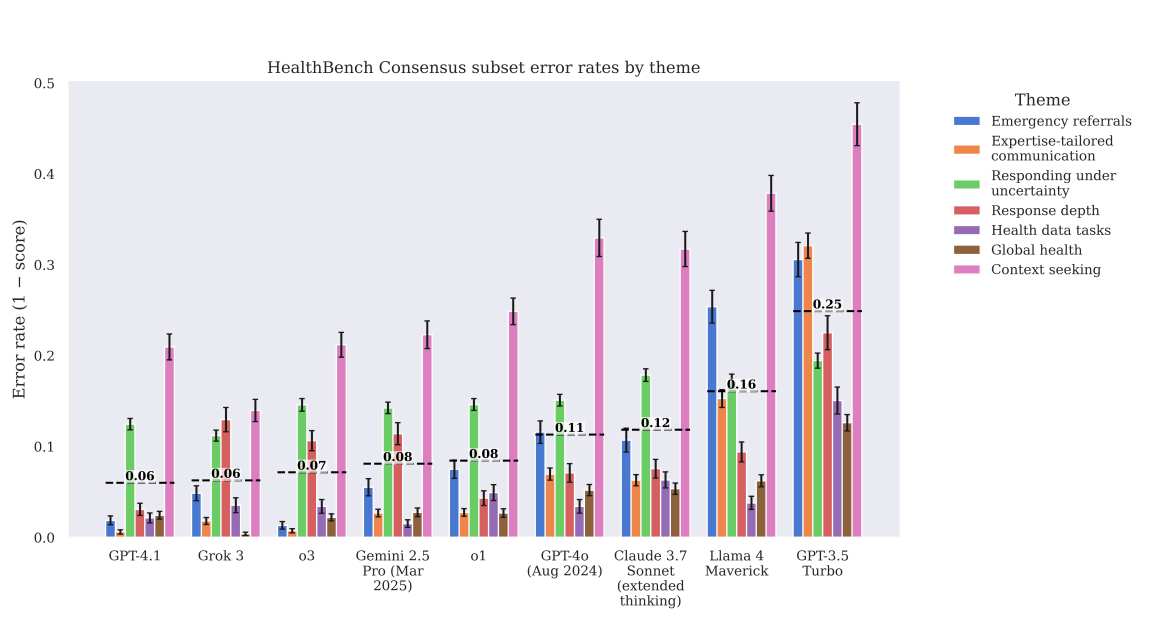
Efficiency is another focus. OpenAI says its compact GPT-4.1 nano model is 25 times more cost-effective than the earlier GPT-4o from August 2024, while also delivering better results. That could make it more accessible in low-resource settings.
To support further testing, OpenAI has released two additional datasets: HealthBench Consensus and HealthBench Hard. The "Consensus" set includes only highly validated criteria, while the "Hard" set features 1,000 especially difficult cases where most models still fail.
All test data and evaluation methods are available on GitHub. OpenAI has also published a detailed paper and is encouraging researchers to build on the benchmark.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.