AI wins 40% of a million dollar budget in OpenAI's latest coding benchmark

A new benchmark from OpenAI reveals both the promise and limitations of AI in software development. While AI models can handle many programming tasks, they still struggle with complex software projects that require deep understanding and comprehensive solutions.
OpenAI's SWE-Lancer benchmark put AI models through their paces using 1,400 actual jobs from Upwork, representing $1 million worth of development work. The evaluation focused on two key areas: direct development tasks and project management decisions.
The development challenges ranged from simple $50 bug fixes to sophisticated $32,000 feature implementations. On the simpler end, AI tackled issues like fixing redundant API calls. More complex tasks included building cross-platform video playback functionality for web, iOS, Android, and desktop applications. A mid-range $1,000 task involved resolving inconsistencies between avatar images on different pages.
Evaluating AI's project management capabilities
The benchmark also tested AI's ability to evaluate different solutions proposed by human developers. For example, when reviewing proposals for an iOS image insertion feature, the AI needed to assess multiple factors: how well each solution handled different clipboard formats, whether it minimized permission requests, and how closely it matched standard iOS behavior.
OpenAI employed end-to-end testing developed and triple-verified by experienced developers. Unlike simple unit tests, these simulations covered complete user workflows - for instance, testing the avatar bug required logging in, uploading profile pictures, and cross-account interactions.
AI models show progress but still trail human developers
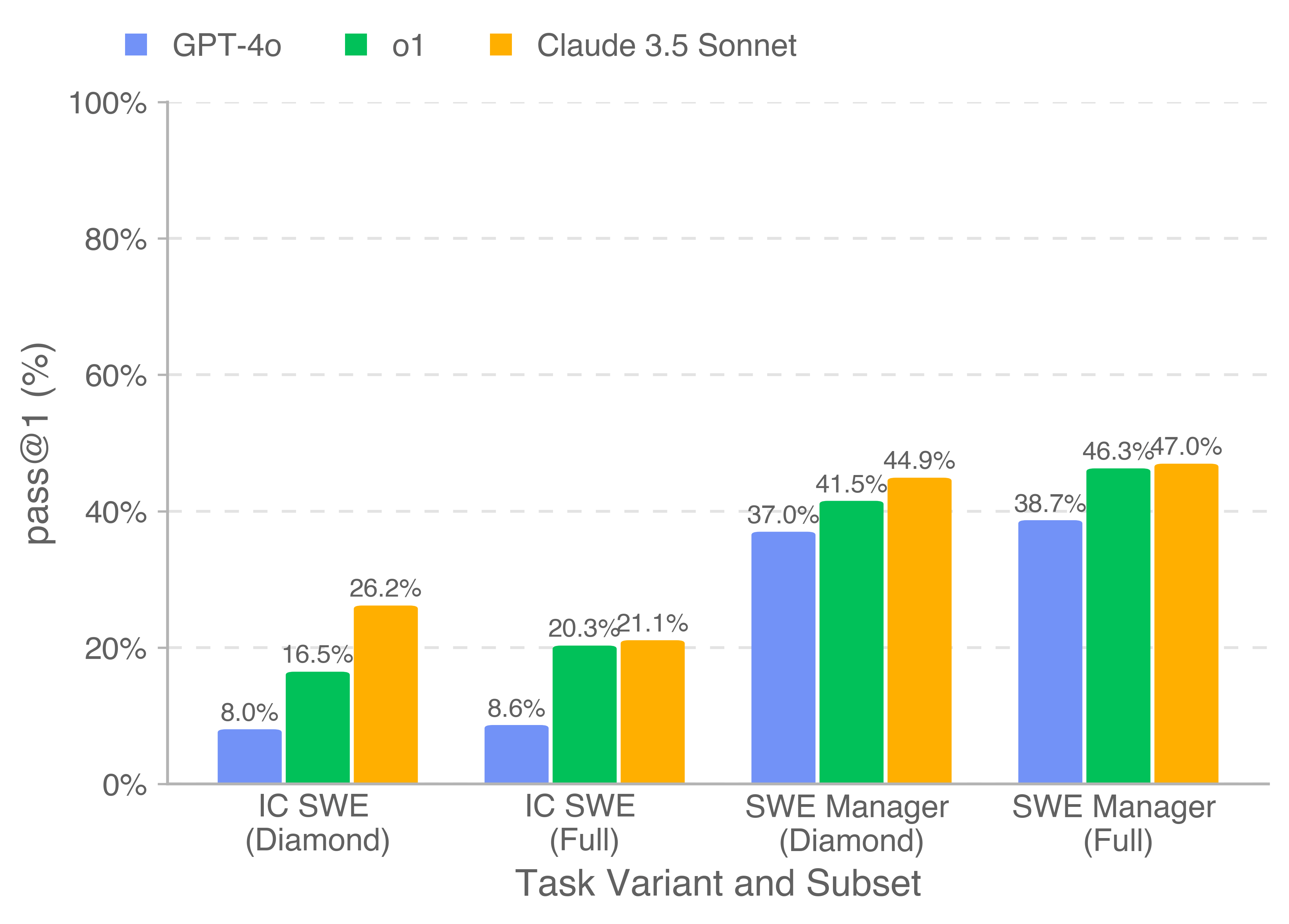
The best-performing model, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, successfully handled 26.2% of coding tasks and 44.9% of project management decisions. While this falls short of human capabilities, it represents significant earning potential.
On the public SWE-Lancer Diamond dataset alone, Claude 3.5 Sonnet could have earned $208,050 from available projects worth $500,800. When scaled to the complete million-dollar dataset, the AI's performance suggests it could handle tasks worth more than $400,000 - nearly half of the total project budget.
A key weakness emerged during detailed analysis: while AI models could often identify problematic code sections, they frequently struggled to understand root causes and develop comprehensive fixes.
To advance research in automated software development, OpenAI has released the SWE-Lancer Diamond dataset and Docker image as open source on GitHub. This open-source release enables researchers and companies to benchmark their own coding models against these standardized tests, particularly those specifically designed for software development tasks.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.