Deepmind's AlphaMissense predicts potentially disease-causing gene mutations

Google Deepmind's AlphaMissense AI system has created a comprehensive catalog of "missense" gene mutations, providing valuable insights into their potential impact.
The AlphaMissense AI model categorizes potentially dangerous missense variants, specific gene mutations that affect the function of human proteins and can potentially lead to diseases such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or cancer.
AlphaMissense could represent a step forward in the rapid diagnosis of disease and pave the way for the development of therapies in human genetics. Deepmind is working with Genomics England to explore how AlphaMissense predictions can support research into the genetics of rare diseases.
AlphaMissense classifies the effects of 71 million gene mutations
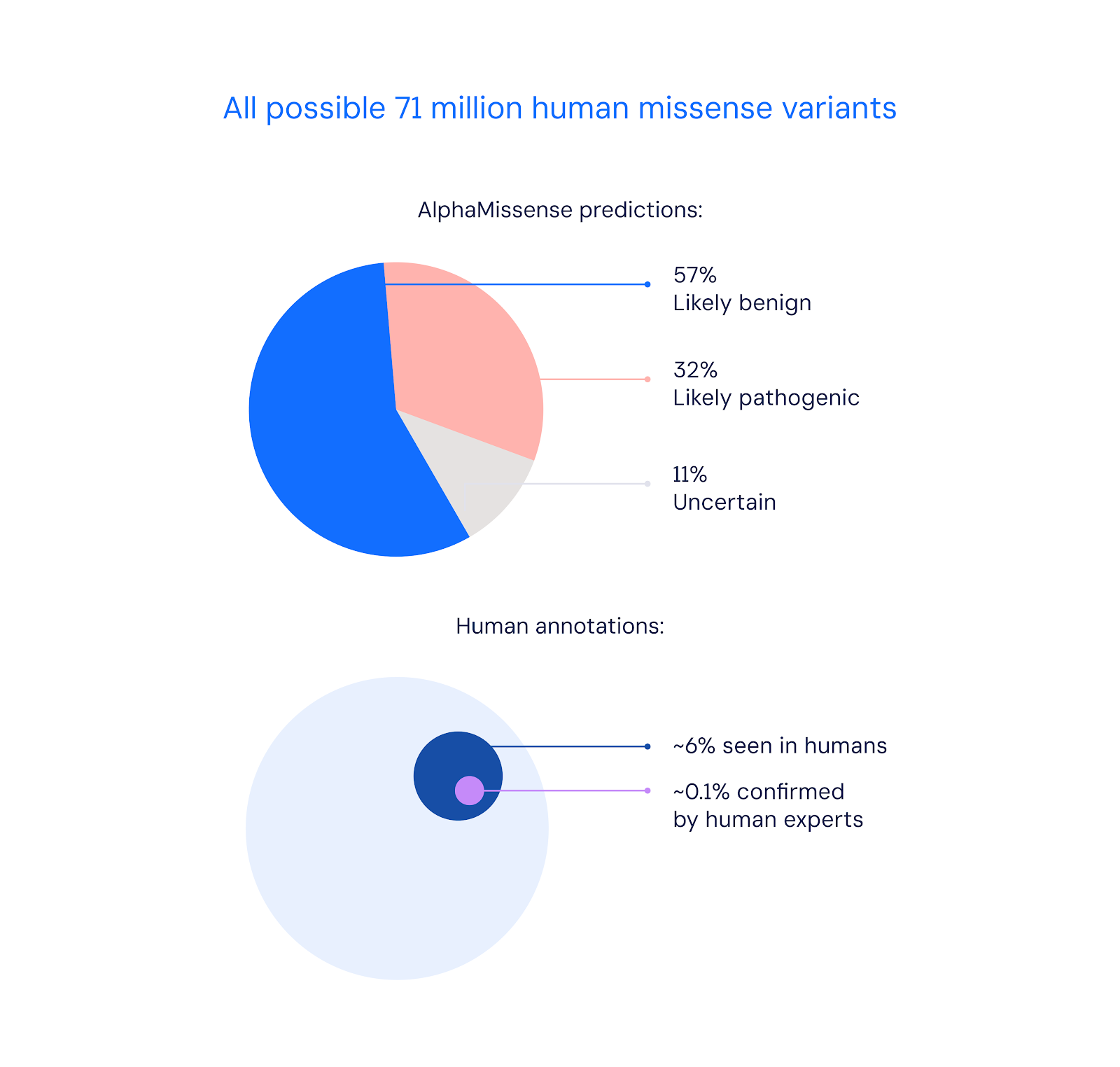
In a research report published in Science, Deepmind shows that AlphaMissense was able to classify 89 percent of all 71 million potential missense variants as either likely to cause disease (pathogenic) or likely to be harmless (benign). By comparison, human experts only validated 0.1 percent of these mutations so far, according to Deepmind.
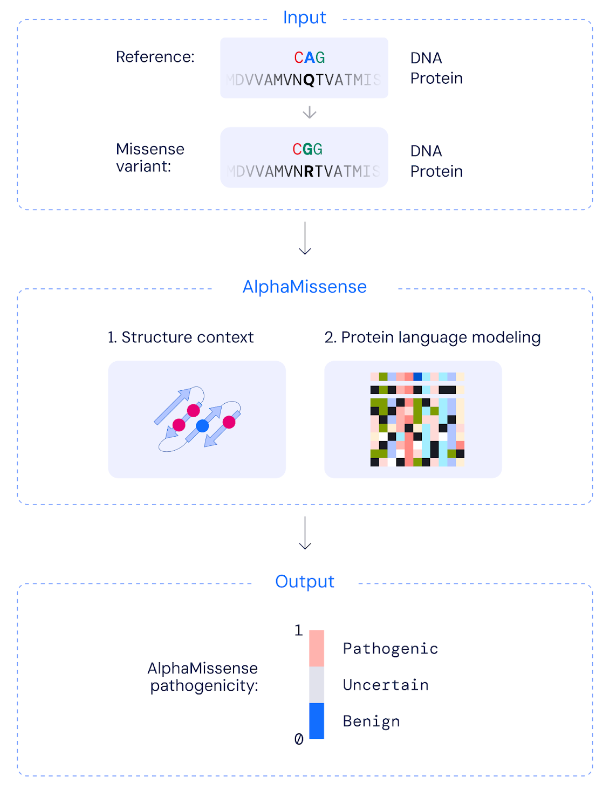
Missense variants are the substitution of a single letter in DNA that results in a different amino acid within a protein. Just as a single letter can change the meaning of a word, a different amino acid can affect the function of a protein.
According to Deepmind, the average person carries more than 9,000 missense variants, most of which have little or no effect. However, some are pathogenic and can severely affect protein function, leading to disease. Categorizing these few potentially dangerous variants is therefore critical to understanding which protein changes can lead to disease.
AlphaMissense is based on Alphafold
AlphaMissense is based on a fine-tuned variant of Deepmind's AlphaFold protein prediction model, which can predict the structure of proteins based on their amino acid sequence.
AlphaMissense has been trained on DNA from humans and related primate populations and distinguishes between common, and therefore likely benign, and rare, and therefore potentially disease-causing missense variants.
It does not predict the effect of the mutation on protein stability or structural changes. Instead, it uses databases of related protein sequences and the structural context of the variants to determine a score between 0 and 1 that indicates the likelihood that a variant is pathogenic.
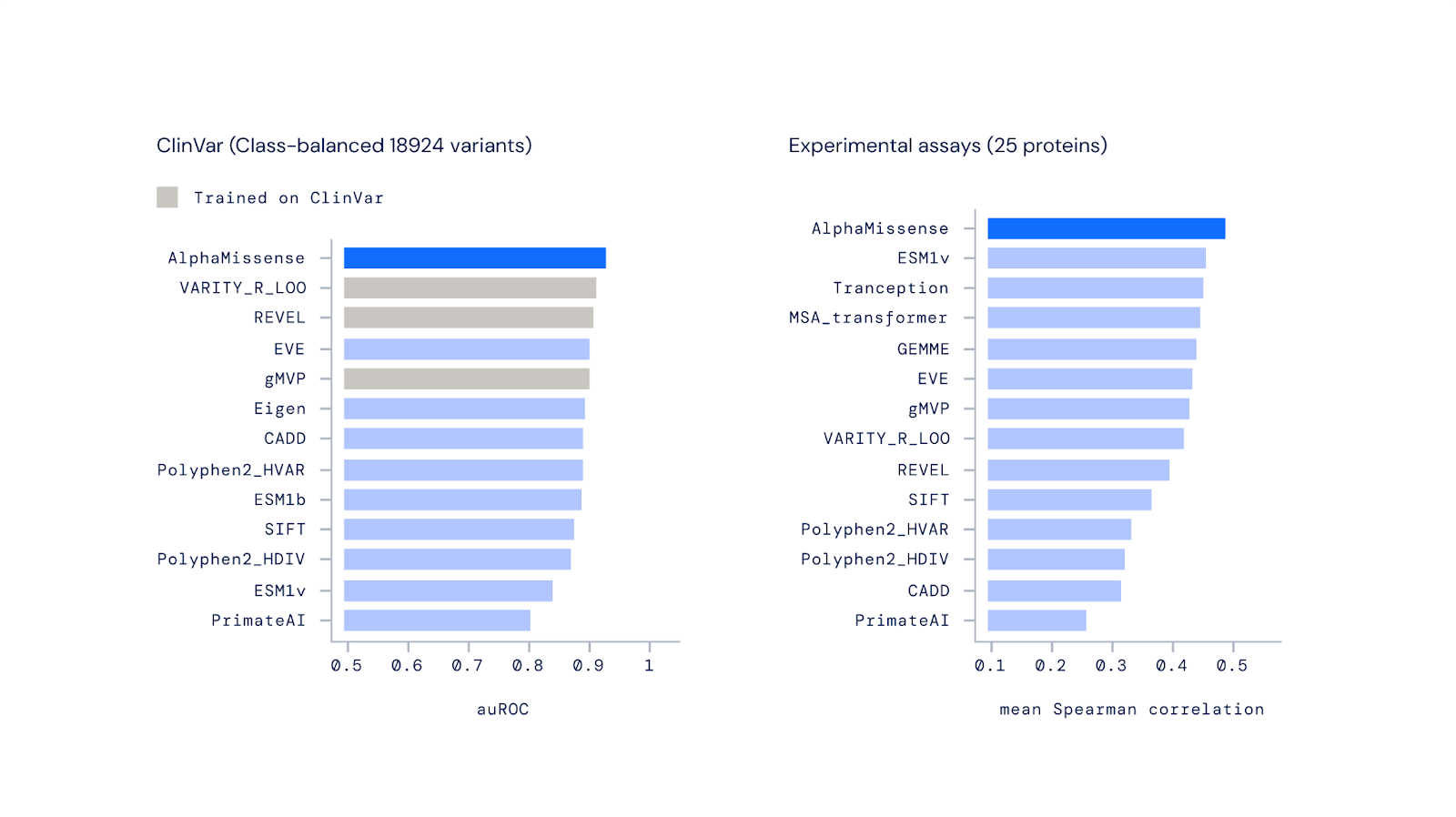
According to Deepmind, AlphaMissense achieves new SOTA scores in benchmarks for predicting disease risk from genetic variants. It outperforms other computational methods in classifying variants from the public ClinVar archive and is the most accurate model for predicting laboratory test results.
Deepmind is making all of AlphaMissense's predictions available to the scientific community and hopes that the model, along with other tools, will help to better understand disease and develop new, life-saving treatments.
With Isomorphic Labs, Google and Deepmind have created their own AI company for disease research and treatment. One of the goals is to speed up drug development.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.