New Google Deepmind Maps algorithm improves routing by up to 24 percent on average

Developers at Google have built an AI algorithm that will make route suggestions in Google Maps more personalized.
According to Google, the model, which includes 360 million parameters, uses real driving data from Maps users to analyze what factors they consider when making route decisions. The AI calculations include information such as travel time, tolls, road conditions and personal preferences.
Google says the technology is based on an approach called "inverse reinforcement learning" (IRL), in which the system learns from user behavior based on a new IRL algorithm called "Receding Horizon Inverse Planning (RHIP)".
"Receding Horizon Inverse Planning" for near and far
Google says it worked with Deepmind on RHIP for several years. In the immediate vicinity of an actual route traveled, the algorithm uses computationally intensive stochastic models to consider unlikely options. For more distant areas, RHIP switches to simpler deterministic methods to save power.
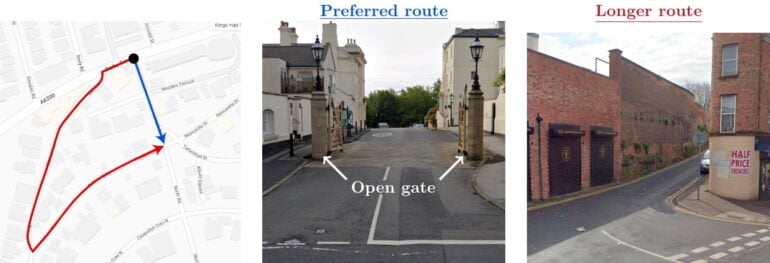
The preferred route is incorrectly marked as private property due to the presence of a gate (which is never closed),
and incorrectly incurs a high cost. The detour route is long and narrow. The sparse model learns to correct the
data error with a large positive reward on the gated segment." | Image: Google
In tests, RHIP was able to improve the accuracy of its route suggestions by an average of 16 to 24 percent for driving and two-wheeled vehicles (e.g., scooters, motorcycles, mopeds) compared to the well-tuned Maps baseline. By combining the AI approaches, the strengths of each can be maximized. The system learns from Maps users' movements and should get better at predicting which route they prefer over time.
In the past, Google says, attempts to use AI systems at scale for route planning have often failed due to the sheer complexity of real-world road networks. The algorithms couldn't handle the myriad possibilities.
RHIP can now overcome this hurdle with a sophisticated approach. Google developers say RHIP is the largest application of inverse reinforcement learning for route planning to date, confirming the trend that better performance is related to scale, both in terms of data set and model complexity.
The algorithm has been applied to Google Maps data worldwide. However, extensive user testing is needed to determine whether the technique works in practice and actually consistently produces better routes.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.