The World Health Organization (WHO) has released new guidelines on the ethics and governance of large multimodal models (LMMs).
The guidelines include more than 40 recommendations for governments, technology companies and healthcare providers to ensure the appropriate use of large multimodal AI models (LMMs) to promote and protect public health, according to the WHO.
LMMs can process different types of data, such as text, images and video, and generate equally diverse outputs.
Dr. Jeremy Farrar, Chief Scientist at WHO, emphasizes the need for transparent information and guidance on the design, development, and use of LMMs to achieve better health outcomes and reduce existing health inequalities.
WHO outlines benefits and risks of LMMs in medicine
The new WHO guideline outlines five broad health applications of LMMs:
- Diagnosis and clinical care, such as responding to patients’ written queries;
- Patient-guided use, such as for investigating symptoms and treatment;
- Clerical and administrative tasks, such as documenting and summarizing patient visits within electronic health records;
- Medical and nursing education, including providing trainees with simulated patient encounters, and;
- Scientific research and drug development, including to identify new compounds.
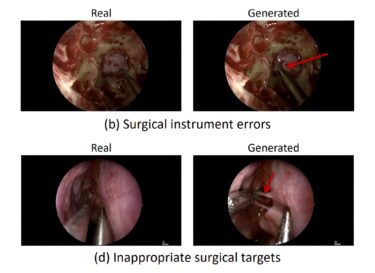
But there are also documented risks that LMMs may provide false, inaccurate, biased, or incomplete information that could harm people who use this information to make health-related decisions.
For example, LMMs could be trained on low-quality or biased data. The guidance also describes broader risks to health systems, such as the accessibility and affordability of the most capable LMMs, automation bias, and cybersecurity risks.
Automation bias refers to healthcare professionals missing errors that would otherwise have been caught, or inappropriately delegating difficult decisions to an LMM.
To create safe and effective LMMs, the WHO says different stakeholders, including governments, technology companies, healthcare providers, patients and civil society, must be involved in all stages of model development and implementation.
Governments should invest in non-profit structures
The new WHO guidelines include recommendations for governments, LMM developers and other stakeholders.
Governments should, for instance, invest in not-for-profit or public infrastructure, use laws and regulations to uphold ethical obligations and human rights standards, establish regulatory bodies and introduce mandatory post-publication review and impact assessment.
Developers of LMMs should ensure that LMMs are not only developed by scientists and engineers, but also involve potential users and all direct and indirect stakeholders. In addition, LMMs should be developed to perform well-defined tasks with the required accuracy and reliability.
The new guidelines are based on the WHO Guidelines on Ethics and Governance of AI for Health, published in June 2021. The LMM Guidelines are available here.
AI is already being used in several areas of medicine, such as diagnostics in various disciplines, psychotherapy, and drug development, and is showing initial success.