Snowflake's Arctic is the next open-source model focused on efficiency

Snowflake has developed its own large language model called Arctic and is now releasing it as open source. Arctic is designed to be highly efficient in both training and inference, especially for business-related tasks.
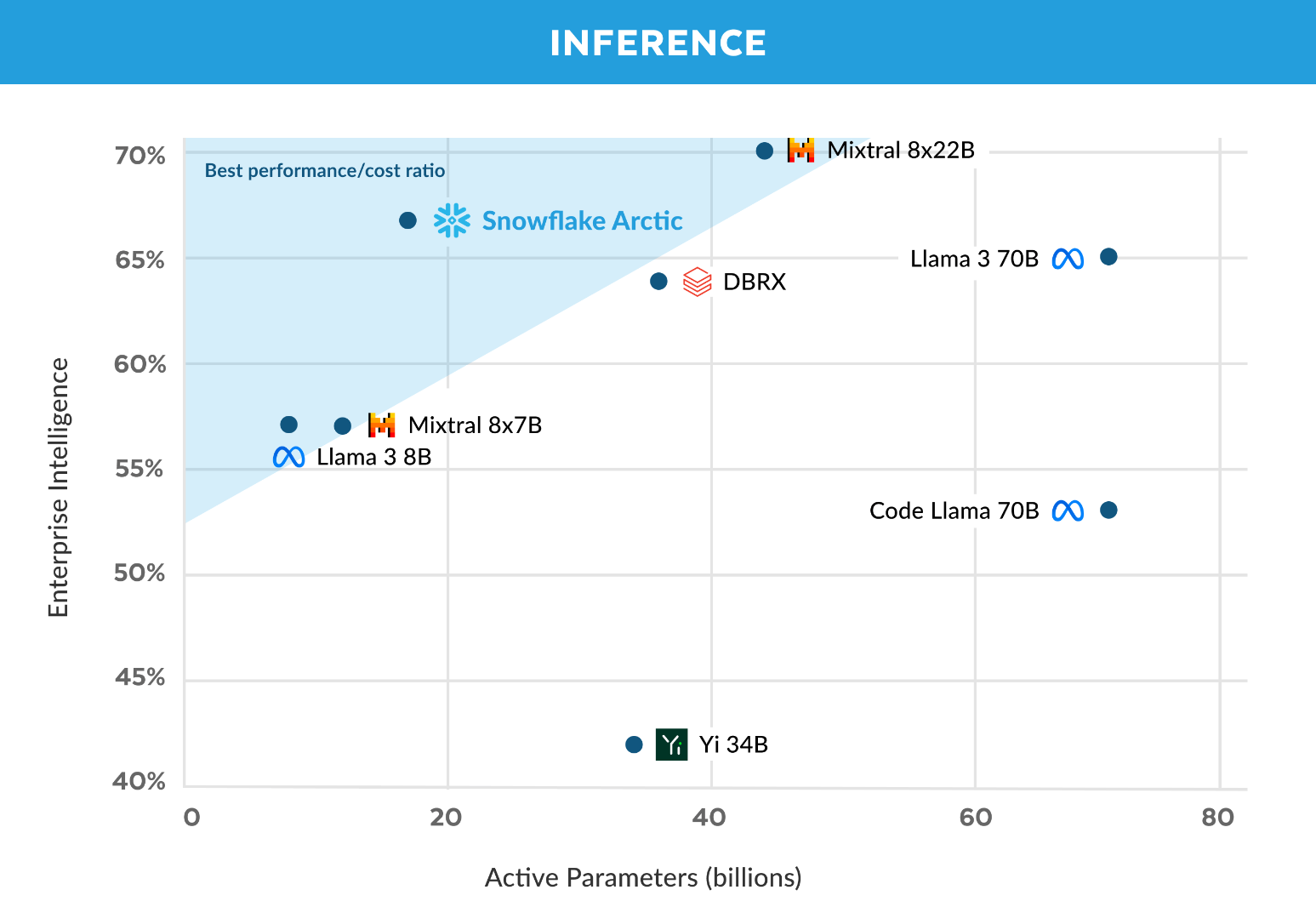
The company positions Arctic for enterprise applications, noting that the model excels at generating SQL code, general programming, and following complex instructions - capabilities that Snowflake groups under the self-defined metric of "enterprise intelligence".
According to Snowflake, Arctic required a training budget of less than $2 million, or about 3,000 GPU weeks. Despite this relatively low cost, the company claims that Arctic matches or exceeds the enterprise intelligence performance of larger models such as Meta's Llama 3 70B.

To achieve this training efficiency, Arctic uses a hybrid architecture that combines a Dense Transformer with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) residual layer. The base model is a Dense Transformer with 10 billion parameters, complemented by an MoE layer with a total of 480 billion parameters and 17 billion active parameters.

Snowflake has published a detailed "Cookbook" describing the model and its training process, and shares insights and best practices for training MoE models. The goal is to enable others to efficiently build large language models without extensive experimentation, the company says.
The model checkpoints for both the base and instructed versions of Arctic are now available for download on Hugging Face under the Apache 2.0 license. Instructions for inference and fine-tuning can be found on GitHub.
Snowflake also plans to work with Nvidia and the vLLM community to provide optimized implementations for fine-tuning and inference. The company is working on additional models in the Arctic series.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.