"Agent Hospital" lets medical AI learn by treating thousands of sim patients
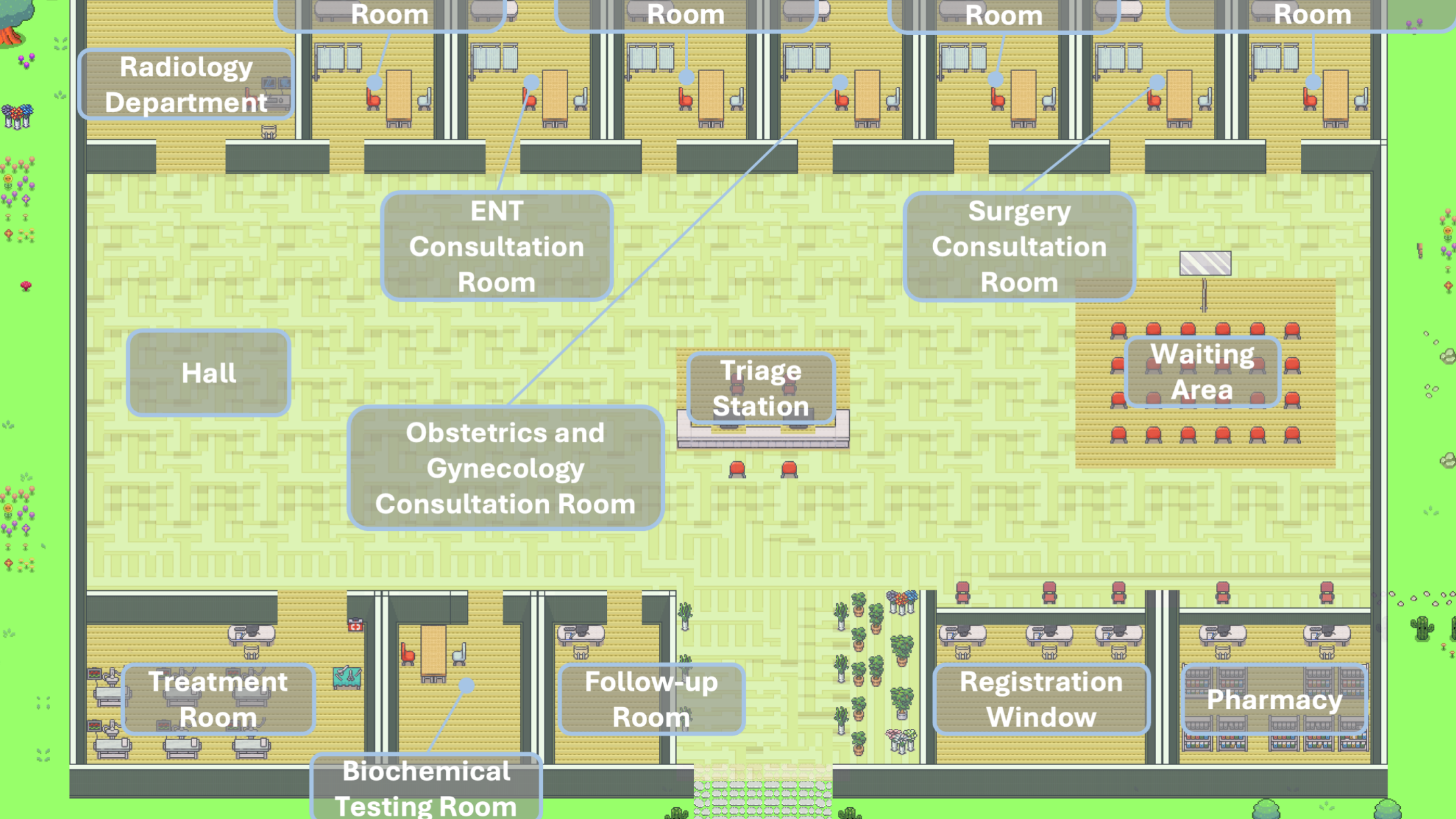
A team of researchers has developed a hospital simulation called Agent Hospital. It allows medical AI agents to evolve independently by interacting with simulated patients.
In a new paper, researchers from Tsinghua University present an AI-powered simulation of a hospital. This " Agent Hospital" replicates many medical processes of a real hospital, from triage to diagnosis and treatment, and serves as a training environment for language model-based AI agents.
The simulation includes two types of AI agents: medical professionals, such as doctors and nurses, and residents, who act as potential patients. When a resident agent becomes ill, he or she goes through a dynamically generated process of triage, registration, examination, diagnosis, and treatment. Their health status is continuously monitored.
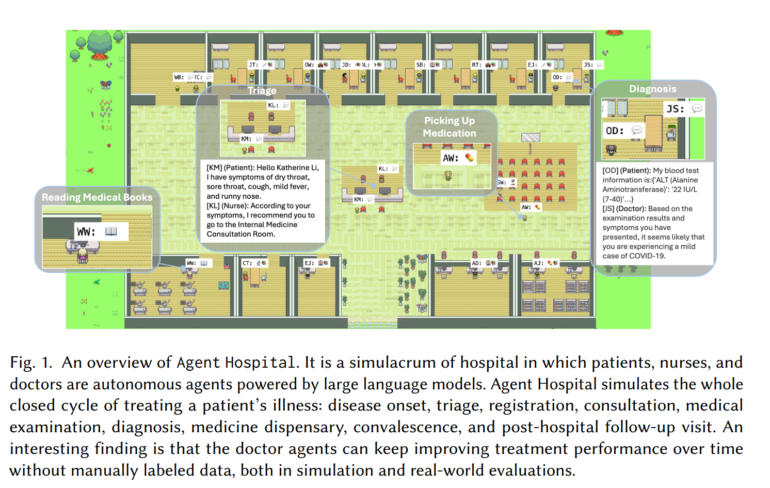
At the heart of the simulation is MedAgent-Zero, developed by the researchers. The doctor agent evolves autonomously through interaction with the patient - without human intervention or manually annotated data. The work combines ideas from the Generative Agents and AlphaZero projects.
It stores successful treatments in a medical record library and gathers experience from misdiagnoses in an experience base. Each time it treats a new patient, it uses these databases to optimize its decisions.
AI agent treats tens of thousands of sim patients in just a few days
In experiments with up to 10,000 simulated patients, the agent got better and better at examination, diagnosis, and treatment. After training, it achieved accuracies of 88 percent, 95.6 percent, and 77.6 percent, respectively. A single agent was able to treat tens of thousands of patients in a matter of days - a task that would require years of experience for a human doctor.
The researchers then tested the trained agents on a subset of the real-world medical question set "MedQA," which covers the major respiratory diseases. Despite the lack of real-world training data, the agents outperformed the current state of the art and even achieved higher accuracy than human experts using GPT-4 as a base model.
For now, however, MedAgent-Zero will not be unleashed on real people. According to the researchers, their study primarily demonstrates how simulation environments can improve the performance of AI agents in certain tasks without the need for annotated real-world data. They plan to add more diseases and medical departments to the ""Agent Hospital"" and to improve the social simulation of the agents, for example by introducing a transportation system for medical staff.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.