Plan Like a Graph: New prompting method helps language models plan

Methods that help people think can also boost language models. Representing step sequences as graphs can significantly improve performance.
Researchers from the University of Oxford, Alan Turing Institute, Allen Institute for AI, and LMU Munich explored how large language models handle complex planning tasks. They wanted to see if LLMs could optimize plans with both sequential and parallel actions under time and resource constraints. The team introduced a method called "Plan Like a Graph" (PLaG) in a recent paper.c
Method can be used for all language models
PLaG works with all language models tested, improving their performance. It's ready to use now and compatible with current models. The newest model tested was GPT-4, which is somewhat outdated by today's AI standards.
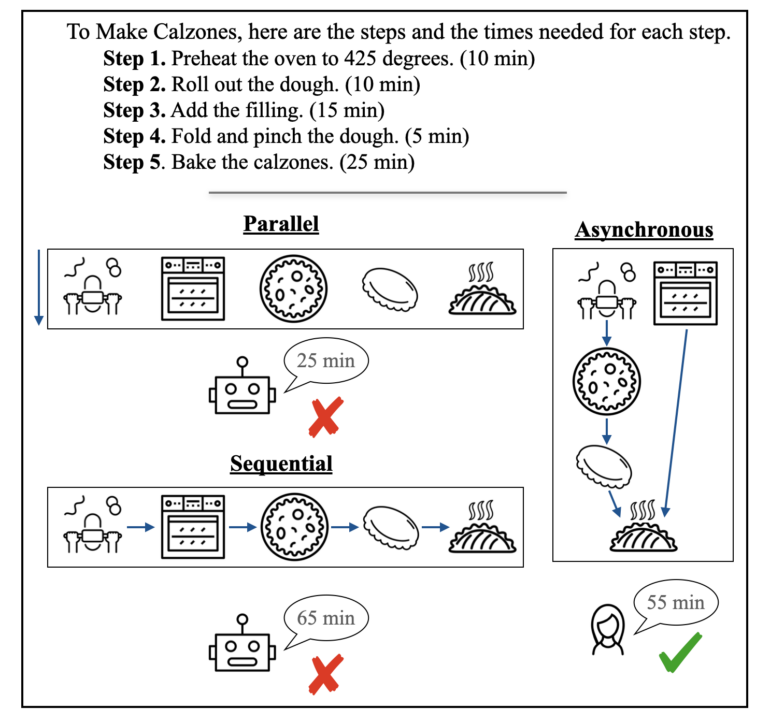
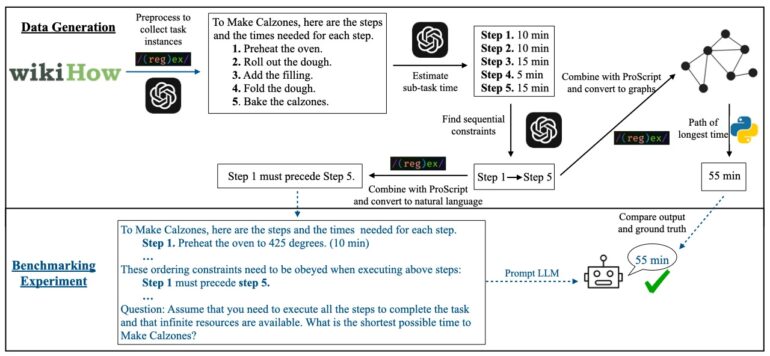
To evaluate PLaG, the researchers created a benchmark dataset called AsyncHow with over 1,600 realistic planning problems. It builds on the existing ProScript set and includes WikiHow instructions.
The team tested PLaG on various language models, including GPT-3.5, GPT-4, Cohere Command, and open-source options like LLaMA-2 and Mistral-7B. They noted that LLM performance drops sharply as tasks become more complex or involve more steps.
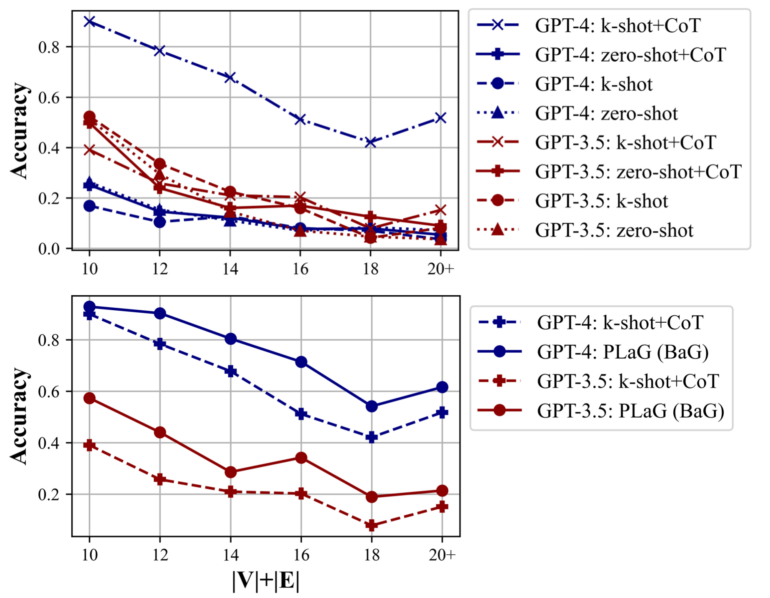
A variant called "Build a Graph" (BaG), where the LLM creates its own graph representation, performed even better than using a given graph. The researchers think this might be because the LLM can tailor the graph to its own reasoning process.
AGI still a long way off
Despite PLaG's improvements, the researchers say LLMs aren't yet robust enough for use as general intelligent agents in complex planning. There are still limits to using LLMs as standalone digital planners, at least for now.
The team sees several ways to expand this work, including adding more constraints to the benchmark and comparing how LLMs and humans perform on the same planning tasks.
Since PLaG's release, OpenAI has introduced its latest model, o1, which focuses on logical reasoning. It would be interesting to see if this technique also enhances its planning abilities.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.