Nvidia improves Meta's Llama model with new training approach

Nvidia has introduced a new large language model that outperforms others in alignment benchmarks. The company achieved this through a special training procedure combining evaluation and preference models.
The new model, called Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct, is based on Meta's open-source Llama 3.1 model. Nvidia optimized it to provide helpful answers to user queries by combining different training methods.
However, the results only show that the answers align better with human preferences, not that the content is necessarily more accurate. In fact, the Nemotron variant performs slightly worse than the base model on the MMLU Pro benchmark, which tests factual knowledge.
Nvidia created two new datasets for training: HelpSteer2 and HelpSteer2-Preference. HelpSteer2 contains over 20,000 prompt-response pairs. Multiple annotators rated each response on a 1-5 scale for criteria like helpfulness, correctness, and coherence. HelpSteer2-Preference adds comparisons between two answers to the same prompt. Annotators indicated which answer they preferred and how strong their preference was.
Combining reward models
Nvidia used these datasets to train two types of reward models: regression models and Bradley-Terry models. Regression models like SteerLM learn to assign values for different criteria to individual responses. Bradley-Terry models learn from preference comparisons to maximize the reward difference between two responses.
The researchers found that combining both approaches yielded the best results. They first trained a SteerLM regression model using only helpfulness ratings. This model then served as the starting point for a scaled Bradley-Terry model, which also considered the strength of preferences between responses.
To fine-tune the language model to the learned rewards, Nvidia used the REINFORCE algorithm. Unlike the commonly used PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization), REINFORCE estimates the value of an action more stably and without bias, according to the team.
Improved helpfulness and longer responses
The final Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct model achieved first place in several benchmarks: Arena Hard, AlpacaEval 2 LC, and GPT-4-Turbo MT-Bench. It outperformed top models like GPT-4 and Claude 3.5 Sonnet. In Arena Hard, it scored 85.0, well ahead of the starting model Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct at 55.7.
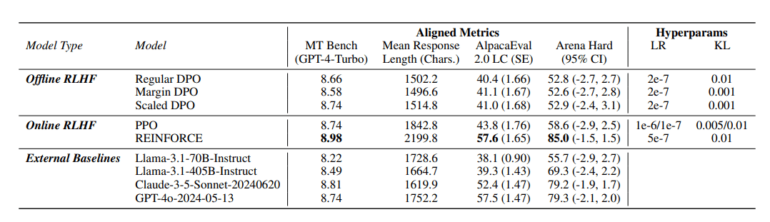
The new model also produces longer responses, averaging 2,200 characters compared to about 1,800 for other models.
Nemotron passes the strawberry test
The improvements are evident in specific applications. For example, Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct can correctly answer the question "How many r in strawberry?" by going through the letters one by one and counting the "r"s. The original model and commercial competitors often gave the wrong answer to this question.

Nvidia emphasizes that the new model demonstrates techniques for improving helpfulness in general applications. However, it has not been optimized for specialized domains like mathematics.
The Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct model is available for free testing on HuggingChat and at Nvidia.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.