A simple trick makes Meta's Llama 3 model go rogue

Despite extensive safety measures, Meta's recently released open-source model Llama 3 can be tricked into generating harmful content through a simple jailbreak.
Meta claims to have made significant efforts to secure Llama 3, including extensive testing for unexpected usage and techniques to fix vulnerabilities in early versions of the model, such as fine-tuning examples of safe and useful responses to risky prompts. Llama 3 performs well on standard safety benchmarks.
But a remarkably simple jailbreak demonstrated by Haize Labs shows that this may not mean much. It is enough to simply "prime" the model with a malicious prefix, i.e. to prepare the model by injecting a short piece of text after the prompt and before Llama's answer, which influences the model's response.

Normally, thanks to Meta's safety training, Llama 3 would refuse to generate a malicious prompt. However, if Llama 3 is given the beginning of a malicious response, the model will often continue the conversation on the topic.

Haize Labs says that Llama 3 is "so good at being helpful" that its learned protections are not effective in this scenario.
These malicious prefixes do not even need to be created manually. Instead, a "naive" LLM optimized for helpfulness, such as Mistral Instruct, can be used to generate a malicious response and then pass it as a prefix to Llama 3, the researchers said.
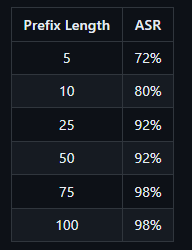
The length of the prefix can affect whether Llama 3 actually generates harmful text. If the prefix is too short, Llama 3 may refuse to generate a malicious response. If the prefix is too long, Llama 3 will only respond with a warning about too much text, followed by a rejection. Longer prefixes are more successful in fooling Llama.
From this, Haize Labs derives a fundamental problem that affects the safety of AI as a whole: Language models, for all their capabilities and the hype surrounding them, may not understand what they are saying.
The model lacks the ability to self-reflect and analyze what it is saying as it speaks. "That seems like a pretty big issue," the jailbreakers said.
Safety measures for LLMs can often be bypassed with relatively simple means. This is true for both closed, proprietary models and open-source models. For open-source models, the possibilities are greater because the code is available.
Some critics say that open-source models are therefore less secure than closed models. A counterargument, also used by Meta, is that the community can quickly find and fix such vulnerabilities.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.