Amazon adds automatic prompt optimization to its Bedrock AI service

Amazon has rolled out automatic prompt optimization for its Bedrock AI service, promising better performance across various AI tasks with minimal user effort.
The new feature lets users optimize prompts for multiple AI models through a single API call or by clicking a button in the Amazon Bedrock console, according to the AWS Machine Learning Blog.
The optimization tool currently works with several leading AI models, including Anthropic's Claude 3, Meta's Llama 3, Mistral's Large, and Amazon's Titan Text Premier.
Amazon's testing with open source datasets showed notable improvements. The company achieved an 18 percent better performance in text summarization using XSUM, an 8 percent improvement in RAG-based dialog continuation with DSTC, and a 22 percent boost in function calls using GLAIVE.
Simplified prompt engineering
AWS demonstrated the tool's practical use with an example of optimizing prompts for chat or call log classification. The system automatically refines the original prompt to be more precise, while making it easy to add and test variables like chat protocols.
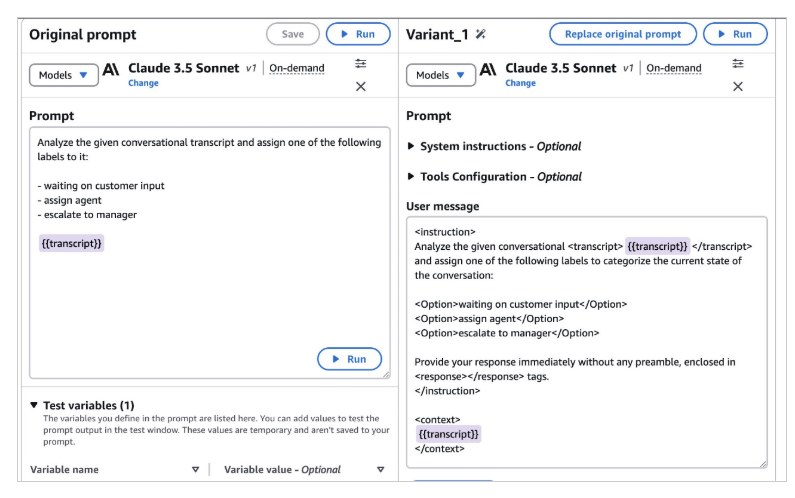
Amazon says this automation aims to reduce the months-long process of manual prompt engineering that developers often face when finding optimal prompts for specific models and tasks.
Humans still need to think for themselves
Both Anthropic and OpenAI have their own prompt optimization tools, but it's still unclear exactly how these systems evaluate improvements or how dependent they are on well-written initial prompts.
In my own experience, these automated tools often fall short when trying to improve carefully constructed prompts that use multiple examples (many-shot prompts). While they can help add structure or occasional detail, there's still no substitute for human expertise when it comes to understanding what a task requires and designing effective prompts to accomplish it.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.