Anthropic study shows leading AI models racking up millions in simulated smart contract exploits
A new study from MATS and Anthropic shows that advanced AI models like Claude Opus 4.5, Sonnet 4.5, and GPT-5 can spot and exploit smart contract vulnerabilities in controlled tests. Using the SCONE-bench benchmark, which includes 405 real smart contract exploits from 2020 to 2025, the models produced simulated damage of up to 4.6 million dollars.
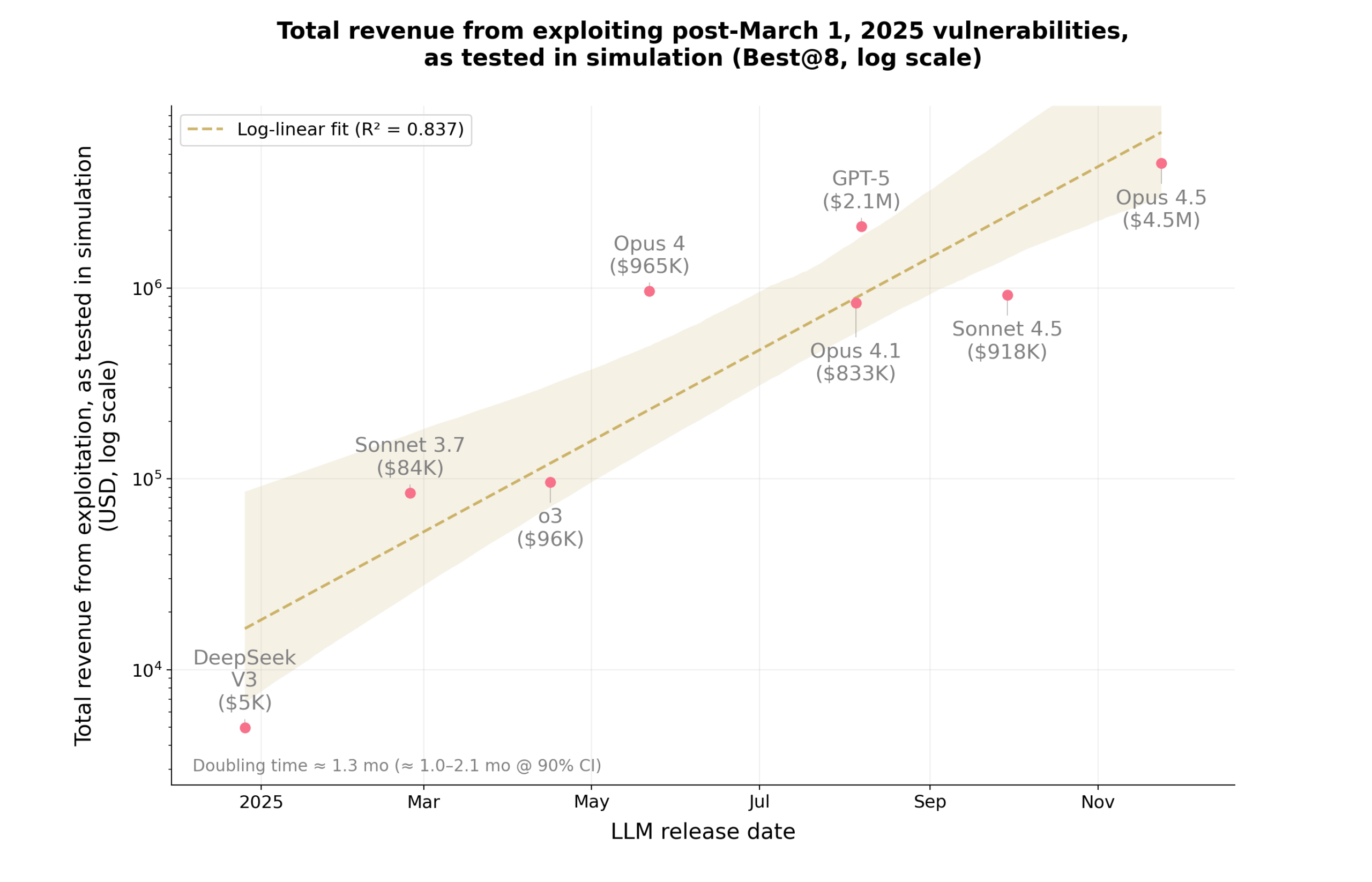
In a separate experiment, AI agents reviewed 2,849 new contracts and uncovered two previously unknown vulnerabilities. GPT-5 generated simulated revenue of 3,694 dollars at an estimated API cost of about 3,476 dollars, averaging a net gain of 109 dollars per exploit. All experiments were run in isolated sandbox environments.
The researchers say the findings point to real security risks but also show how the same models could help build stronger defensive tools. Anthropic recently released a study suggesting that AI systems can play a meaningful role in improving cybersecurity.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe now