ChatGPT vs. Google: Who wins at 500 searches?
Data labeling platform Surge AI compared Google and ChatGPT results for 500 search queries - and calls ChatGPT an "existential threat" to Google.
For the study, Surge obtained five basic information search queries from 100 workers. The search queries had to relate to knowledge before 2022, as ChatGPT training only covers knowledge up to then.
ChatGPT is slightly ahead of Google
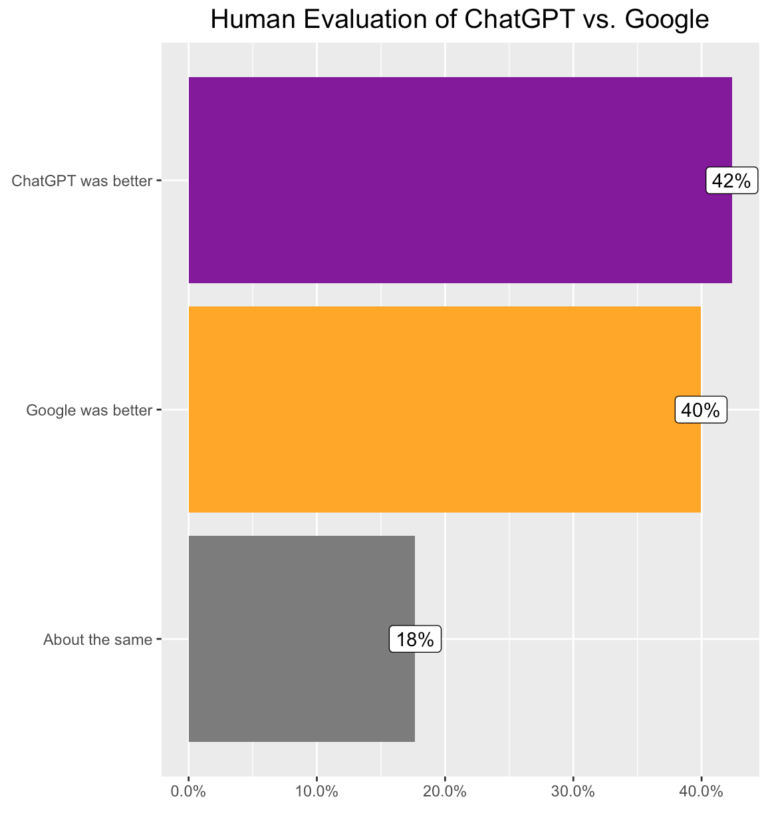
Employees resubmitted their query to Google and as a prompt to ChatGPT. They then rated the results and responses: ChatGPT came out ahead in 42 percent of the cases, and Google in 40 percent - even though ChatGPT is not optimized for search.
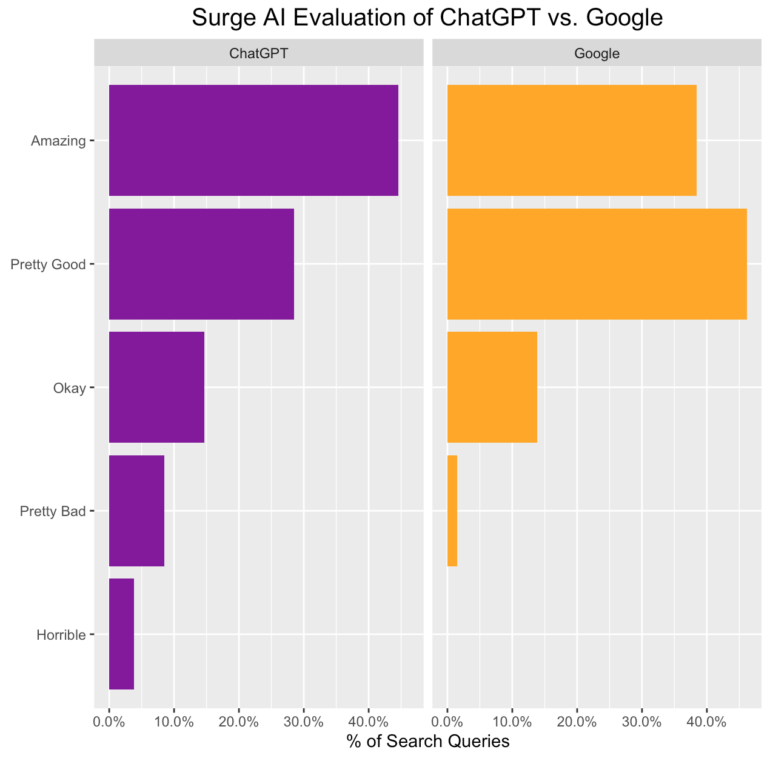
The qualitative evaluation shows that ChatGPT had more outliers up and down, results that were categorized as "amazing" but also as "pretty bad" and "horrible".
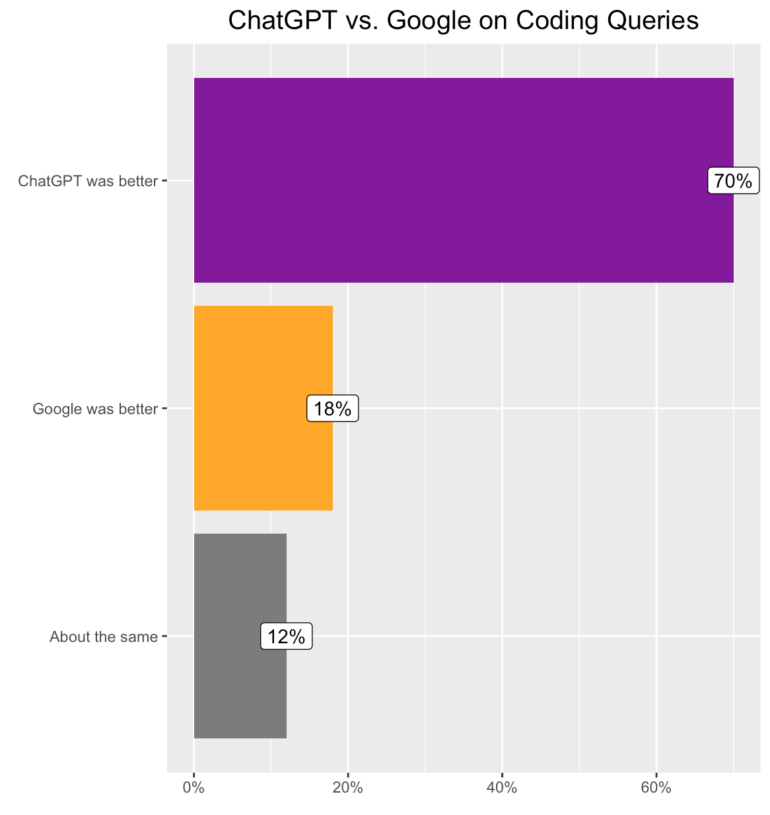
Especially for code queries, ChatGPT is said to be superior, since it directly plays out the concrete code instead of links to websites that contain the matching code - or not.
Edwin Chen of Surge, a former Google employee, sees the results of the study as very positive for ChatGPT, since its interface is not even optimized for search or connected to the Internet. With WebGPT, OpenAI has already introduced an AI technology that can look up information on the Internet.
"Google was supposed to be the killer AI company; for a while, it was. But with transformative language models racing forward, is its reign – and dominance as the world's smartest search engine – about to be usurped?" writes Chen.
Formatting and convenience vs. accuracy and multimedia
A look at the detailed analysis of individual search results and chat responses shows that Surge AI's employees particularly preferred the convenience and pre-written responses of ChatGPT over manual searches across multiple websites.
"While Google offered me ample amounts of information, which did eventually lead me to a helpful answer, ChatGPT simplified the results I was looking for," writes one study participant.
In ChatGPT's favor, according to the study, are its ability to consolidate information from multiple sources into one answer, its minimalist interface with no ads, and ChatGPT's ability to handle complex queries.
"ChatGPT is very useful in eliminating the need to visit multiple web pages to get a complete answer," assessed one study participant.
The negative ChatGPT examples are answers with incorrect information that the model nevertheless presents with the same confidence as correct information, and refusal to answer, e.g., on topics related to more current references.
"I like the format of the AI's response - namely the fact that it provides an example citation instantly - but it's too inaccurate to be valuable," writes one study participant who compared a query about a specific citation format.
One study participant criticized ChatGPT for having problems with any topic that was not established knowledge. "Given the lack of correct answers, I was not impressed and wouldn't use it over a search engine in its current state," writes another participant.
In addition, ChatGPT answers still lack images, videos, and audio. Google has already solved the latter problem with its LaMDA multimodal dialog AI.
Chat AI as search replacement still has many open questions to answer
In the context of systems such as ChatGPT as a search substitute, many questions arise, the most important of which are the citability of ChatGPT, ultimately the question of responsibility for the content, the verification of the information and its timeliness.
As I wrote elsewhere, I think it is more likely that Google and other search engine providers will use systems like ChatGPT to enrich their regular search results with verified AI responses as a first step.
Google has already integrated a corresponding interface with no-click search, i.e., displaying information from a web page directly in Google search. In the future, the information displayed there could be written by an AI and backed up with sources that confirm the AI answer.
This would have the charm for Google and Co. that they could provide even more precise answers to suitable search queries. They could circumvent the weaknesses of the AI systems by, for example, deactivating AI responses to search queries with a current reference.
In this scenario, a search provider like Google could attract even more users and retain them for longer. The original providers of information, such as publishers, would lose out because they would receive fewer hits via search. Further consolidation of the online media industry could be the result.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.