This is how Google Assistant answers your follow-up questions

Google Assistant now understands more context and can thus better handle follow-up questions. Google explains how this works.
In natural conversations, context and references play a central role, for example in the use of pronouns. What we take for granted can be a real challenge for virtual assistants. For example, if we first ask "How many episodes are in the first season of Rick and Morty?" and then follow up with "What about season 6?", it is clear to humans that we are continuing to refer to "Rick and Morty" when we ask.
For artificial intelligence, this connection is not immediately obvious. But thanks to advances in natural language machine processing, Google Assistant can now better handle such context-based queries.
Google Assistant: context through rephrasing
In a new blog post, Google documents the technology that allows Google Assistant to handle references. It's called context handling by rephrasing.
Essentially, the system reformulates the query taking into account the context of previous questions so that missing contextual information is included in the reformulation at the end. This new question is then answered by Google Assistant.
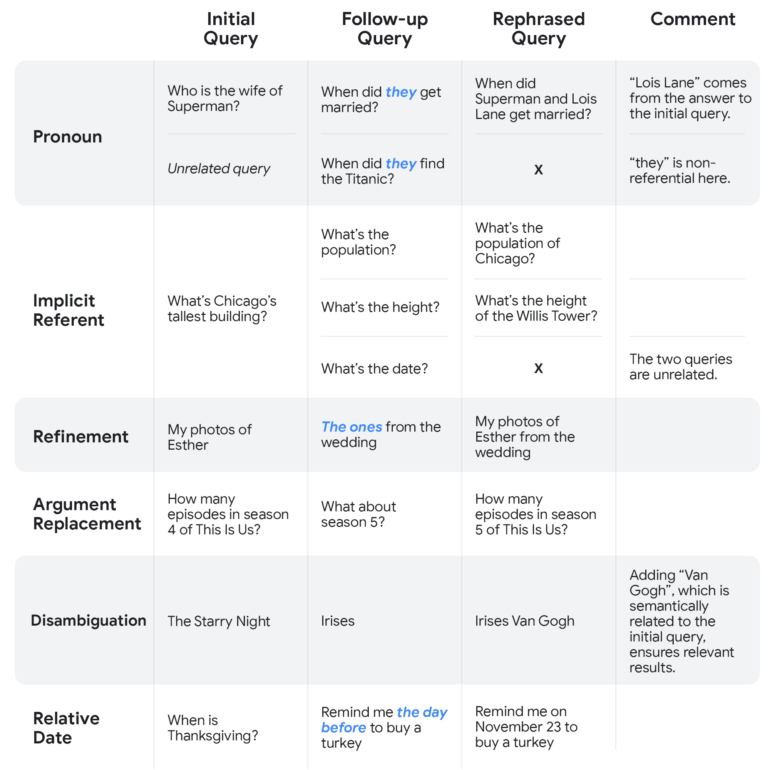
Google assistant also recognizes whether the question is a follow-up question at all. A question in which a pronoun appears without context is not rephrased by the assistant and is answered normally.
Together with the "Continued Conversation" mode, in which the Google Assistant remains active for a few seconds after answering, this makes it easier to find information or control the smartphone.
Google's Assistant uses the context of previous questions to deal with follow-up questions. | Video: Google
Google relies on rephrasing and AI scoring
However, rephrasing is often more challenging than simply replacing pronouns - for example, when users simply ask "When?". Google therefore relies on a system that generates multiple rephrasings using different types of generators. The different candidates are then evaluated by a machine learning model and the variant with the highest score is selected.
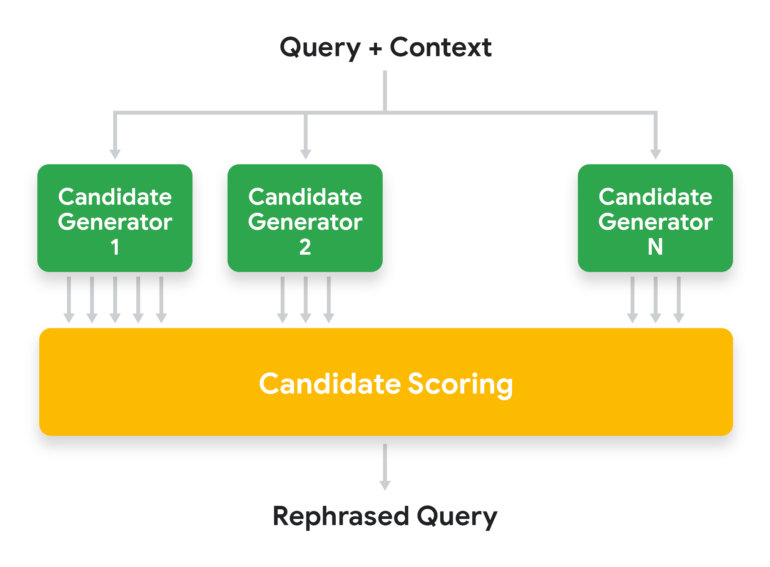
The generators rely on various methods, such as the analysis of linguistic structures of context and demand, statistics of frequent search queries, and transformation models that generate context-based reformulations.
Google selects several candidates for each generator and evaluates them using a ranking model according to different signals. As examples, Google mentions the proximity of the reformulated topic to the context, how much information of the context the generator received or the autonomy of the query.
Thanks to additional signals generated by BERT and MUM for evaluation, the ranking model has improved significantly in recent months, the researchers said. Meanwhile, Google Assistant can correctly interpret most contextual queries.
Incidentally, the technology is also used away from linguistic references: The virtual assistant also interprets context seen on a screen or heard over a speaker, Google said.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.