Artificial intelligence from Facebook and Carnegie Mellon University has beaten five players simultaneously in a poker tournament. Why it's a big deal.
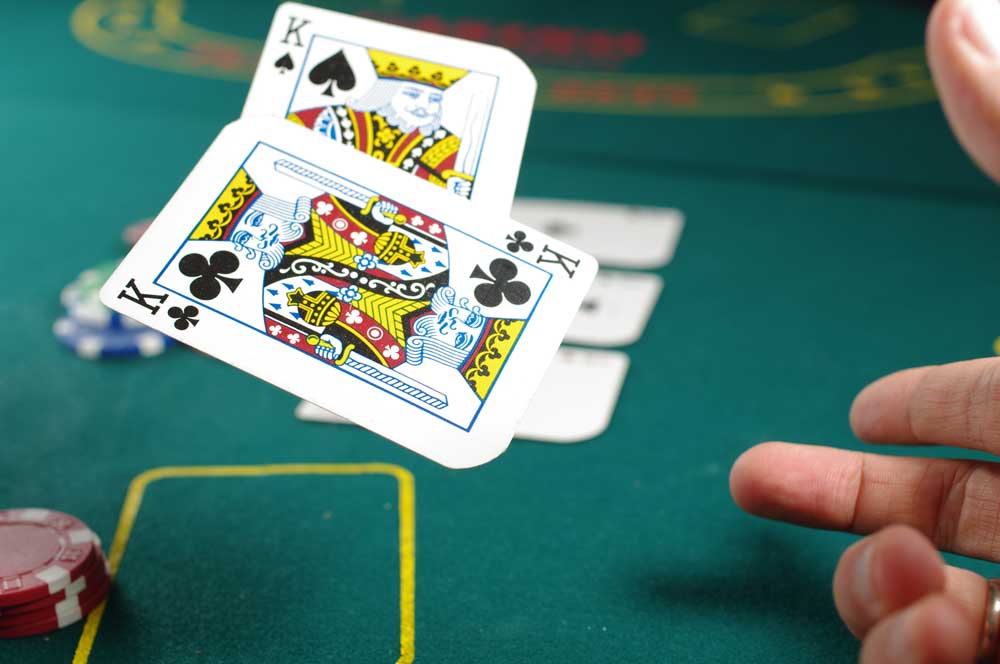
Dubbed "Pluribus," the artificial intelligence has defeated five professional players simultaneously in the world's most popular poker variant, "No Limit Texas Hold'em." The opponents were no lightweights: Among others, six-time poker world champion Chris "Jesus" Ferguson faced the AI system.
It's the first time an AI has won at this level against five opponents simultaneously. In 2017, the same researchers succeeded in defeating top players several times with the predecessor AI "Libratus." At that time, however, the AI only faced two players at a time. The developers continued to tinker with the poker AI for many years.
12 years ago I tried making my first poker AI in college and dreamed of beating the world's best pros. After seven years of a PhD, I'm excited to announce that I finally did it! It's been quite an adventure. Looking forward to the next one! https://t.co/jqRjKPUru4
- Noam Brown (@polynoamial) July 11, 2019
Poker is a tough game
Poker is considered a great challenge for artificial intelligence, as the game has some peculiarities not found in, say, chess or Go.
Due to the hidden cards of the other players, the information that the AI can work with is incomplete. Assessing the opponents and concealing one's own hand becomes an essential part of the strategy.
This creates complexity: the AI needs a good understanding of the game, has to react flexibly to new information and at the same time keep its poker face.
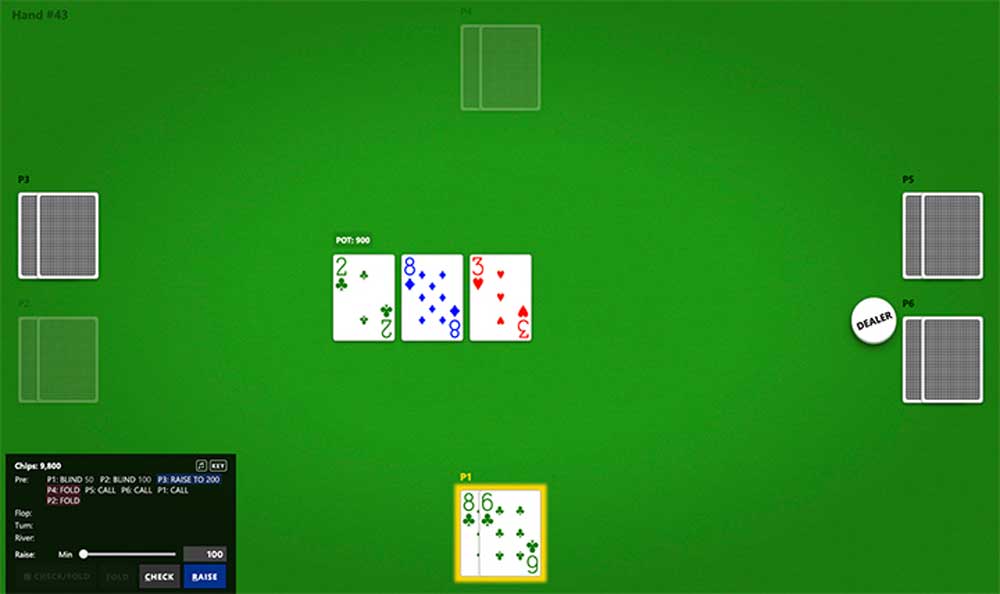
poker with more players is even harder
If there is only one opponent, the variables are kept within limits and the AI can develop a so-called optimal strategy. All known game AIs with "superhuman abilities" try to do this - whether in chess, Go or Starcraft.
Such optimal strategies, also called Nash equilibrium in game theory, make it theoretically impossible to lose on a large scale. For example, the Nash equilibrium strategy for rock-scissors-paper is to randomly select rock, scissors, or paper with equal probability. In practice, you can still lose individual games, but on average, you win the day.
However, in poker, as soon as several players are involved who develop a strategy independently, there are too many possibilities to still find an optimal solution - the possible moves are no longer predictable.
In addition, players react to each other and change their strategy, for example, in response to new cards or increased bets.
The AI, therefore, faces a major challenge: each player has information that the other players do not have. A successful poker AI must anticipate this hidden information, incorporate it into its decision-making, and develop a strategy based on it.
However, this strategy must not be predictable: Human players would otherwise exploit it. If the AI immediately plays a high bet on a good hand, the opponents will always withdraw from the game. The poker AI must therefore additionally act unpredictably.
Using a combination of methods, Facebook's AI researchers developed an almost unbeatable poker AI, despite this complexity. Their solution could become the blueprint for other AI software that works outside a game of poker.
What makes Facebook's AI special
It can't calculate an optimal strategy
For the poker AI, multiple players mean: it cannot develop an optimal strategy and is forced to rely on a combination of (only) promising strategy and flexible reaction. At the same time, it must keep its hand secret.
The researchers rely on a mixture of a strategy blueprint, which the AI uses at the beginning of each round, and a search algorithm, which flexibly tries to find the best strategy for the respective game situation during the ongoing game.
The AI developed the blueprint by playing against itself. The method is known from Deepmind's board game AI AlphaZero and its Starcraft AI Alphastar, for example. After about seven hours, the AI reached the performance of average players, after 20 hours that of professionals.
It compensates for possible strategy changes
In the game, the AI uses its trained strategy blueprint and also draws on the search algorithm to flexibly adjust its strategy. The search algorithm calculates the probabilities of possible moves as far as the computing power allows.
Here, too, the peculiarities of the poker game play a role: In chess, the possible moves can be calculated far in advance; there is a clear best solution. In poker, players can always pursue different strategies, the cards are unknown - there is more than one solution.
The AI calculates various probabilities for up to four strategies in advance. From these, it derives the most promising strategy on average.
It does not show its cards
To disguise its cards, the AI takes a similar approach: it does not follow the most obvious solution that corresponds to its cards. Rather, it calculates different possible moves with different hands and makes a compromise.
In this way, the AI finds a winning strategy and keeps its opponents guessing. It bluffs and sees through bluffs. So you could say Facebook's AI has learned to deal with liars - and to lie itself.
It reaches world-class level for only 150 US dollars
The AI was trained in eight days on a 64-core CPU server with 512 GB of RAM. In total, the training cost about 150 US dollars. By comparison, Google's AlphaGo used 1,920 CPUs and 280 GPUs for training and probably cost several million US dollars.
Contrary to the trend of investing more and more computing power in AI training, the researchers actually needed less power for Pluribus than for the weaker predecessor AI.
This shows that the future of AI research may not be held back by the ever-increasing performance hunger after all. Even developers who do not have access to large cloud servers and billions of US dollars can contribute to AI progress.
Poker AI without poker?
AI could also be used outside of poker in the future: Facebook itself sees potential applications in fraud analysis, cybersecurity, and controlling cab fleets or robots. All of these areas are comparable to poker: Multiple players exist in an environment with incomplete information.
The capabilities of AI could also be used for business games or simulated negotiations. This could be useful for the military, diplomacy, or business.
To work in areas outside of poker, the AI must, of course, be adapted and further developed - currently, it can only play poker. But it can do this so well that Facebook has decided not to publish the AI. It fears that players could use it to empty online casinos.