Wikipedia's new Chrome extension fact-checks the web with ChatGPT
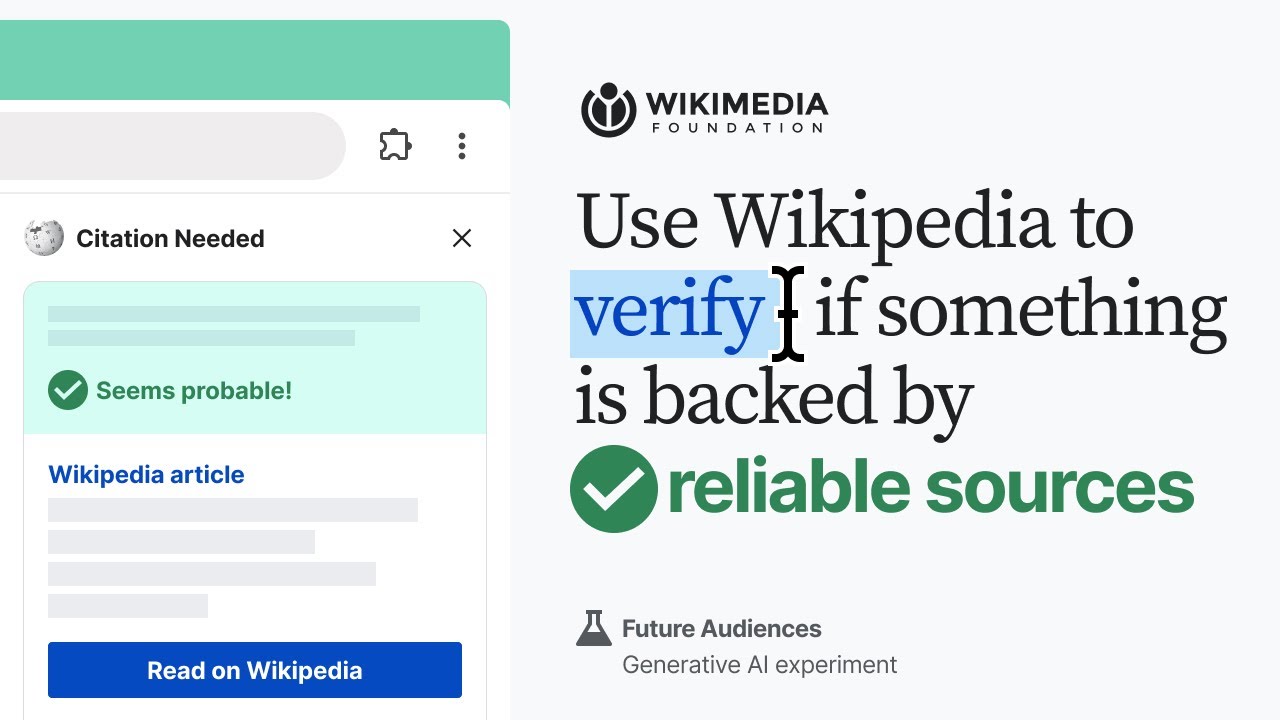
The Wikimedia Foundation has created an experimental Chrome extension called "Citation Needed" that uses ChatGPT and Wikipedia to verify the accuracy of content on websites.
Users can install the extension, enter their OpenAI API key, and then select sentences to check while browsing the web. The extension finds relevant Wikipedia articles and sections, returns matching citations, and uses ChatGPT to determine if the Wikipedia content supports the claim.
The extension shows the user the original claim, links to relevant Wikipedia articles, a supporting citation, signals about the article's quality, and an assessment of whether Wikipedia backs up the claim or not.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XJ_EPfTbjBM
Through this experiment, the Wikimedia Foundation wants to learn if web users are interested in fact-checking content, if they see Wikipedia as a reliable source, and if this can attract new audiences to Wikipedia. It will also test whether AI can help search and evaluate Wikipedia content.
The experiment is currently limited to English and Chrome. The goal is to quickly see if users want to compare web content to Wikipedia before investing more resources. If demand is high, it could become a full product in other languages. The test will run until June.
The Citation Needed extension is available for Chrome in the Chrome Store, with open-source code on GitLab. The app is developed by the Wikimedia Foundation Future Audiences team.
It builds on a first ChatGPT project which Wikimedia ended in February, six months after its launch in July 2023.
The plugin was developed to learn about the impact of large language models (LLMs) on Wikipedia's traffic and funding model, as well as to explore new ways of reading and editing Wikipedia content.
The experiment found that ChatGPT did not have a significant impact on the public's use of the Internet, with the plugin primarily reaching middle-aged North American and European males.
The answers generated by the plugin were generally relevant and accurate, and users had more confidence in the answers when the Wikipedia brand was associated with them.
The experiment ended because OpenAI moved away from its plugin marketplace and toward customizable GPTs, making the plugin largely redundant, Wikimedia said.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.