Tencent researchers unleash an army of AI-generated personas for data generation
Key Points
- Researchers at Tencent AI Lab Seattle have developed a way to use synthetic personalities to generate billions of data sets for training AI models.
- The team created the "Persona Hub" with one billion virtual characters that act as multipliers for synthetic data by being able to generate multiple data variants through their backgrounds.
- The method could enable a paradigm shift in which large language models generate training data independently, but also poses risks such as replicating a model's entire knowledge base.
Researchers at the Tencent AI Lab in Seattle have introduced a new method for generating synthetic data: synthetic personalities.
The Tencent AI Lab calls them "personas" and creates substitutes for real people to generate billions of synthetic datasets for developing AI systems.
As part of the research, the team created the "Persona Hub," a collection of 1 billion virtual characters. The researchers use two approaches: "Text-to-Persona" derives personalities from web texts, while "Persona-to-Persona" generates new personas based on relationships with previously created personalities. In principle, the personas serve as a kind of multiplier for synthetic data, as the different backgrounds can each generate their own data variants, similar to how an assigned role influences the output of language models during prompting.
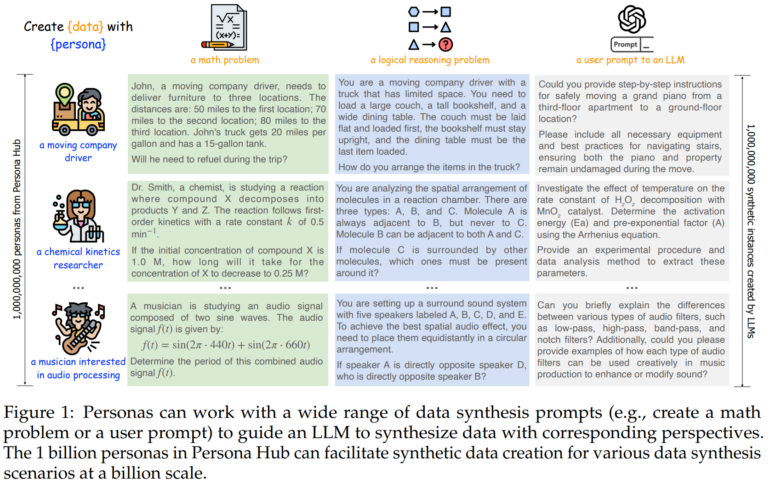
Synthetic personas can be used to generate a wide variety of data for training AI models. The researchers give examples such as mathematical problems, logical thinking tasks, and instructions for language models.
Personas can "read" knowledge from large language models
In one experiment, the researchers used Persona Hub to generate 1.07 million math problems. A model with 7 billion parameters trained on this data achieved an accuracy of 64.9 percent on the MATH benchmark, matching the performance of OpenAI's gpt-4-turbo-preview at a fraction of the model size.
The scientists see the potential for a paradigm shift in data generation for AI in their method. Instead of relying on human-generated data, large language models could generate diverse synthetic data themselves in the future. The team sees further potential applications for NPCs in video games or in the development of profession-specific tools.
However, the publication also points out possible risks and ethical concerns. For example, the method could make it possible to effectively "read out" and replicate the entire knowledge base stored in a language model.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe now