NeRFPlayer streams realistic, dynamic volumetric scenes

Key Points
- Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) represent 3D scenes based on 2D images and can render them from new angles.
- However, NeRFs often have problems with dynamic scenes in which objects or people are moving.
- A new method splits scenes into static, dynamic, and new areas, allowing for quickly trainable and renderable NeRFs of scenes with motion.
- The team also demonstrates a way to stream NeRFs using NeRFPlayer. The research team sees virtual reality as an application scenario.
NeRFs represent 3D scenes in a neural network. A new work opens AI technology to dynamic scenes.
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) learn 3D representations from images and can then render 3D scenes from previously unseen angles. This enables, for example, a 360-degree camera tour around an object, a flight tour through drone footage, or a walk through the interior of a restaurant. The technology can also create photorealistic 3D objects.

In almost all cases, however, NeRF scenes or objects are static, as motion introduces a temporal dimension to the training process that is difficult to resolve. A new process could solve this problem.
NeRFs for dynamic scenes
In a new research paper, a team from the University at Buffalo, ETH Zurich, InnoPeak Technology, and the University of Tübingen now shows how NeRFs can represent dynamic scenes and thus learn a 4D representation from 2D images.
RGB images from different cameras or a single moving camera serve as input. On the images, for example, a person is moving or someone is pouring coffee into a glass.
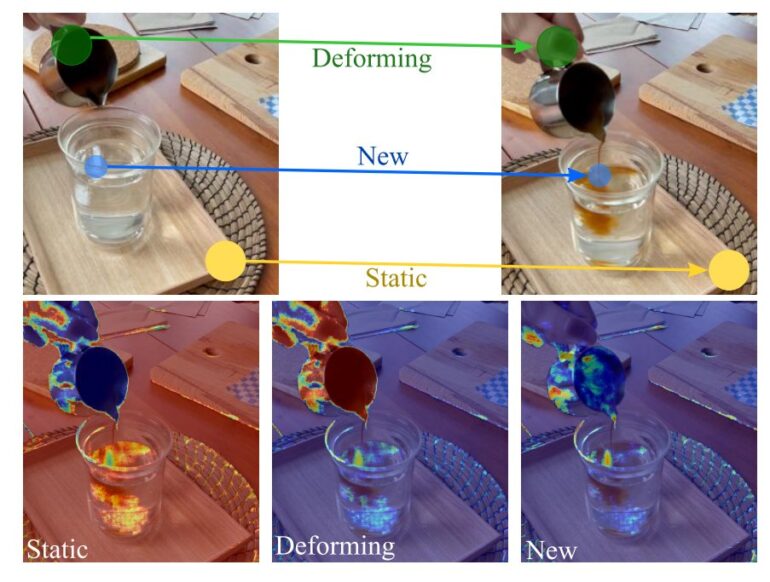
To make a dynamic scene adaptive, the team divides it into three temporal patterns: static, deforming, and new areas.
In the coffee example, the wooden board on which the glass is placed remains static. The contents of the glass are classified as new and the visible hand as deforming. A decomposition field provides the division of the scene into three categories. Each area is represented by its own neural field.
In their approach, the researchers also decouple temporal and spatial dimensions to improve representation.
NeRFPlayer enables NeRF streaming
The decompositional representation of the dynamic scene significantly reduces visual artifacts compared to other approaches. The team also demonstrates NeRFPlayer, a way to stream the learned representations in real-time with limited bit rates.
Nvidia's InstantNGP framework, which allows a neural network to learn representations of gigapixel images, 3D objects, and NeRFs within seconds, also makes the presented method fast.
We present a framework for representing dynamic scenes from both multi- and single-camera captured images. The key components of our framework are the decomposition module and the feature streaming module. The decomposition module decomposes the scene into static, deforming, and new areas. A sliding window based hybrid representation is then designed for efficiently modeling the decomposed neural fields. Experiments on multi- and singlecamera datasets validate our method’s efficiency and effectiveness.
Excerpt from the paper
In the paper, the team calls the visual exploration of a true 4D space-time environment in virtual reality a vision and arguably sees its work as contributing to that goal.
The 3D scenes shown in the NeRF demonstrations originated in a 2020 Google research paper on spatially filmed light-field videos.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe now