AI-generated research ideas are more novel, but there is a catch

A large-scale study involving over 100 natural language processing researchers reveals that AI-generated research ideas are considered more novel than those from human experts. However, the AI-generated ideas may face challenges in terms of feasibility.
Stanford University researchers conducted a carefully controlled comparative study to examine whether large language models can produce novel research ideas comparable to those of human experts. The study involved more than 100 highly qualified researchers in the NLP field.
AI ideas seen as more innovative but impractical
Nearly 300 evaluations across all experimental conditions showed that AI-generated ideas were consistently rated as more novel than human-generated ideas. This finding remained robust even after multiple hypothesis corrections and various statistical tests.
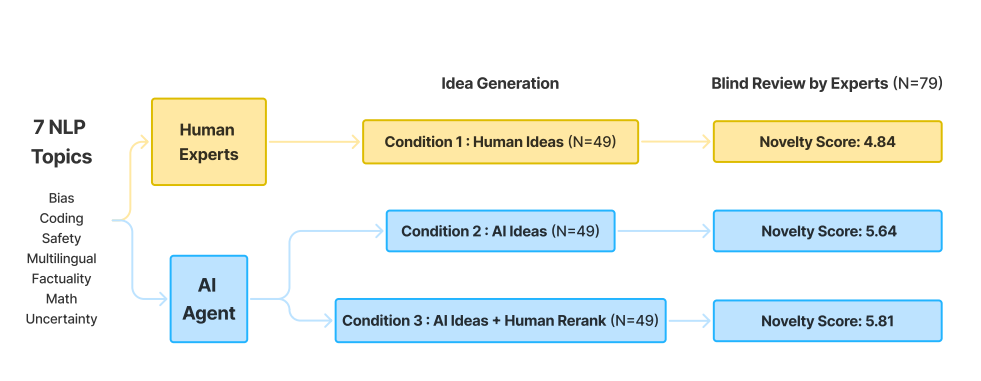
However, the study suggested that the increased novelty may come at a slight cost to feasibility. The sample size was not large enough to definitively confirm these effects.
Potential drawbacks of AI-generated ideas
The study identified several recurring issues with AI-generated research ideas:
1. Lack of implementation details
2. Incorrect use of datasets
3. Missing or inappropriate benchmarks
4. Unrealistic assumptions
5. Excessive resource requirements
6. Insufficient motivation
7. Inadequate consideration of existing best practices
In contrast, human-generated ideas tended to be more grounded in existing research and practical considerations, though possibly less innovative. Human ideas often focused on common problems or datasets and prioritized feasibility over novelty.
Study methods and future directions
The study used GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Llama-2-70B to generate AI ideas, with external source retrieval via RAG. To minimize bias, researchers standardized the style of human and AI ideas and aligned topic distributions. They did not test more advanced models like GPT-4o, Llama 3 or o1.
The research team proposed several approaches to build on their findings: Comparing AI ideas with accepted papers from top conferences, having researchers develop both AI and human ideas into complete projects and exploring the automation of idea execution through code-generating AI agents.
Existing examples of AI contributions to research include Google's AI-accelerated chips in Pixel smartphones and applications in medicine.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.