OpenAI's o3 model outperforms the newer GPT-5 model on complex, multi-app office tasks

A new benchmark called OdysseyBench puts AI agents through realistic, multi-day office workflows, and the results are surprising: OpenAI's older o3 model consistently outperforms the newer GPT-5 on many complex tasks.
Created by researchers at Microsoft and the University of Edinburgh, OdysseyBench is designed to move beyond isolated "atomic tasks" and test how models handle scenarios that unfold over several days.
The benchmark covers 602 tasks across Word, Excel, PDF, email, and calendar apps, split between 300 realistic tasks from OfficeBench (OdysseyBench+) and 302 newly constructed, especially challenging scenarios (OdysseyBench-Neo). Both sections require models to pull information from multi-day conversations, plan multi-step sequences, and coordinate actions across different office tools.
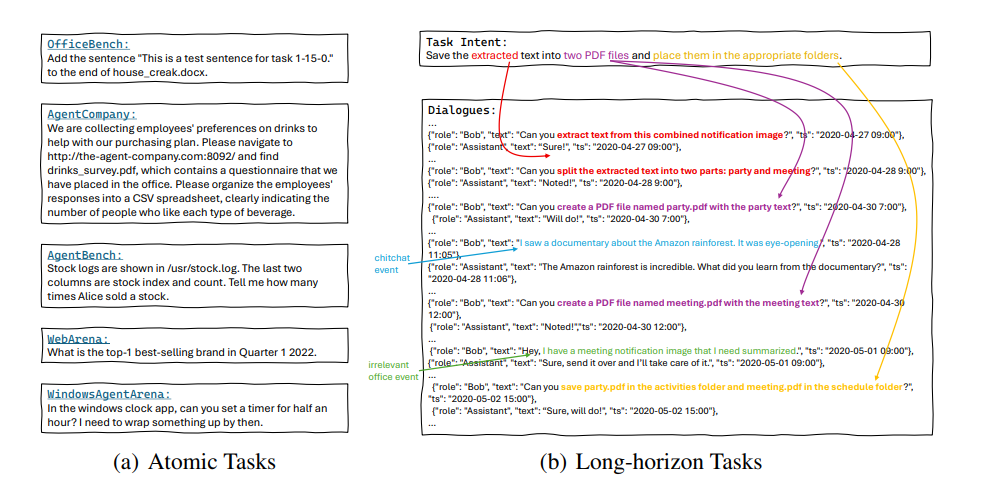
Long-term tasks with Word, Excel, email, and calendar
The main challenge for these AI agents is solving dialog-driven, long-term office tasks. In both OdysseyBench+ and OdysseyBench-Neo, OpenAI's o3 consistently comes out ahead of GPT-5.
On OdysseyBench-Neo, which features the most demanding, hand-crafted tasks, o3 achieves a 61.26% success rate, compared to GPT-5's 55.96% and GPT-5-chat's 57.62%. The gap widens on tasks that require using three applications at once: o3 scores 59.06%, while GPT-5 manages just 53.80%.
Results on OdysseyBench+ tell a similar story. Here, o3 scores 56.2%, beating GPT-5 at 54.0% and GPT-5-chat at 40.3%. The difference is even more pronounced on tasks that involve coordinating two or three apps, where context and planning matter most.
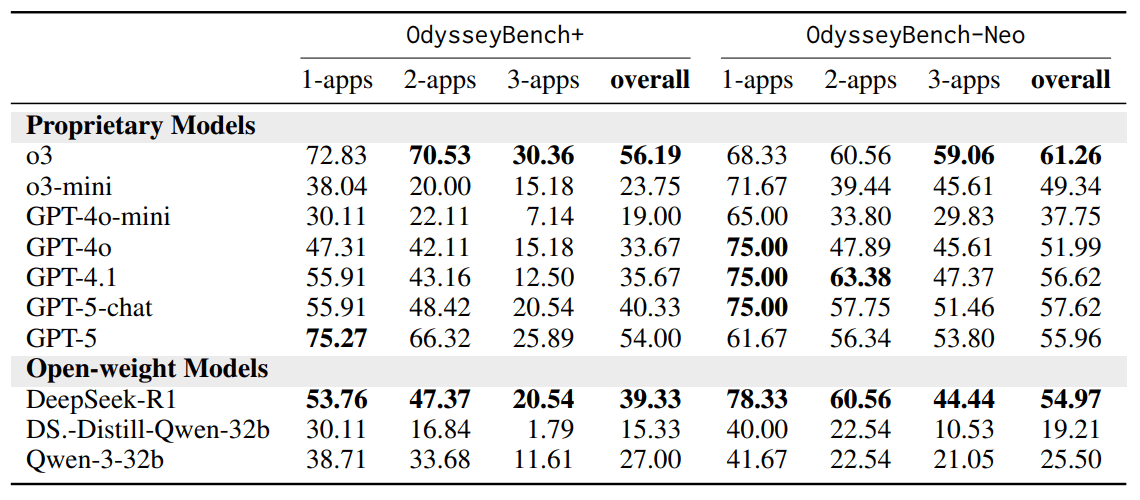
Interestingly, GPT-5-chat actually outperforms GPT-5 on OdysseyBench-Neo. This is likely because Neo tasks focus on dialog-based assistance, playing to GPT-5-chat's strengths. Meanwhile, OdysseyBench+ includes more fragmented, less conversational scenarios, where the reasoning-foucsed GPT-5 can better extract relevant information from disjointed input.
The paper doesn't specify the reasoning settings for GPT-5, such as thinking time or agent parameters, and a more advanced GPT-5 Pro model wasn't part of the evaluation.
These findings are especially relevant as OpenAI is working on AI agents that can "think" for hours or even days, with the goal of generating new ideas and automating research in fields like medicine and AI safety. OdysseyBench could become a key benchmark for these long-horizon systems. At the same time, the results highlight that progress is slowing down: while both o3 and GPT-5 are clear improvements over older models, there's no evidence of a jump from o3 to GPT-5. It's worth noting that o3 was only officially released in April.
AI agents still have trouble with complex workflows
A closer look at the results highlights some recurring problems. Agents often overlook important files, skip necessary steps, or use the wrong tools. For instance, some models tried to create PDF files before generating the original text in Word or failed to extract content from PDFs before writing a review document.
Tasks that involve creating or editing DOCX and XLSX files are especially error-prone. These require careful, multi-step coordination—an area where the agents consistently struggle.
The researchers say this points to a bigger challenge: today's AI agents still have trouble with precise, multi-stage planning that spans different tools, timeframes, and contexts. OdysseyBench and the HOMERAGENTS framework are available on GitHub, and full details on the benchmark setup and evaluation prompts are in the paper appendix.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.