Apple Intelligence is efficient, but its "intelligence" is average

Key Points
- At WWDC 2024, Apple introduced Apple Intelligence, a new generative AI system consisting of multiple AI models built into iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia.
- Internal benchmarks show that Apple's AI server models perform on par with GPT-3.5, while smaller on-device models can outperform larger small models. To improve performance for certain tasks, such as summarization, Apple uses an adapter strategy.
- In addition, Apple partners with OpenAI and integrates ChatGPT into iOS and Siri to gain access to capable multimodal SOTA models and extend the capabilities of Apple Intelligence for sophisticated tasks.
Apple's own benchmarks show that the company's on-device and cloud LLMs achieve middling performance compared to other AI models. To boost performance for certain tasks, Apple has an adapter strategy - and ChatGPT.
At the 2024 Worldwide Developers Conference, Apple showed off its new "Apple Intelligence" generative AI system, built into iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia. It has several generative AI models that take the user's context into account.
Apple says it uses licensed data, public data from its AppleBot web crawler, and human labeled and synthetic data to train its models. According to Apple, private user data is not part of the training set.
Apple's server model is on par with GPT-3.5 Turbo
Internal benchmarks pitting the models against open-source and commercial models of similar size, such as GPT-3.5, show that Apple's AI models, while efficient for their size, perform well below SOTA models such as GPT-4.
With around three billion parameters, the on-device model beats larger models like Phi-3-mini, Mistral-7B, and Gemma-7B. The server model performs similar to DBRX-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22B, and GPT-3.5-Turbo, Apple says.
The server model can't compete with GPT-4. So don't expect any new "wow" moments from Apple Intelligence. For now, Apple Intelligence's main advantage is how deeply it's embedded in Apple's operating systems.
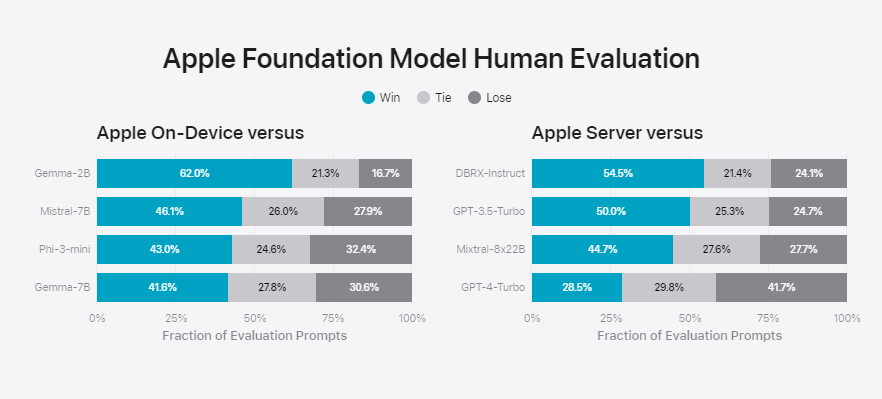
Apple says it tested prompts with varying levels of difficulty in areas such as brainstorming, sorting, answering yes/no questions, coding, pulling out key points, math, answering open-ended questions, paraphrasing, security, summarizing, and writing for the results above. People rated the output of the models.
When testing writing skills on internal benchmarks just for summarizing and composing text, Apple's on-device models outperformed larger models. The server model is as good as GPT-4 Turbo on these tasks. The results are only for how the models perform without task-specific adapters (see below).
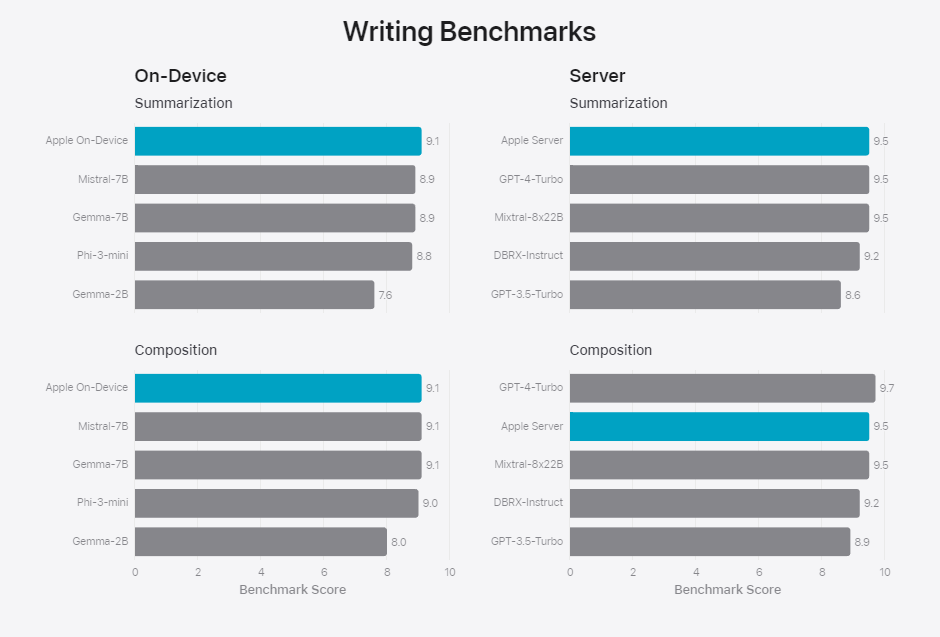
To improve the performance of the base models, Apple uses an adapter strategy. Adapters are small neural network modules that are optimized for specific tasks, such as summarization or spell checking, and can be controlled by the base model after being fine-tuned for that task.
Video: Apple
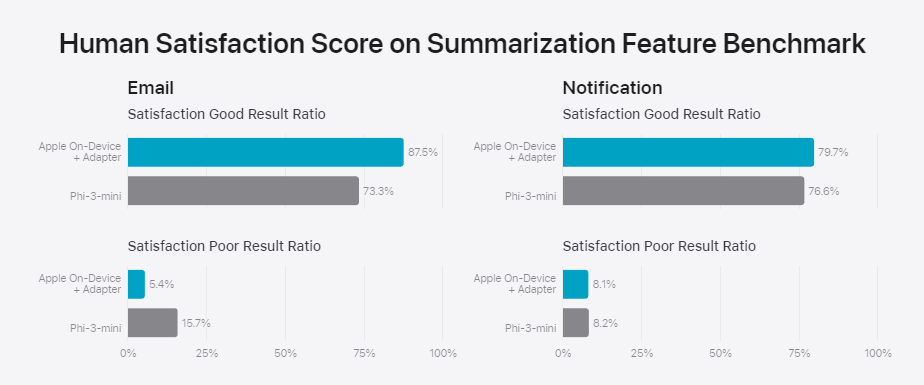
Apple says that adapters can make the base models better at specific tasks in a dynamic, memory-efficient way without losing the general knowledge of the model. In some cases, Apple's on-device model with an adapter is much better than Microsoft's Phi-3-mini at summarizing emails and notifications. Notably, user satisfaction is increased by about ten percent due to fewer bad summaries.
Other than that, Apple is relying on its team-up with OpenAI and adding ChatGPT to expand what Apple Intelligence can do. By adding ChatGPT to iOS and Siri, Apple can use OpenAI's more capable multimodal models like GPT-4o when they're needed, like for hard writing tasks in the text editor or complex requests to Siri. It's not yet clear exactly when and how many requests will be sent to OpenAI.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe now