Apple's new Ferret-UI 2 AI system can control apps across iPhones, iPads, Android, and Apple TV
Apple has developed a new AI system called Ferret-UI 2 that can read and control apps across iPhones, iPads, Android devices, web browsers, and Apple TV.
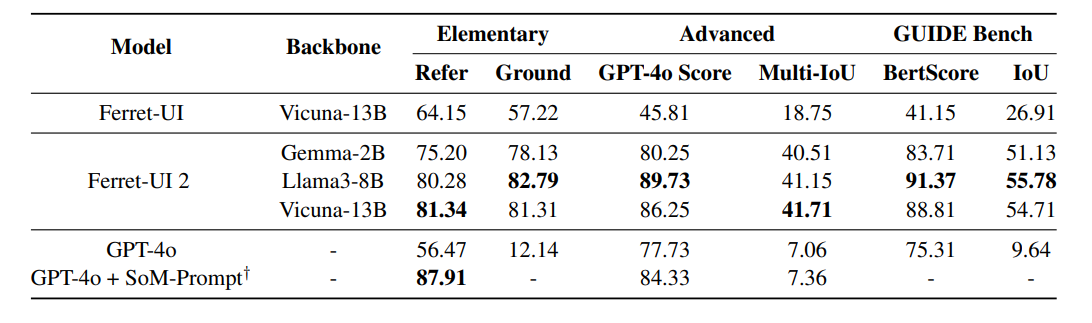
The system scored 89.73 in UI element recognition tests, significantly higher than GPT-4o's score of 77.73. It also shows significant improvements over its predecessor in basic tasks such as text and button recognition, as well as more complex operations.
Understanding user intent
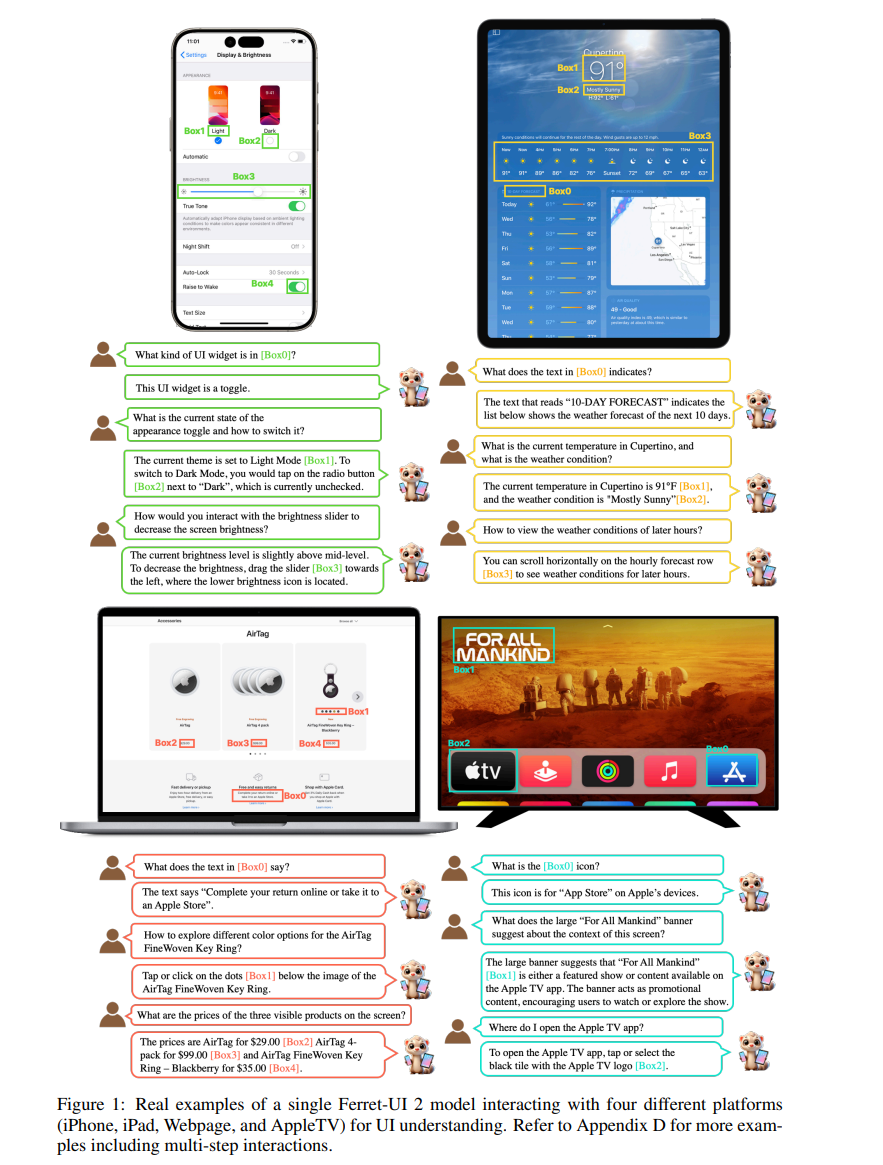
Instead of relying on specific click coordinates, Ferret-UI 2 aims to understand user intent. When given a command such as "Please confirm your input," the system can identify the appropriate button without requiring precise location data. Apple's research team used GPT-4o's visual capabilities to generate high-quality training data that helped the system better understand how UI elements relate to each other spatially.
Ferret-UI 2 uses an adaptive architecture that recognizes UI elements across platforms. It includes an algorithm that automatically balances image resolution and processing requirements for each platform. According to the researchers, this approach is "both information-preserving and efficient for local encoding."
Testing showed strong cross-platform performance, with models trained on iPhone data achieving 68 percent accuracy on iPads and 71 percent accuracy on Android devices. However, the system had more difficulty transitioning between mobile devices and TV or Web interfaces, which the researchers attribute to differences in screen layouts.
Llama- and Gemma-based Ferret UI models are available from Hugging Face, along with a demo.
Microsoft releases UI understanding tool as open source
Apple's work comes as other companies push forward with their own UI understanding AI systems. Anthropic recently released an updated Claude 3.5 Sonnet with UI interaction, while Microsoft released OmniParser, an open-source tool that converts screen content into structured data, for the same purpose.
Apple also recently unveiled CAMPHOR, a framework that uses specialized AI agents coordinated by a master reasoning agent to handle complex tasks. Combined with Ferret-UI 2, this technology could enable voice assistants like Siri to analyze and perform complex tasks, such as finding and booking a specific restaurant, that involve navigating apps or the web using only voice commands.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.