Deepseek's R1 model closes the gap with OpenAI and Google after major update
Deepseek has rolled out a significant update to its R1 model, putting it back in the running with top AI models from major Western tech companies, while still offering open weights.
The new version, Deepseek-R1-0528, keeps the original architecture but uses improved algorithms and more computing power to boost performance across the board. According to Deepseek, the update especially improves the model's reasoning abilities, enabling what the company calls "significantly improved depth of reasoning."
On the AIME 2025 math test, the model's accuracy climbed from 70 to 87.5 percent. It's also handling more information per question now, with the average number of tokens per prompt rising from 12,000 to 23,000—evidence that the model is performing deeper analysis without any changes to its core architecture. Deepseek notes that the update not only improved performance but also reduced hallucinations and expanded support for JSON output and function calling.
Gains across math, code, and logic
Deepseek's own benchmarks show broad improvements. On AIME 2024, accuracy went from 79.8 to 91.4 percent. HMMT 2025 saw a leap from 41.7 to 79.4 percent, and CNMO 2024 improved from 78.8 to 86.9 percent.
Programming benchmarks tell a similar story. LiveCodeBench scores rose from 63.5 to 73.3 percent, Aider-Polyglot from 53.3 to 71.6 percent, and SWE Verified from 49.2 to 57.6 percent. The model's Codeforces rating also climbed from 1530 to 1930 points.
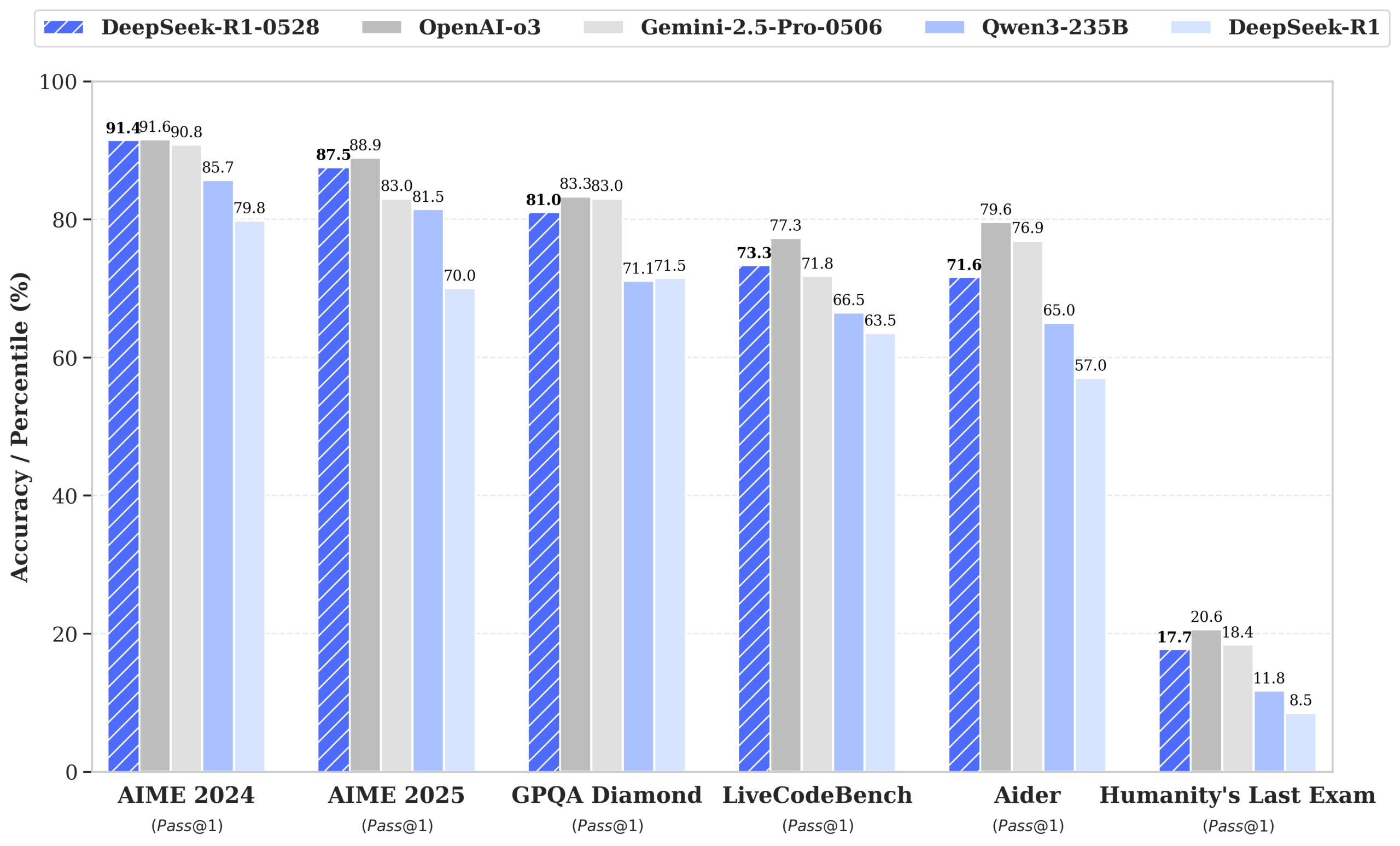
General knowledge and logic tasks also benefited. GPQA-Diamond scores rose from 71.5 to 81.0 percent, Humanity's Last Exam from 8.5 to 17.7 percent, MMLU-Pro from 84.0 to 85.0 percent, and MMLU-Redux from 92.9 to 93.4 percent. The only exception was OpenAI's SimpleQA, which dropped slightly from 30.1 to 27.8 percent. Deepseek says all tests used standardized parameters and a maximum context length of 64,000 tokens.
Independent review backs up the gains
The independent platform Artificial Analysis gave Deepseek-R1-0528 a score of 68 on its Intelligence Index, up from 60 for the January version. That's a jump comparable to the leap from OpenAI's o1 (62) to o3 (70), putting Deepseek in the same league as Google's Gemini 2.5 Pro.
Artificial Analysis currently ranks Deepseek-R1-0528 ahead of xAI's Grok 3 mini (high), Meta's Llama 4 Maverick, Nvidia's Nemotron Ultra, and Alibaba's Qwen3 253. In coding, the model is just shy of OpenAI o4-mini (high) and o3.
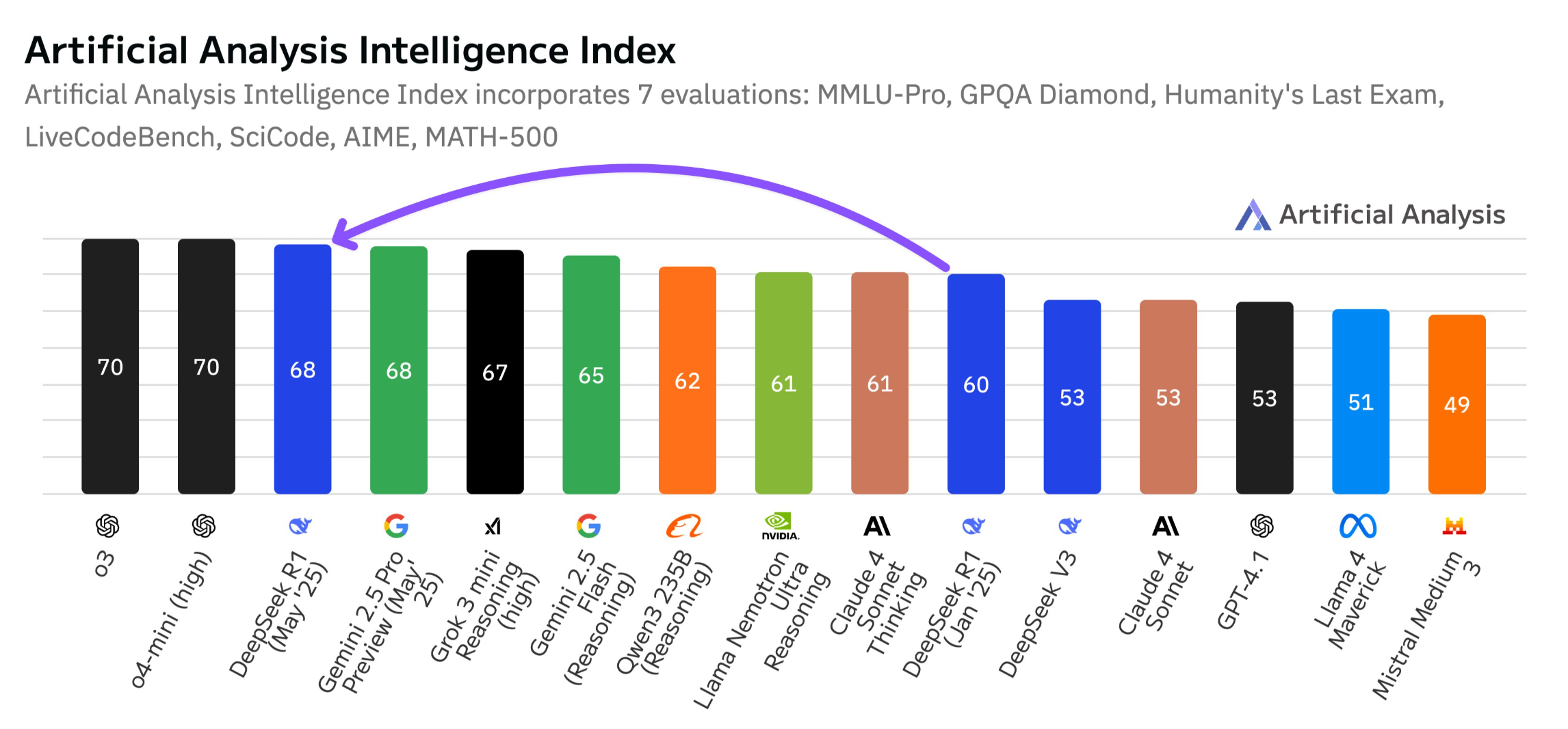
Artificial Analysis points to increased post-training with reinforcement learning as the main reason for the improvements. Token usage in evaluation rose by 40 percent—from 71 to 99 million tokens—so the model now produces longer, more detailed answers.
With this update, open models like Deepseek-R1 are closing in on the performance of proprietary US models. Deepseek-R1 still leads the open-weight field, delivering a major performance boost without changing its architecture.
Smaller model, strong math results
Alongside the main R1 update, Deepseek is also releasing a distilled model: Deepseek-R1-0528-Qwen3-8B, which is built on top of Alibaba's Qwen3 8B and retrained using chain-of-thoughts from R1-0528.
Deepseek says this compact model scores 86 percent on AIME 2024—ten points higher than the original Qwen3 8B and on par with the much larger Qwen3-235B-thinking, but designed to run efficiently on an Nvidia H100. Deepseek sees this as proof that reasoning-focused compact models can deliver competitive results while using far fewer resources.
"We believe that the chain-of-thought from DeepSeek-R1-0528 will hold significant importance for both academic research on reasoning models and industrial development focused on small-scale models," the company writes.
Deepseek-R1-0528 is released under the MIT License, which is one of the most permissive open-source licenses available. Unlike the more restrictive licenses attached to models like Llama 3 or Gemma, the MIT License allows anyone to use, modify, and distribute the model—even for commercial projects—with almost no limitations.
Deepseek's Qwen-based models, such as Deepseek-R1-0528-Qwen3-8B, are released under the Qianwen License. The license requires preservation of copyright and license notices, grants express patent rights, and lets users redistribute modified or larger works under different terms—even without sharing source code.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.