DiffSensei: AI pioneers Hinton, LeCun, and Bengio star in fictional manga created by new AI system
Researchers have developed an AI system that can turn written stories into manga-style comics automatically. The system, called DiffSensei, can maintain consistent character appearances and control page layouts throughout a story.
The project comes from a collaboration between Peking University, the Shanghai AI Laboratory, and Nanyang Technological University. DiffSensei combines diffusion models with large language models to handle both the visual and narrative elements of manga creation.
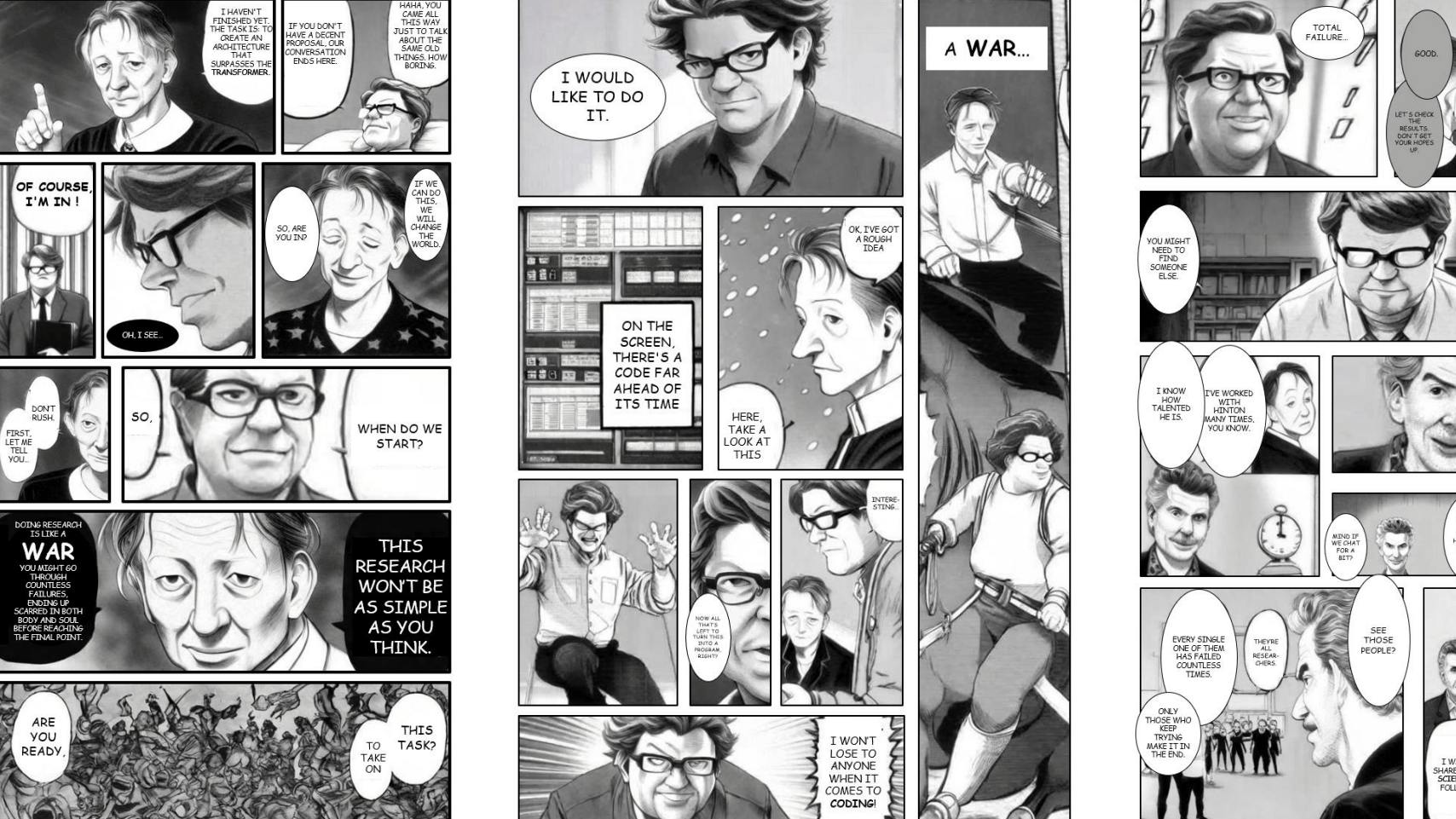
To showcase the system's capabilities, the team created a fictional manga about AI pioneers Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun, and Yoshua Bengio. The story follows their quest to develop an AI model that could outperform the Transformer architecture, capturing their struggles, self-doubt, and eventual triumph - culminating in their Nobel Prize win years later.


DiffSensei generates personalized manga
The system uses multimodal models and LoRAs to keep characters looking consistent from panel to panel. It creates manga in three steps: generating page layouts, drawing the characters, and adding dialogue.
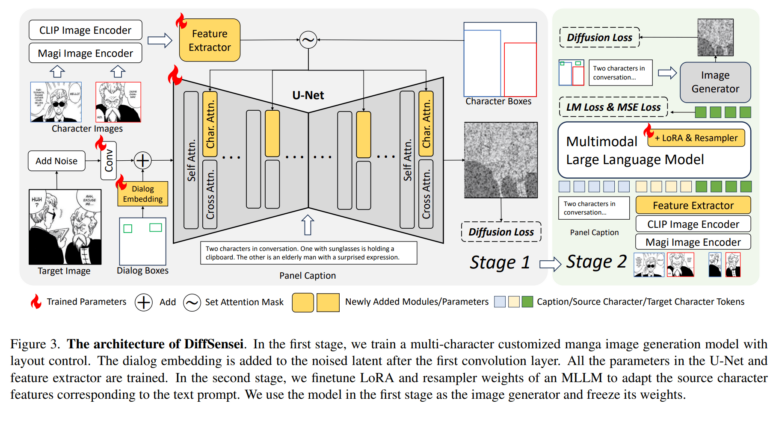
To train DiffSensei, the researchers built a custom dataset called MangaZero, containing more than 43,000 manga pages and 427,000 individual panels from 48 different series. Each panel was carefully annotated to mark character positions and dialogue placement - details the team says are essential for the system to work properly.
Researchers see potential in manga production
The system isn't perfect yet. It struggles when character reference images are unclear, and sometimes similar-looking characters end up blending together in unexpected ways. Without specific character references, the artwork tends to look generic rather than matching a particular manga style.
Despite these limitations, the researchers believe DiffSensei could help streamline manga production in the future. The technology gives artists, publishers, and creators a new tool for making personalized manga stories while maintaining control over characters and layouts.
The research team has made more examples and their dataset available on the DiffSensei project page.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.