Google Deepmind goes open source with Gemini-based Gemma models

Google has introduced Gemma, a new generation of open AI models that builds on the experience of the Gemini models and aims for responsible AI development.
Google DeepMind and other Google teams created Gemma to provide developers and researchers around the world with accessible, capable models, the company said. The model comes in two sizes: Gemma-2B and Gemma-7B, each with pre-trained and instruction-based variants.
The Gemma models have been trained on up to 6 trillion mostly English-language tokens from web pages, math problems, and code, using similar architectures, data, and training methods as the Gemini family of models. Unlike Gemini, Gemma is not multimodal and has not been trained for peak performance on multilingual tasks.
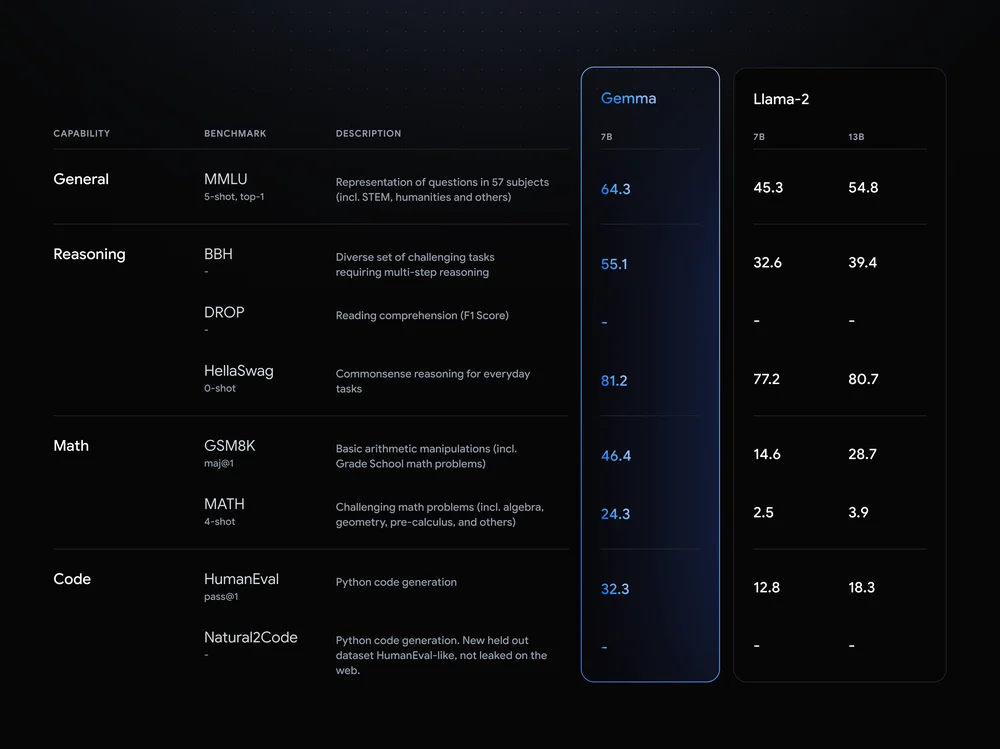
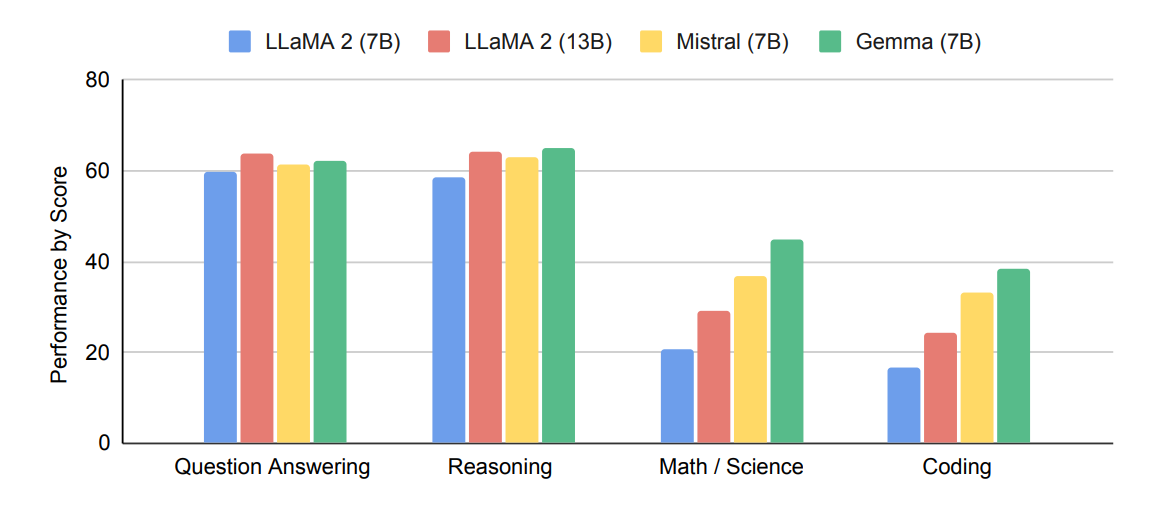
According to Google's technical report, Gemma outperforms similarly sized open models such as LLaMA 2 with 7 and 13 billion parameters and Mistral-7B in 11 out of 18 text-based tasks. The largest lead is seen in math and coding, although there is a lot of room for improvement in general.
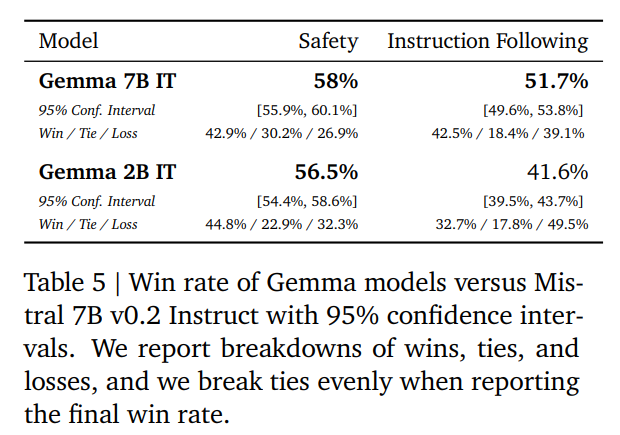
Google's progress is also notable in that Gemma-2B, a much smaller model, outperformed Mistral-7B with more than three times as many parameters in safety tests. The Gemma-7B model also outperformed in experiments evaluating the accuracy of following prompts. However, Gemma cannot currently compete with commercial alternatives or larger open-source models such as LLaMA-2-70B or Mixtral-8x7B.
Google says it is aware that open-source LLMs can be exploited for harmful purposes. These include the creation of counterfeit images, AI-generated misinformation, and illegal and disturbing content.
Making the weights freely available, rather than hiding the model behind an API, poses an additional risk. But Google says it has taken several steps to ensure the safety and reliability of Gemma. The pre-trained models have been stripped of personal information and other sensitive data.
In addition, they were adapted to behave responsibly through extensive fine-tuning and human feedback (RLHF). Google then evaluated the models through manual red-teaming, automated adversarial testing, and performance assessments for dangerous activities.
To help external developers build safe AI applications, Google also introduced the new Responsible Generative AI Toolkit. This toolkit includes safety classification methods, debugging tools, and best practices based on Google's experience with large-scale language models.
Gemma is optimized for multiple AI hardware platforms, including NVIDIA GPUs and Google Cloud TPUs. Nvidia will integrate the Gemma models into its data chatbot app "Chat with RTX" and offers test versions of the Gemma 2B and Gemma 7B models in its Playground.
Compatibility with key frameworks such as JAX, PyTorch, and TensorFlow makes Gemma a versatile model in the AI development portfolio. Google also provides access to Gemma through free credits for research and development on platforms such as Kaggle and Google Cloud. New cloud users receive a $300 credit, and researchers can also apply for funding of up to $500,000 in credits.
Gemma appears to be a very strategic move by Google Deepmind
Gemma could be an attempt by Google Deepmind to get its foot in the open-source door. It's still difficult to predict how the model market will evolve and whether proprietary models will remain as dominant as OpenAI's GPT models currently are.
So far, Meta has been a pioneer in Big Tech open-source language models with its LLaMA family. With its open-source policy, Meta wants to dominate the developer scene and get them used to its AI ecosystem to later develop higher quality AI products more efficiently.
Gemma could be a strategic move to enter the open-source market, just in case Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg is right. Google has played a similar game before - and won: Android is the leading mobile operating system.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.