Google unveils new AI models, infrastructure, and agent protocol at Cloud Next
At its annual Cloud Next conference, Google introduced a range of new AI technologies. Here's an overview of its most important AI announcements.
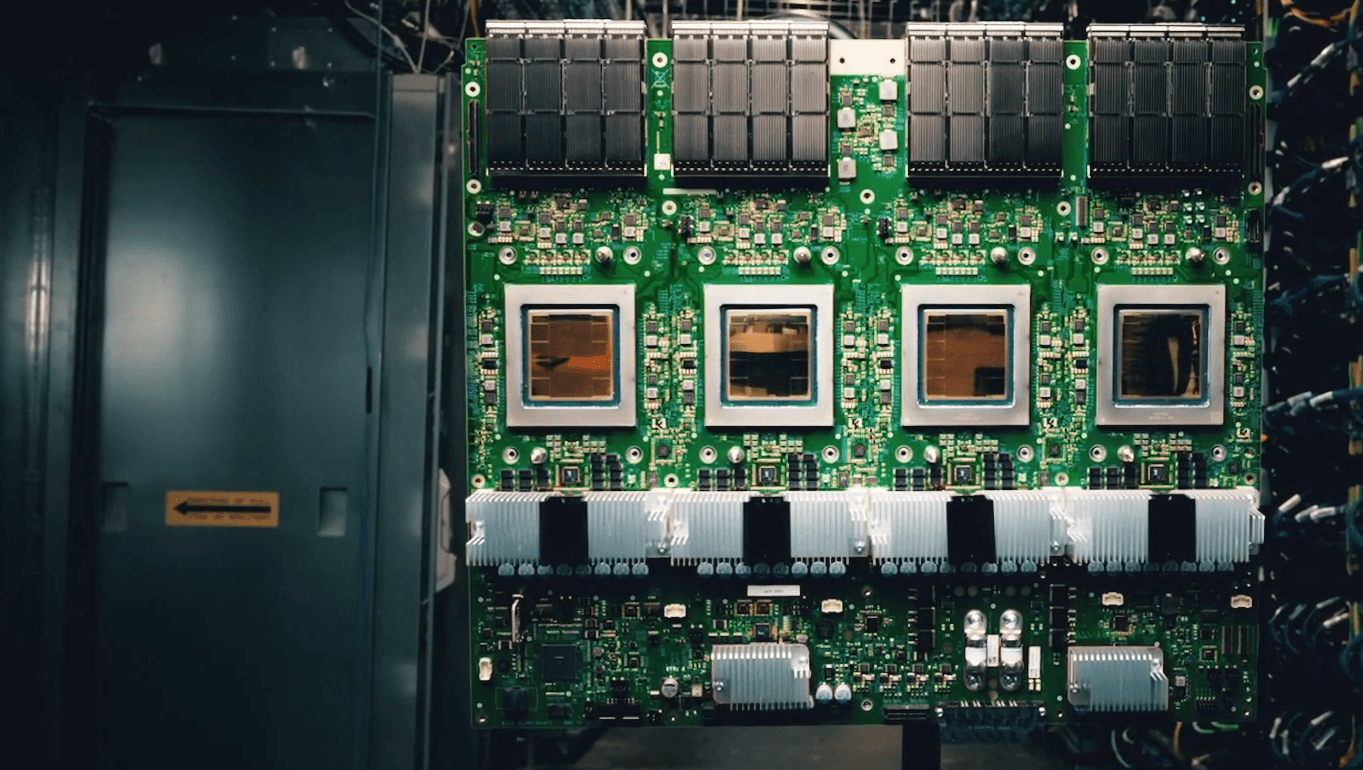
Ironwood TPU: Google's most powerful chip for inference
Google has unveiled Ironwood, its seventh-generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), designed specifically for inference—the process of generating AI model outputs. According to Google, Ironwood delivers up to 3,600 times the performance of the original TPU and is the company’s most powerful and energy-efficient version to date.
Ironwood uses liquid-cooled chips and is offered in configurations ranging from 256 to 9,216 chips per pod. Its largest setup reaches 42.5 exaflops of computing power—24 times greater than the projected peak of El Capitan, currently the fastest supercomputer. Each chip includes 192 GB of high-bandwidth memory, 7.2 terabits per second of bandwidth, and 1.2 terabits per second of interconnect speed.
Gemini 2.5 Flash: A faster, lower-cost reasoning model
Google has introduced Gemini 2.5 Flash, a faster and more cost-efficient variant of its Gemini 2.5 Pro model that performs well in recent benchmarks. According to the company, Gemini 2.5 Flash allows organizations to adjust the level of reasoning, making it possible to balance performance and cost. The model will be available soon through Google’s Vertex AI platform.
The core Gemini 2.5 model also now powers Google’s Deep Research feature, and Google's product manager Logan Kilpatrick says that "early tests show users prefer this 2:1 vs "other products."
Standardizing agent collaboration with Agent2Agent protocol
Google is introducing the open Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol, which aims to enable cross-platform collaboration between autonomous AI agents. Built on standards such as HTTP and JSON-RPC, A2A supports various input formats—including text, audio, and video—and complies with security standards via OpenAPI.
Agents can advertise their capabilities using "agent cards" and negotiate task formats or user interfaces dynamically. In a video demonstration of an automated hiring process, Google uses its Agentspace interface to show how an agent can coordinate with others to identify suitable candidates, schedule interviews, and conduct background checks. A production-ready version of the Agent2Agent protocol is expected later this year.
Video: Google AI
Updates for Google's media models
Google has updated several generative AI models for media generation, adding features across video, music, images, and voice synthesis. The Veo 2 video model now supports editing functions such as inpainting (removing elements), outpainting (expanding content), camera control, and interpolation for smoother transitions. These features are available in preview for selected testers.
Google's Veo 2 video model now supports outpainting. | Video: Google AI
Lyria, Google’s text-to-music model, is also now available. It generates music based on short text prompts and can adapt to genre, mood, and tempo—useful for podcasts, marketing, or video content.
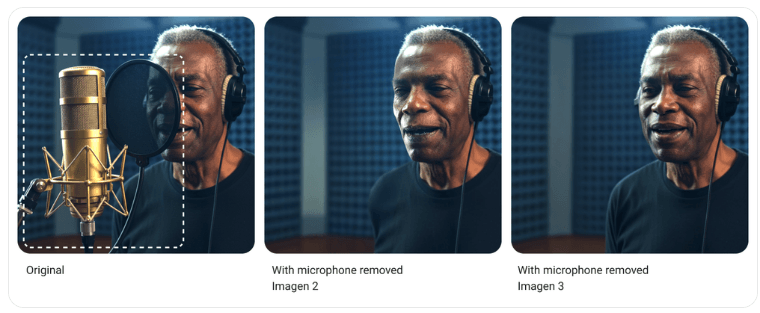
The Imagen 3 image model features improved inpainting capabilities for removing objects or reconstructing damaged areas. Google reports significantly enhanced transitions and detail reproduction.
Chirp 3, the company’s sound generation model, adds two new features: "Instant Custom Voice," which can synthesize a voice from just ten seconds of audio, and speaker segmentation for multi-person recordings.
Google says all generative models include safeguards such as SynthID digital watermarks, content filters, and privacy controls. A liability guarantee is also offered in case of copyright disputes involving generated content.
AI-powered automation in Google Workspace
In addition, Google is expanding AI capabilities within its enterprise suite through Workspace Flows, a new automation platform that integrates across Docs, Sheets, Meet, and Chat. Using custom Gemini-powered chatbots called "Gems," users can automate workflows such as handling customer service requests, reviewing policy documents, or triaging support tickets.
Individual Workspace apps are also receiving new AI features. In Google Docs, users can generate full audio versions of documents or receive podcast-style summaries. A "Help me refine" feature offers suggestions to improve clarity, structure, and tone.
In Google Sheets, the "Help me analyze" tool can automatically evaluate data and suggest visualizations or next steps. The new Google Vids app allows users to create realistic video content using the Veo 2 model—without needing external editing software.
In Google Meet, Gemini can summarize meetings or answer specific questions. In Google Chat, Gemini can be summoned with the @ command to extract decisions, open questions, or next steps from conversations.
Supporting science with cloud-based AI infrastructure
Google Cloud is expanding its role in scientific computing with new H4D virtual machines optimized for highly parallel, CPU-based workloads. These are designed for use cases such as molecular dynamics, climate modeling, and materials science.
The VMs use AMD processors and Google’s Titanium network to improve data transmission and support cloud-based supercomputing clusters. Management tools such as Cluster Toolkit and Cluster Director are available to coordinate multi-node deployments.
Google is also rolling out AI-supported scientific applications. AlphaFold 3, developed by Google DeepMind, can predict the structure and interactions of biological molecules. The high-throughput version on Google Cloud can process large sequence datasets to accelerate disease research.
WeatherNext, another model based on Google Research, provides customizable, high-resolution weather forecasting via the Vertex AI platform.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.