Google's MedGemma 1.5 brings 3D CT and MRI analysis to open-source medical AI

Key Points
- Google has launched MedGemma 1.5, an open-source AI model capable of analyzing three-dimensional medical scans like CTs and MRIs by processing every layer of an image at the same time.
- The model improves diagnostic accuracy for MRI scans by 14 percentage points, reaching 65 percent, while its new speech recognition tool, MedASR, makes 82 percent fewer errors in medical dictations compared to OpenAI's Whisper large-v3.
- Competition in the healthcare AI sector is heating up, with OpenAI recently acquiring the startup Torch for approximately $100 million and Anthropic releasing its own Claude for Healthcare solution.
Google has updated its open-source medical AI model, MedGemma 1.5, making it the first publicly available language model capable of interpreting three-dimensional CT and MRI images.
The healthcare industry is adopting generative AI at roughly twice the rate of the broader economy, according to Google Research. To support this shift, the company introduced MedGemma 1.5 4B, an updated version of its open-source medical image interpretation model, alongside MedASR, a new speech recognition model built specifically for medical dictation.
Since its launch last year, the original MedGemma has seen millions of downloads, according to Google, spawning hundreds of community variants on Hugging Face.
The update marks a significant expansion in capability. While the previous version was limited to 2D inputs like X-rays or skin images, MedGemma 1.5 processes 3D volumetric data from CT and MRI scans, along with histopathology slides. This allows developers to feed entire CT scan volumes into the model at once, rather than processing them slice by slice.
This approach also applies to histopathology, where the model analyzes multiple sections of a tissue sample simultaneously. By viewing these sections together, the AI can identify correlations that might be missed in individual slides. Google claims MedGemma 1.5 is the first open-source model to handle this type of 3D medical data while retaining its understanding of standard images and text.
Significant gains in diagnostic accuracy
Internal benchmarks indicate significant performance improvements over the previous version. CT classification accuracy rose three percentage points to 61 percent, while MRI classification jumped 14 points to nearly 65 percent.
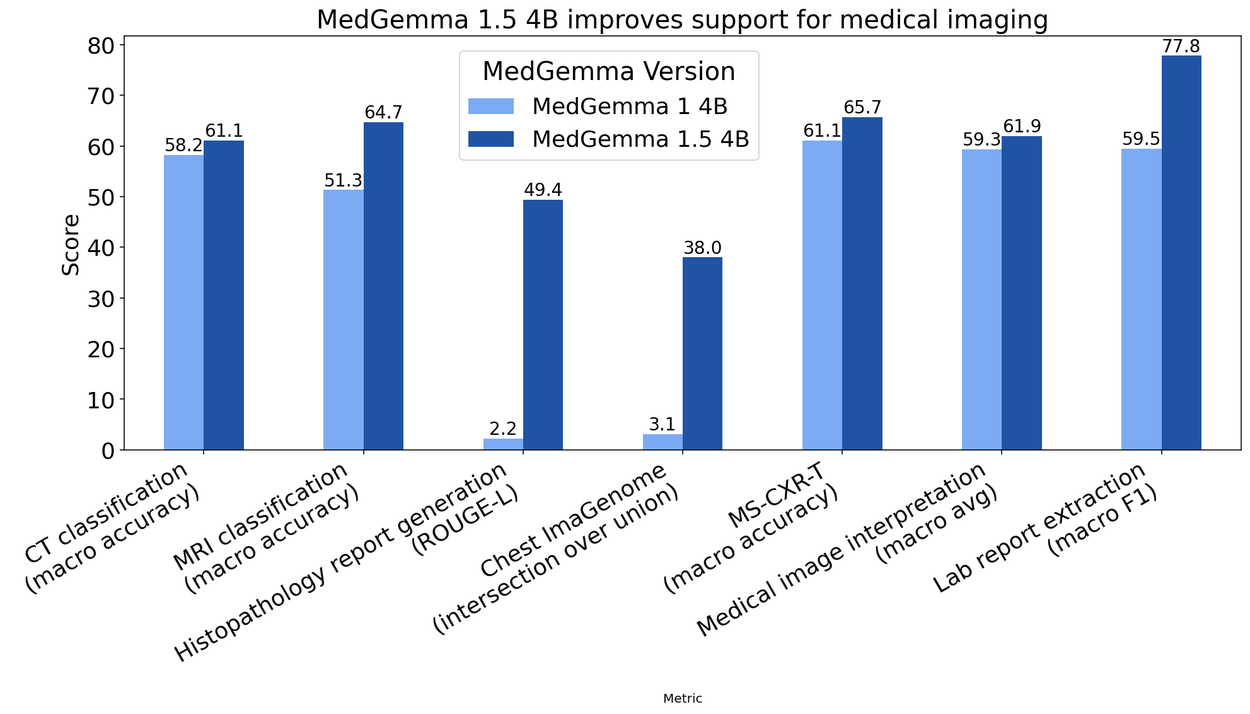
The model also shows progress in text-based tasks. On the MedQA medical reasoning benchmark, MedGemma 1.5 4B scored 69 percent, up from 64 percent in the previous version. Accuracy in extracting information from electronic patient records saw the largest improvement, jumping from 68 percent to 90 percent.
Despite these gains, Google emphasizes that the technology is still in its early stages. The company notes the model remains incomplete, though developers can likely achieve better results by fine-tuning it on their own specific datasets.
Reducing transcription errors in clinical workflows
Google also introduced MedASR, a speech recognition tool trained specifically on medical vocabulary. According to Google, MedASR outperforms OpenAI's generalist Whisper large-v3 model, producing 58 percent fewer errors on X-ray dictations and 82 percent fewer errors on general medical dictations.
The model serves a dual purpose: it functions as a transcription tool and acts as a voice interface for MedGemma, potentially allowing doctors to interact with AI systems entirely through speech.

Early adopters are already testing the technology. Malaysian firm Qmed Asia uses MedGemma to power a conversational interface for clinical treatment guidelines, while Taiwan's National Health Insurance Administration has used the model to analyze over 30,000 pathology reports related to lung cancer surgeries.
Both models are free for research and commercial use via Hugging Face and Google Cloud Vertex AI. However, Google stresses that these models are starting points for developers rather than finished clinical products. They require validation and customization, and their outputs should not be used for direct diagnosis or treatment.
Regulatory hurdles for patient care
While MedGemma is open source, it falls under the "Health AI Developer Foundations Terms of Use". This license imposes restrictions beyond the standard Apache 2.0 agreement used for the source code. Specifically, using the model weights for direct patient diagnosis or treatment requires approval as a medical device by relevant authorities.
Developers building on MedGemma must pass these restrictions down to third parties. Google explicitly states it assumes no liability and provides no medical advice through the models. While the company claims no copyright over the output, users bear sole responsibility for how that output is used.
AI labs race for medical AI dominance
Google's release comes amid intensified competition in the sector. OpenAI recently acquired the startup Torch for approximately $100 million to build a "medical memory for AI" and launched a dedicated ChatGPT Health feature alongside a new AI service for healthcare providers.
Anthropic has also entered the fray with Claude for Healthcare, a HIPAA-compliant solution capable of accessing US databases like Medicare and PubMed. These moves reflect the industry's belief in a massive market opportunity, driven by the hundreds of millions of health-related queries users already ask chatbots globally.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe now