LAION and Intel introduce tools that help AI gauge the intensity of 40 distinct emotions

One of the latest open-source projects from LAION and Intel aims to give AI systems a better grasp of human emotion.
The "Empathic Insight" suite includes models and datasets designed to analyze facial images or audio files and rate the intensity of 40 different emotion categories. For faces, emotions are scored on a scale from 0 to 7; for voices, the system labels emotions as absent, slightly pronounced, or strongly pronounced.
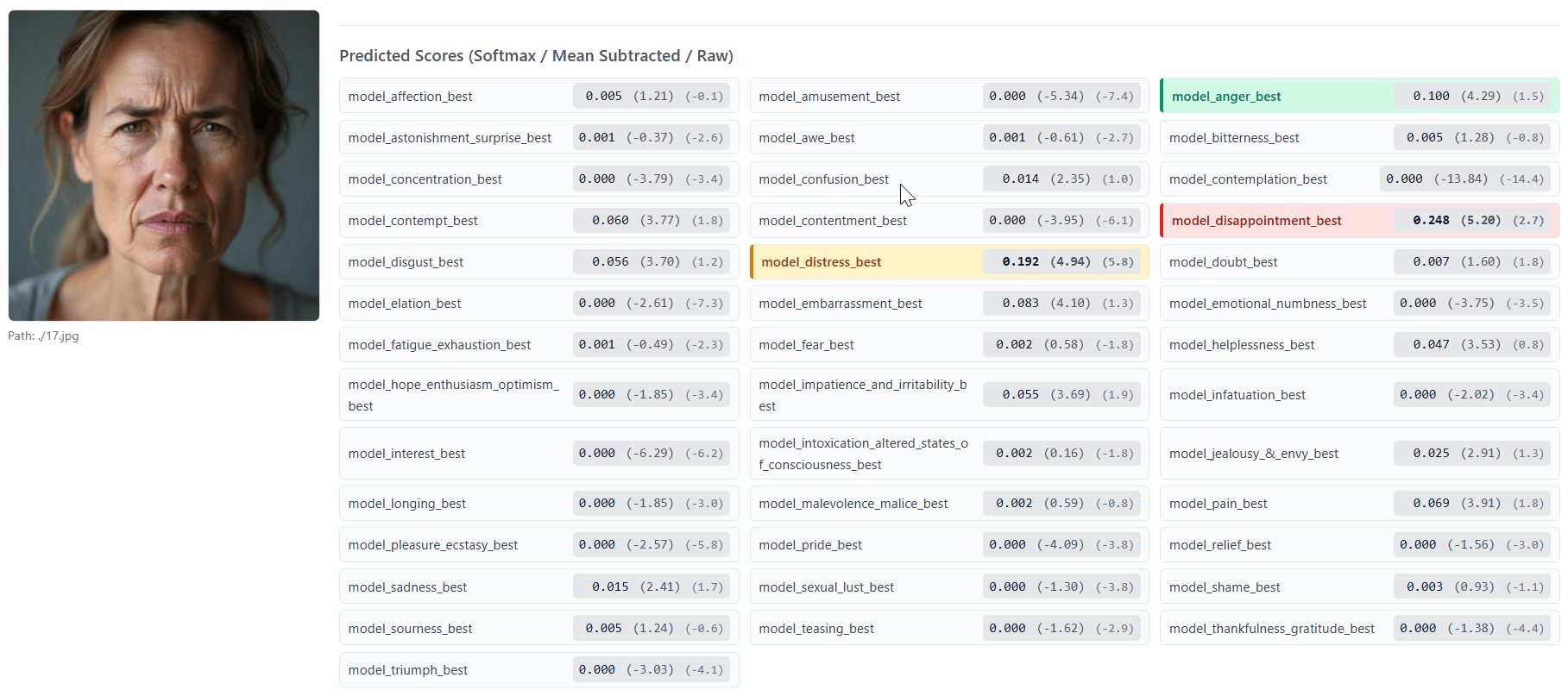
EmoNet, the backbone of these models, draws on a taxonomy of 40 emotion categories developed from the "Handbook of Emotions," a landmark reference in psychology. The researchers expanded the usual list of basic emotions, adding cognitive states like concentration and confusion, physical states such as pain and fatigue, and social emotions including shame and pride. They argue that emotions aren't universally readable - instead, the brain constructs them from a range of signals. As a result, their models work with probability estimates, not fixed labels.
Training with synthetic faces and voices
To train the models, the team used over 203,000 facial images and 4,692 audio samples. The speech data comes from the Laion's Got Talent dataset, which includes more than 5,000 hours of synthetic recordings in English, German, Spanish, and French, all generated using OpenAI's GPT-4o audio model.
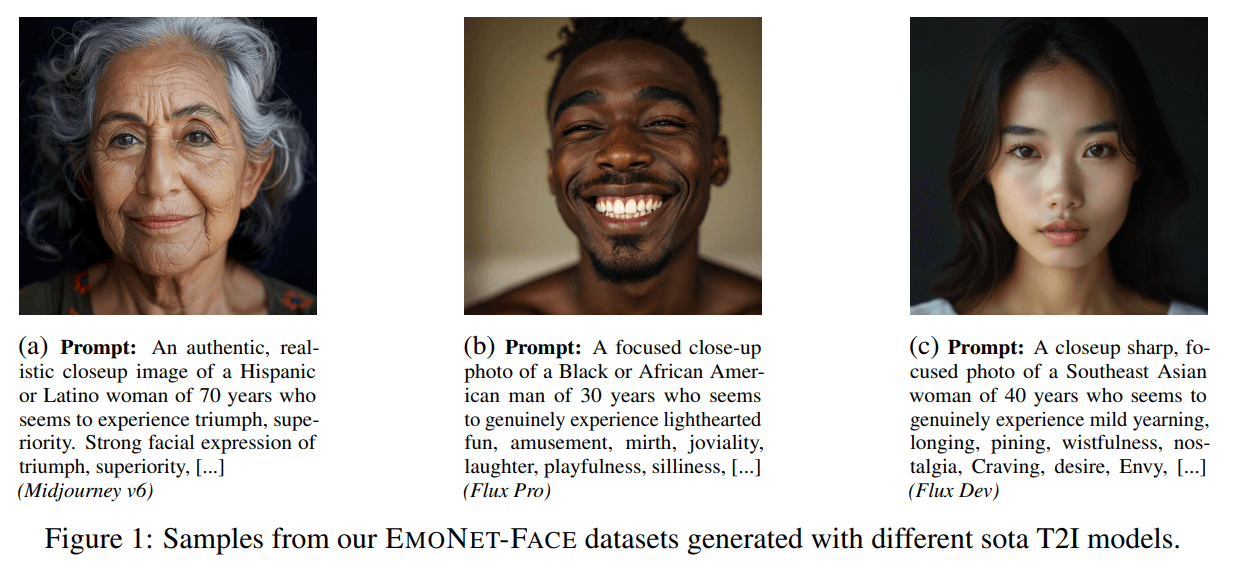
To avoid privacy problems and improve demographic diversity, LAION relied entirely on synthetic data. The facial images were created with text-to-image models like Midjourney and Flux, then programmatically varied by age, gender, and ethnicity. All audio samples were reviewed by psychology-trained experts, and only ratings that three independent reviewers agreed on made it into the dataset.
Outperforming established emotion AI
According to LAION, the Empathic Insight models outperform existing competitors in benchmarks. On the EmoNet Face HQ benchmark, the Empathic Insight Face model showed a higher correlation with human expert ratings than Gemini 2.5 Pro or closed-source APIs like Hume AI. The key metric was how closely the AI's assessments matched those of psychology professionals.
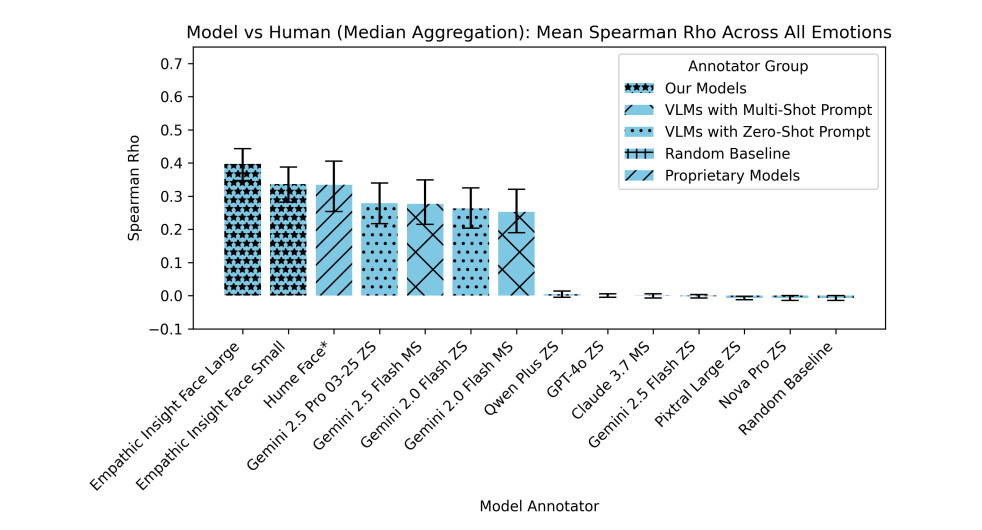
The researchers also report strong results in speech emotion recognition. The Empathic Insight Voice model performed better than existing audio models on the EmoNet Voice Benchmark, correctly identifying all 40 emotion categories. The team experimented with different model sizes and audio processing methods to optimize results.
Enhanced transcription with BUD-E Whisper
Beyond emotion recognition, LAION developed BUD-E Whisper, an upgraded version of OpenAI's Whisper model. While Whisper transcribes speech to text, BUD-E Whisper adds structured descriptions of emotional tone, detects vocal outbursts like laughter and sighs, and estimates speaker traits such as age and gender.
All EmoNet models are available under Creative Commons (for the models) and Apache 2.0 (for the code). Datasets and models can be downloaded from Hugging Face. Both Empathic Insight models come in "Small" and "Large" versions on Hugging Face, making them accessible for different use cases and hardware requirements.
Intel has supported the project since 2021 as part of its open-source AI strategy, with a focus on optimizing models for Intel hardware.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.