Microsoft's "Interactive Agent Foundation Model" learns in Minecraft

Foundation models have dominated AI research over the past few years. Now, Microsoft is unveiling an Interactive Agent Foundation Model designed to perform better in the virtual and real world.
In their new work, researchers from Microsoft Research, Stanford University, and the University of California present the Interactive Agent Foundation Model, which has been trained for a variety of applications using text, image, and action data. The team uses a unified framework that combines different pre-training strategies for image, text, and action. With this work, the team aims to demonstrate the feasibility of such a versatile and adaptable AI framework and test it in three domains: robotics, game AI, and healthcare.
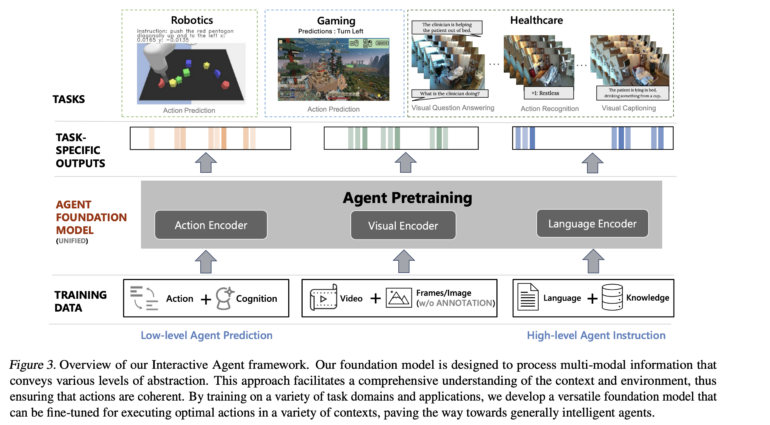
The 277 million parameter model was pre-trained with 13.4 million video frames. These included a variety of robotics and gaming tasks, including Minecraft, with the data including text descriptions and robot action tokens along with the videos. In tests, the model demonstrated its ability to effectively model actions in a variety of domains, such as controlling a robot or predicting actions in Minecraft. The team has also shown that the model can be used in domains such as healthcare, where it was fine-tuned with additional video and text data and its performance benefited from the other data sources.
Microsoft's "Interactive Agent Foundation Model" as an embodied agent
The work can be seen as a contribution to basic research on the path from static, task-specific models to dynamic, agent-based systems, and is reminiscent of work such as Deepmind's GATO. The researchers emphasize the need to generate dynamic behavior that is grounded in an understanding of environmental contexts. To this end, they also define a new paradigm for embodied agents:
We define the embodied agent paradigm as “any intelligent agent capable of autonomously taking suitable and seamless action based on sensory input, whether in the physical world or in a virtual or mixed-reality environment representing the physical world.”
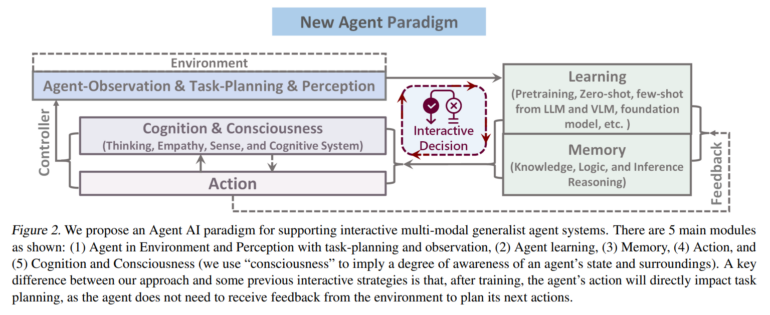
Importantly, an embodied agent is conceptualized as a member of a collaborative system in which it communicates with humans and performs a variety of actions based on human needs. In this way, according to the team, embodied agents can facilitate tedious tasks in the virtual and physical world.
The researchers plan to make their code and models publicly available soon.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.