OpenAI equips DALL-E 3 with C2PA metadata to increase transparency of AI images
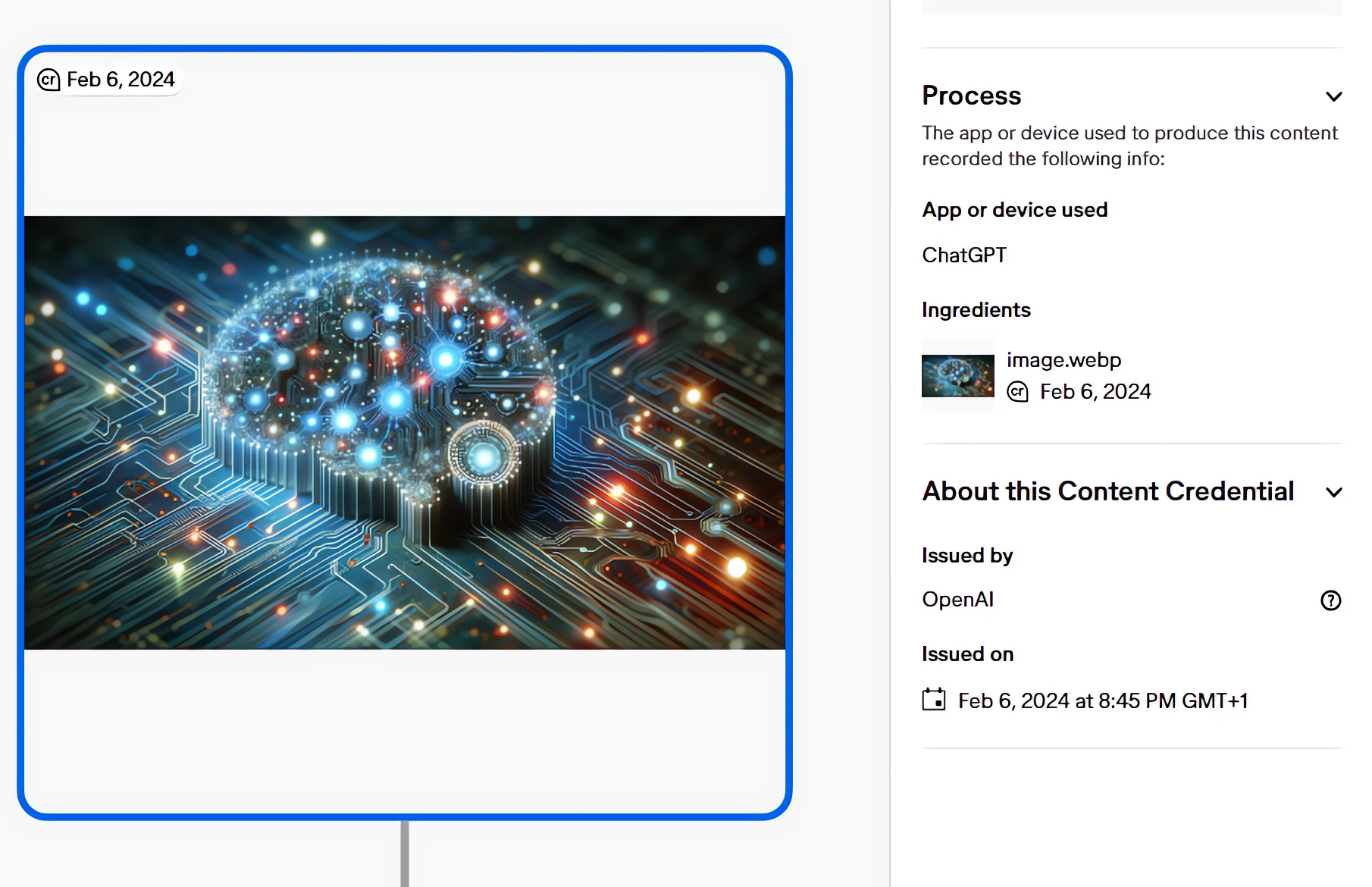
OpenAI has implemented the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) standard in its DALL-E 3 model, which embeds metadata in generated images to verify their origin and associated information.
Images generated with ChatGPT on the web and the API for the DALL-E 3 model now contain C2PA metadata that can be verified on sites such as Content Credentials Verify.
API images include a signature indicating that they were generated using the DALL-E 3 model. Images generated by ChatGPT include an additional reference to their ChatGPT origin. This allows you to distinguish between chat and API.
According to OpenAI, C2PA metadata has an impact on file size. For example, an API-generated PNG image may be three percent larger, an API-generated WebP image may be five percent larger, and a ChatGPT-generated WebP image may be 32 percent larger.
According to OpenAI, the impact on latency should be negligible and the quality of image generation should not be affected.
C2PA is not a solution to fake AI images
C2PA is not a solution to the AI image problem, as metadata can be easily deleted. But it could at least slow down the flood of images or make it more transparent.
OpenAI also notes that metadata can be removed and that some social media platforms today automatically remove metadata from uploaded images.
Meta has announced that it will verify C2PA on its social platforms. Adobe, Microsoft, Intel, and other platform and technology providers also support or plan to support C2PA.
The Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) is an organization that has worked with Adobe to develop a "transparency mark." This mark can be added to the metadata of content to indicate its origin and the use of AI tools.
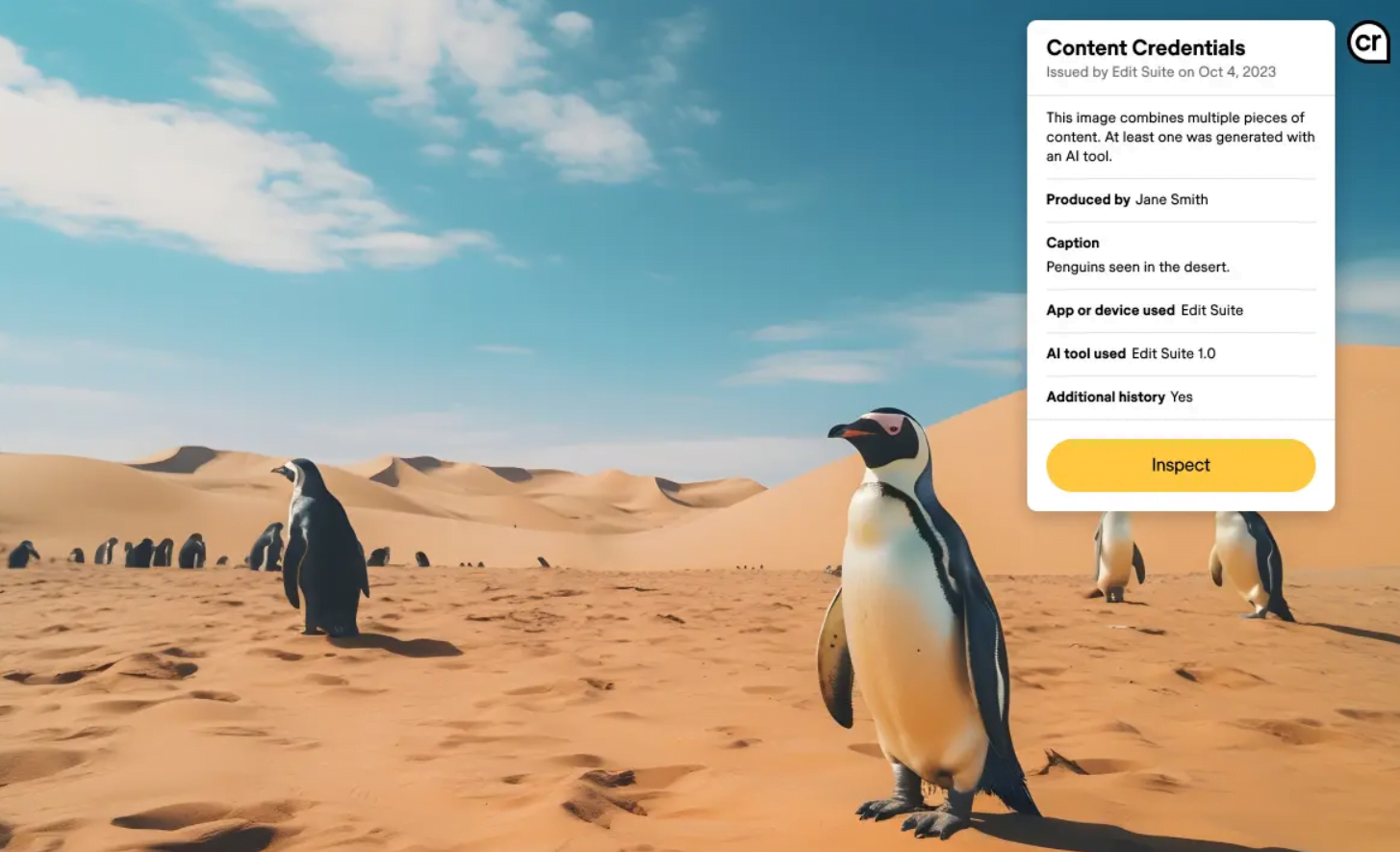
The C2PA standard is also used by some camera manufacturers and news organizations to certify the source and history of media content.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.