OpenAI has yet another new coding model and this time it's really fast
Key Points
- OpenAI has introduced GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark, a compact coding model built for real-time programming that runs on an inference-optimized Cerebras chip, delivering more than 1,000 tokens per second.
- The speed allows developers to interrupt and redirect the model in real time, seeing results immediately.
- However, the smaller model trades precision for speed: on the Terminal-Bench 2.0 benchmark, Codex-Spark scores 58.4% accuracy compared to 77.3% for the larger GPT-5.3-Codex.
OpenAI has released GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark, a smaller version of its GPT-5.3 Codex coding model built for real-time programming. Running on Cerebras chips, it hits more than 1,000 tokens per second.
Codex-Spark is the first product to come out of the Cerebras partnership OpenAI announced in January. The model runs on Cerebras' Wafer Scale Engine 3, an AI accelerator designed for fast inference.
The Research Preview is available now for ChatGPT Pro users in the Codex app, the CLI, and the VS Code extension. OpenAI says it plans to expand access over the coming weeks. Because the model runs on specialized hardware, separate rate limits apply and may be tweaked during periods of high demand, according to the company.
Codex-Spark prioritizes speed over autonomy
OpenAI's larger frontier models, like the newly released Codex 5.3, are designed to work autonomously for minutes or hours on complex programming tasks. Codex-Spark takes a different approach: the model is optimized for interactive work, where latency matters just as much as intelligence, OpenAI says. Developers can interrupt and redirect the model in real time and see results right away.
Codex-Spark is deliberately conservative in how it operates, according to OpenAI. Compared to larger models, it makes minimal, targeted changes by default and won't kick off automatic tests unless you explicitly ask it to. The model has a 128k context window and only handles text.
Less accuracy at a fraction of the time
OpenAI says Codex-Spark posts strong results on the SWE-Bench Pro and Terminal-Bench 2.0 benchmarks, which evaluate agent-based software engineering capabilities, but finishes tasks in a fraction of the time compared to GPT-5.3-Codex. On SWE-Bench Pro, Codex-Spark hits similar accuracy in roughly two to three minutes, while GPT-5.3-Codex needs around 15 to 17 minutes for the same tasks.
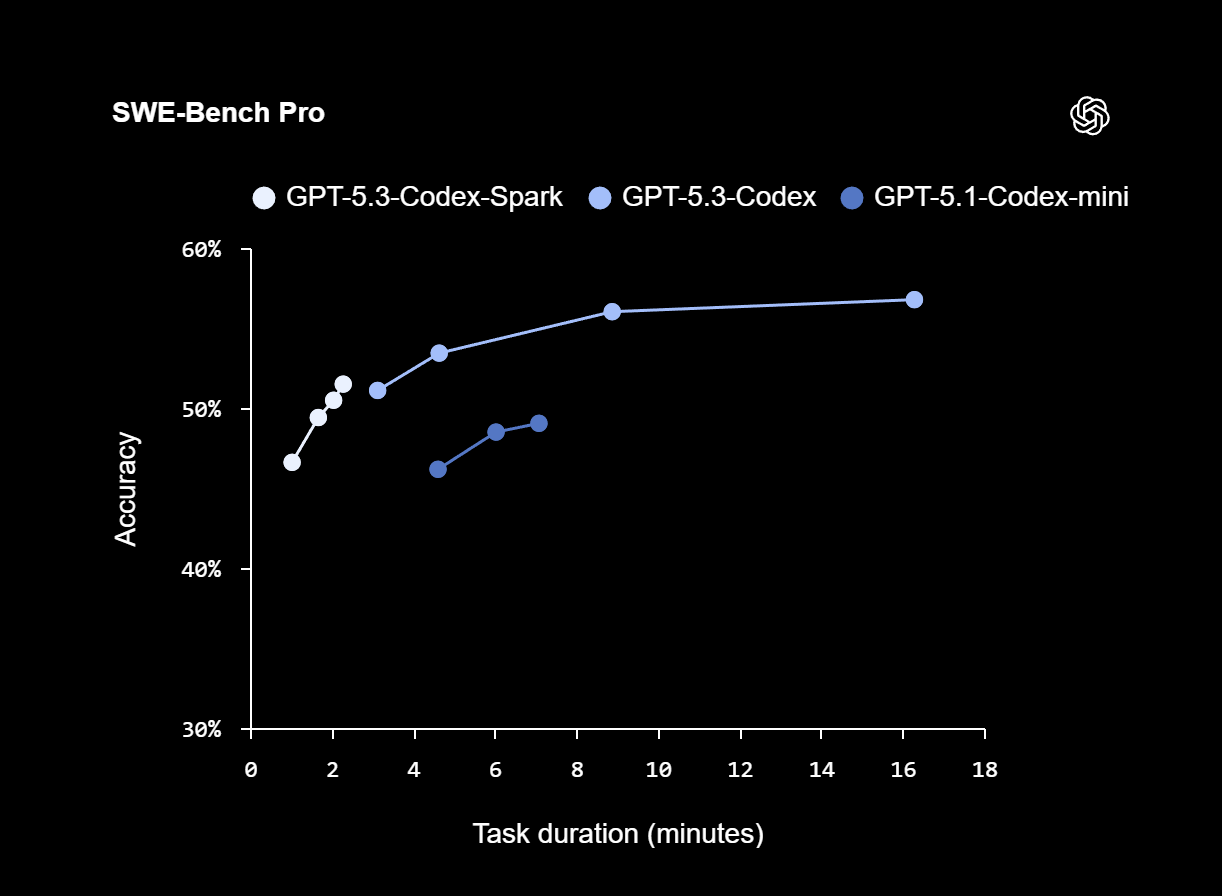
On Terminal-Bench 2.0, Codex-Spark scores 58.4 percent accuracy. The larger GPT-5.3-Codex hits 77.3 percent, while the older GPT-5.1-Codex-mini comes in at 46.1 percent. Both smaller models trade precision for speed.
| Model | Terminal-Bench 2.0 (Accuracy) |
|---|---|
| GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark | 58,4 % |
| GPT-5.3-Codex | 77,3 % |
| GPT-5.1-Codex-mini | 46,1 % |
Building Codex-Spark forced OpenAI to speed up more than just the model itself. To hit its latency targets, the company rewrote key parts of its inference stack, streamlined how responses stream between client and server, and reworked session startup so the first token shows up faster. The result: per-roundtrip overhead dropped 80 percent, per-token overhead fell 30 percent, and time-to-first-token was cut in half, OpenAI says. These improvements apply to Codex-Spark by default and will roll out to all models soon.
OpenAI wants to merge real-time and reasoning modes down the road
OpenAI says Codex-Spark is the first model in a planned family of "ultra-fast" models. More capabilities are on the way, including larger models, longer context windows, and multimodal input support.
Long-term, the company is working toward two complementary modes for Codex: one for extended reasoning and autonomous execution, and one for real-time collaboration. OpenAI says it plans to merge these modes over time, keeping developers in a fast interactive loop while handing off longer tasks to sub-agents in the background or spreading them across multiple models running in parallel.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe now