Researchers improve AI logic by focusing on critical tokens

Researchers have developed a new method that improves the reasoning ability of AI language models. The key lies in identifying particularly important tokens.
Scientists at Tsinghua University and Tencent AI Lab have created a new method called "cDPO" (contrastive Direct Preference Optimization) that makes AI language models better at logical reasoning by focusing on specific words that affect their performance.
The research team found that certain words, which they call "critical tokens," have an outsized impact on how well AI systems can reason through problems. Their tests showed that changing these specific words can significantly increase the likelihood of getting correct answers. For example, when an AI encounters the word "owed," it often leads to wrong conclusions. But using alternative words like "paid" helps the AI reach more accurate results.
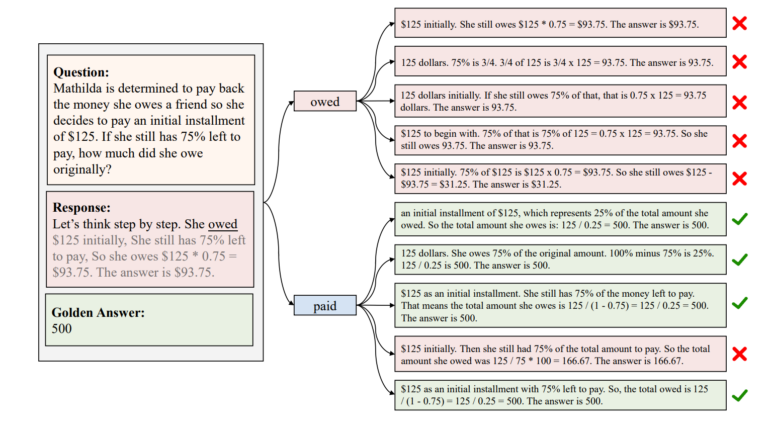
cDPO automatically identifies critical tokens
The new method automatically spots these important words during the AI training process. It does this by training two different models - one that learns from correct reasoning examples and another that learns from incorrect ones. By comparing how these models handle different words, the system can identify which words are most likely to cause problems.
The difference between how these two models process specific words helps show which ones are most critical. The bigger the difference, the more likely that word is to cause reasoning errors.
cDPO beats other alignment methods
The research team tested cDPO using several AI models, including Llama-3 (8B and 70B) and deepseek-math (7B). They ran tests using the benchmarks GSM8K and MATH500. The results showed that cDPO performed better than existing methods for improving AI reasoning.
While the improvements were modest - just a few percentage points better than current best practices - the results show that identifying and managing these critical words can help make AI systems more reliable at reasoning tasks. However, this approach alone won't solve all the logical limitations that current AI language models face.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.