Maximilian Schreiner
Max is the managing editor of THE DECODER, bringing his background in philosophy to explore questions of consciousness and whether machines truly think or just pretend to.
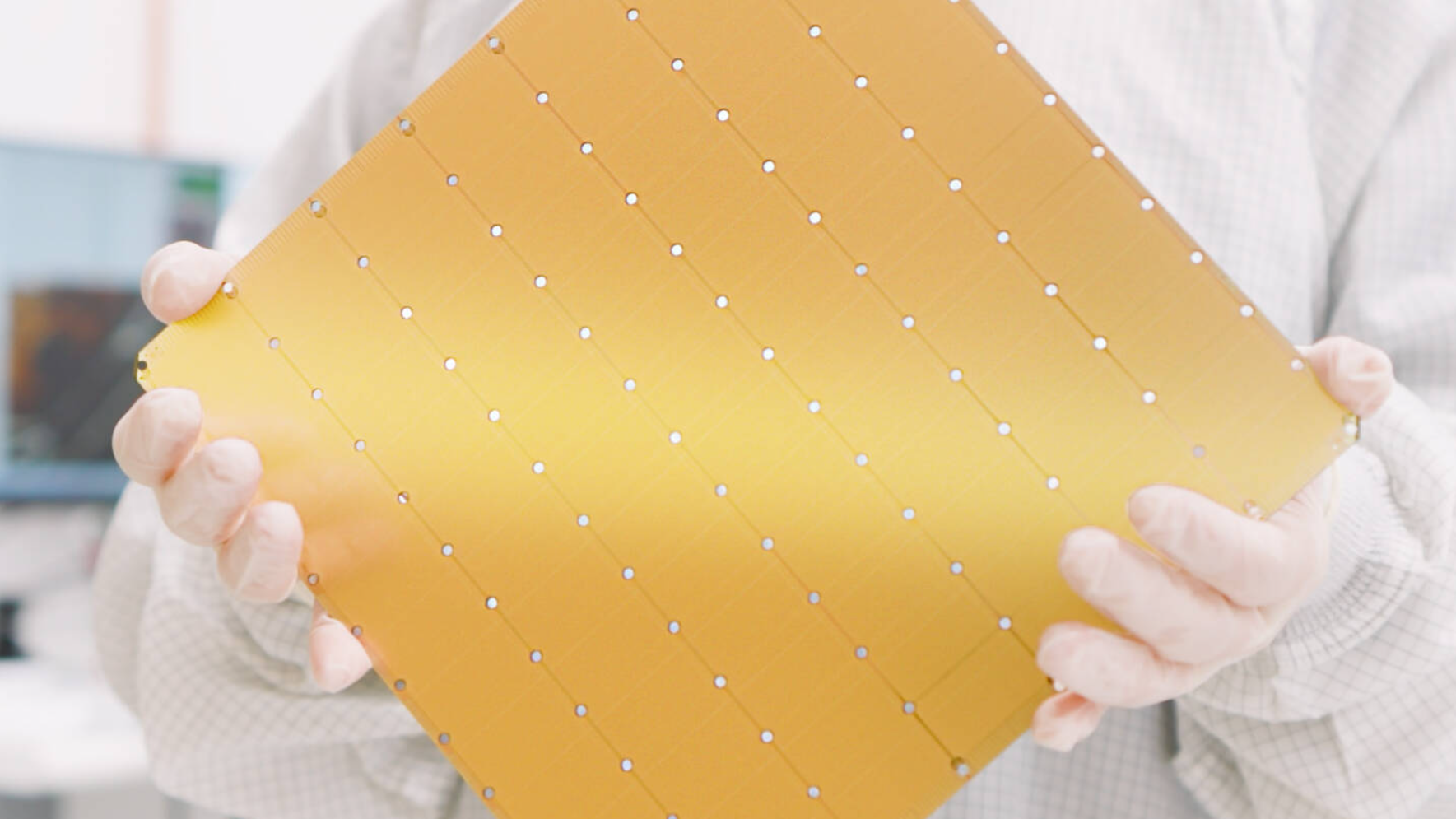
Taiwan agrees to $250 billion US chip investment as Washington cuts tariffs
A sweeping US–Taiwan trade deal ties lower tariffs to massive onshore investment: Taiwanese chipmakers are pledging at least $250 billion for American fabs, while Washington wields quotas—and the threat of 100 percent tariffs—to pull more of the world’s most advanced semiconductor production onto US soil.
Read full article about: Cloudflare acquires Human Native to build new payment model for AI training data
Cloudflare is acquiring British startup Human Native to create a new payment system for AI training data. The company runs a marketplace for AI training data and converts multimedia content into structured, licensable datasets.
The move addresses a growing problem: AI crawlers scrape the web on a massive scale without paying website operators. Instead of letting AI companies grab content for free, publishers could make their data available through an index and get paid for it.
Cloudflare has already been developing tools like "AI Crawl Control" and "Pay Per Crawl" that let website operators control who can use their content for AI training. The company also co-founded the x402 Foundation with Coinbase to enable automatic machine-to-machine payments. Cloudflare runs its own AI platform and recently expanded it by acquiring Replicate.
Comment
Source: Cloudflare | Human Native
Read full article about: OpenAI safety researcher joins Anthropic's alignment team
Andrea Vallone, a senior safety researcher at OpenAI, has moved to Anthropic. She'll be working on the alignment team, which focuses on AI model risks. Vallone spent three years at OpenAI, where she founded the "Model Policy" research team and contributed to major projects including GPT-4, GPT-5, and the company's reasoning models.
Over the past year, Vallone led OpenAI's research on an increasingly urgent question: how should AI models respond when users show signs of emotional dependency or mental health struggles? Some users, including teenagers, have taken their own lives after conversations with chatbots. Several families have filed lawsuits, and the U.S. Senate has held hearings on the issue.
At Anthropic, Vallone will report to Jan Leike. Leike himself was head of safety research at OpenAI before leaving the company in May 2024. At the time, Leike publicly criticized OpenAI, saying safety had taken a backseat to shipping new products.
OpenAI reportedly walked away from Apple to focus on building its own AI hardware instead
Apple is betting billions on Google to power Siri’s AI future, and OpenAI says it walked away from the deal on purpose.
Read full article about: Bandcamp bans AI-generated music
Music platform Bandcamp now prohibits music created entirely or substantially by generative AI. The company says the new policy protects human creativity and the direct connection between artists and fans. The updated rules also strictly ban using AI tools to imitate specific artists or styles.
Unlike most streaming services, Bandcamp focuses on direct purchases of music and merchandise, letting fans support creators financially without intermediaries.
Users can now report content that sounds heavily AI-generated. Bandcamp reserves the right to remove music from the platform based on suspected AI origins alone.