Google AudioPaLM can translate text with your voice

With AudioPaLM, Google is adding audio capabilities to its large PaLM-2 language model. This enables spoken translations with the original speaker's voice.
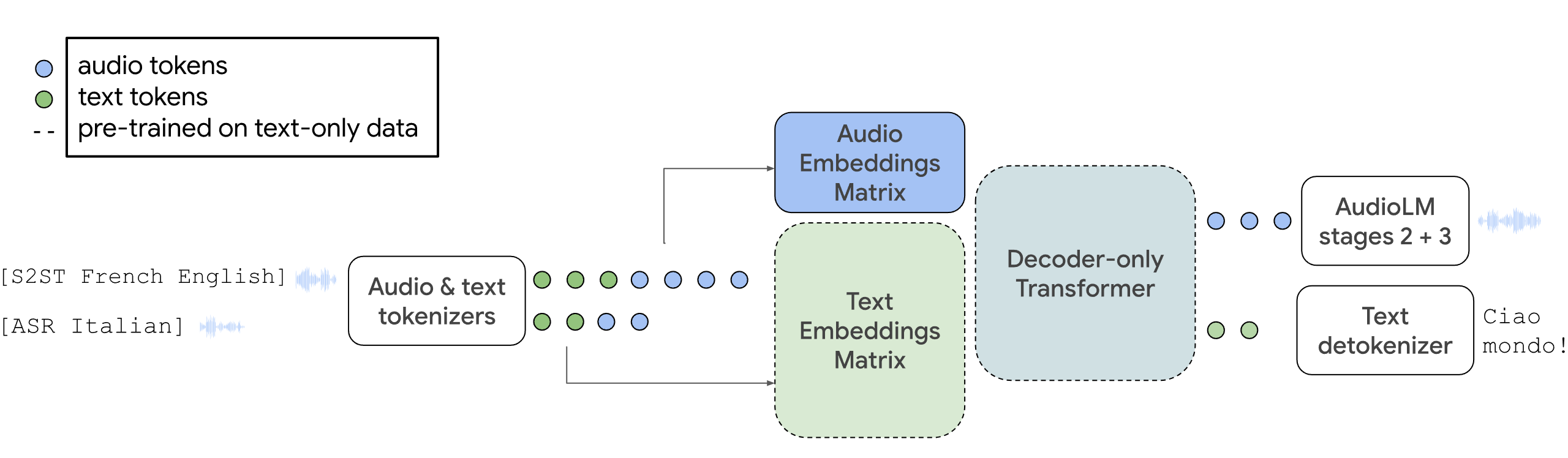
With AudioPaLM, Google combines the large language model PaLM-2, which was introduced in May, with its generative audio model AudioLM in a central multimodal architecture. The system can process and generate text and speech, and can be used for speech recognition or to generate translations with original voices.
Babelfish gets closer
The latter feature is particularly noteworthy, as it allows a person to speak in multiple languages simultaneously, as the following demo shows.
Conditioning to the original voice requires only a three-second sample, passed as an audio and SoundStream token. If the audio file is shorter, it is repeated until the three seconds are reached.
AudioPaLM demo. | Video: Google
By integrating AudioLM, AudioPaLM can produce high-quality audio with long-term consistency. This includes the ability to produce semantically plausible speech continuations while preserving speaker identity and prosody for speakers not seen during training.
The model can also perform zero-shot speech-to-text translations for many languages, including speech combinations not encountered during training. This capability can be important for real-world applications such as real-time multilingual communication.
AudioPaLM can also preserve paralinguistic information such as speaker identity and intonation, which is often lost in traditional speech-to-text translation systems. The system is expected to outperform existing solutions in terms of speech quality, based on automatic and human evaluation.
In addition to speech generation, AudioPaLM can also generate transcripts, either in the original language or directly as a translation, or generate speech in the original source. AudioPaLM has achieved top results in speech translation benchmarks and has demonstrated competitive performance in speech recognition tasks.
From voice assistants to automated multilingualism
The potential applications are many: multilingual voice assistants, automated transcription services, and any other system that needs to understand or generate written or spoken human language.
Google could see use cases for AI-generated multilingual videos, especially on YouTube: For example, it could help create multilingual subtitles or dub videos in multiple languages without losing the original speaker's voice.
The researchers point to several areas for future research, including understanding the optimal properties of audio tokens and how to measure and optimize them. They also emphasize the need for established benchmarks and metrics for generative audio tasks, which would help further accelerate research in this area.
More information and demos are available on the project page on Github.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.