GPT-4 passes Japan's National Physical Therapy Examination

A new peer-reviewed study shows that OpenAI's GPT-4 language model can pass the Japanese National Physical Therapy Examination without any additional training.
The research, published in the journal Cureus, tested GPT-4 on both text and visual questions. Japan's physical therapist exam includes 160 general and 40 practical questions, testing memory, comprehension, application, analysis, and evaluation.
Researchers input 1,000 questions into GPT-4 and compared the answers to official solutions. GPT-4 passed all five test sections, correctly answering 73.4 percent of questions overall. However, the AI struggled with technical questions and those containing images or tables.

The model performed much better on general questions (80.1% correct) than practical ones (46.6% correct). Similarly, GPT-4 handled text-only questions (80.5% correct) far better than those with pictures and tables (35.4% correct). These findings align with previous research on GPT-4's visual comprehension limitations.
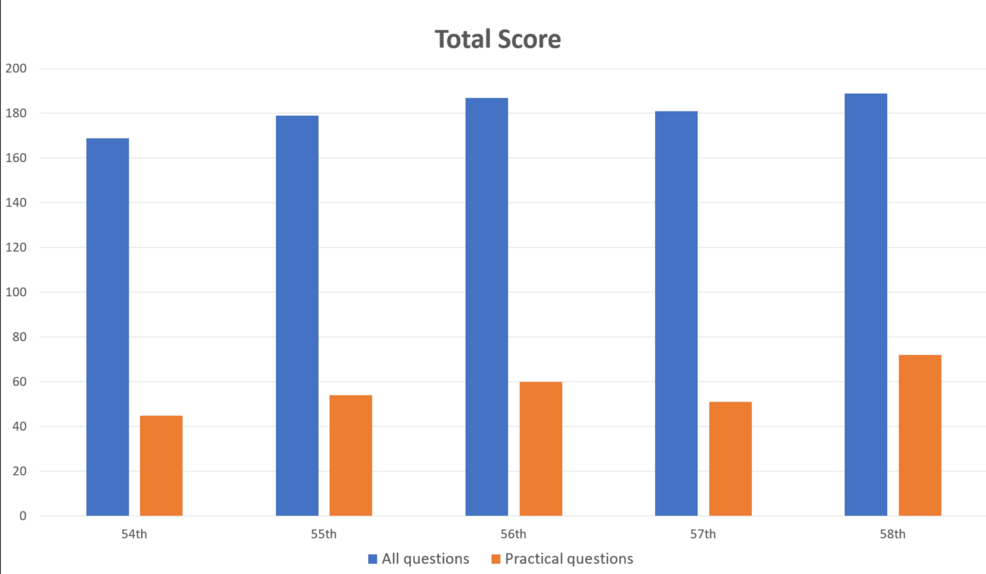
Interestingly, question difficulty and text length didn't significantly impact GPT-4's performance. The model also performed well with Japanese input, despite being primarily trained on English data.
Multimodal models could bring further improvements
While the study shows GPT-4's potential in clinical rehabilitation and medical education, the researchers caution that it doesn't answer all questions correctly. They stress the need to evaluate newer versions and the model's capabilities in written and reasoning tests. Multimodal models such as GPT-4o could potentially yield better results in visual comprehension.
Large language models have shown promise in medicine for some time. Specialized versions like Google's Med-PaLM 2 and Med-Gemini aim to outperform general models like GPT-4 in medical tasks. Meta also has Llama 3-based models designed for the medical sector.
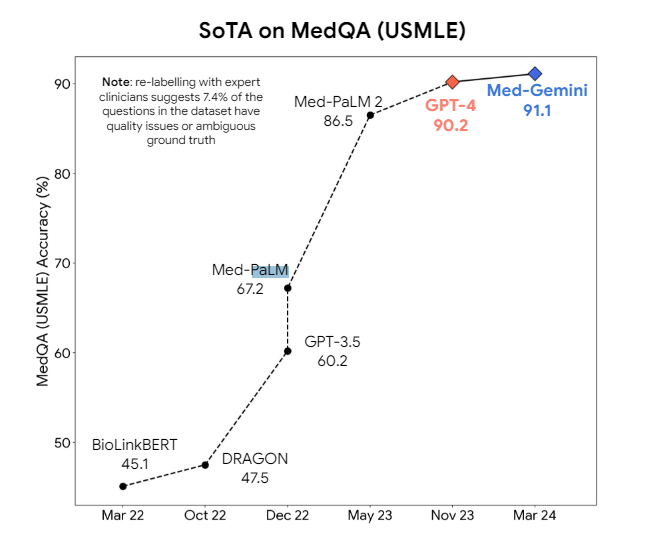
However, it is likely to be a long time before medical AI models are widely used in practice. Even current benchmarks leave too much room for error, which is particularly critical in medical contexts. As in many other applications where precision and correctness are key, significant improvements in reasoning skills seem necessary to safely integrate these models into everyday practice.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.