When ChatGPT & Co. have to check their answers themselves, they make fewer mistakes, according to a new study by Meta.
ChatGPT and other language models repeatedly reproduce incorrect information - even when they have learned the correct information. There are several approaches to reducing hallucination. Researchers at Meta AI now present Chain-of-Verification (CoVe), a prompt-based method that significantly reduces this problem.
New method relies on self-verification of the language model
With CoVe, the chatbot first responds to a prompt such as "Name some politicians who were born in New York." Based on this output, which often already contains errors, the language model then generates questions to verify the statements, such as "Where was Donald Trump born?"
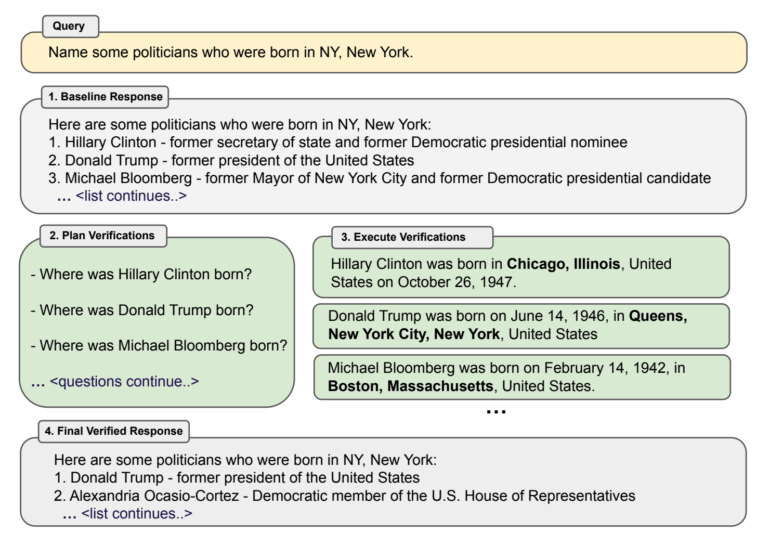
These "verification questions" are then executed as a new prompt, independent of the first input, to prevent the possible adoption of incorrect information from the first output. The language model then verifies the first input against the separately collected facts. All testing was done with Llama 65B.
Chain-of-verification significantly reduces hallucinations in language models
The team shows that answers to individual questions contain significantly fewer errors, allowing CoVe to significantly improve the final output to a prompt. For list-based questions, such as the politician example, CoVe can more than double accuracy, significantly reducing the error rate.
For more complex question-and-answer scenarios, the method still yields a 23 percent improvement, and even for long-form content, CoVe increases factual accuracy by 28 percent. However, with longer content, the team also needs to check the verification answers for inconsistencies.
In their tests, the Meta team can also show that instruction tuning and chain-of-thought prompting do not reduce hallucinations, so Llama 65B with CoVe beats the newer, instruction-tuned model Llama 2. In longer content, the model with CoVe also outperforms ChatGPT and PerplexityAI, which can even collect external facts for its generations. CoVe works entirely with knowledge stored in the model.
In the future, however, the method could be improved by external knowledge, e.g. by allowing the language model to answer verification questions by accessing an external database.