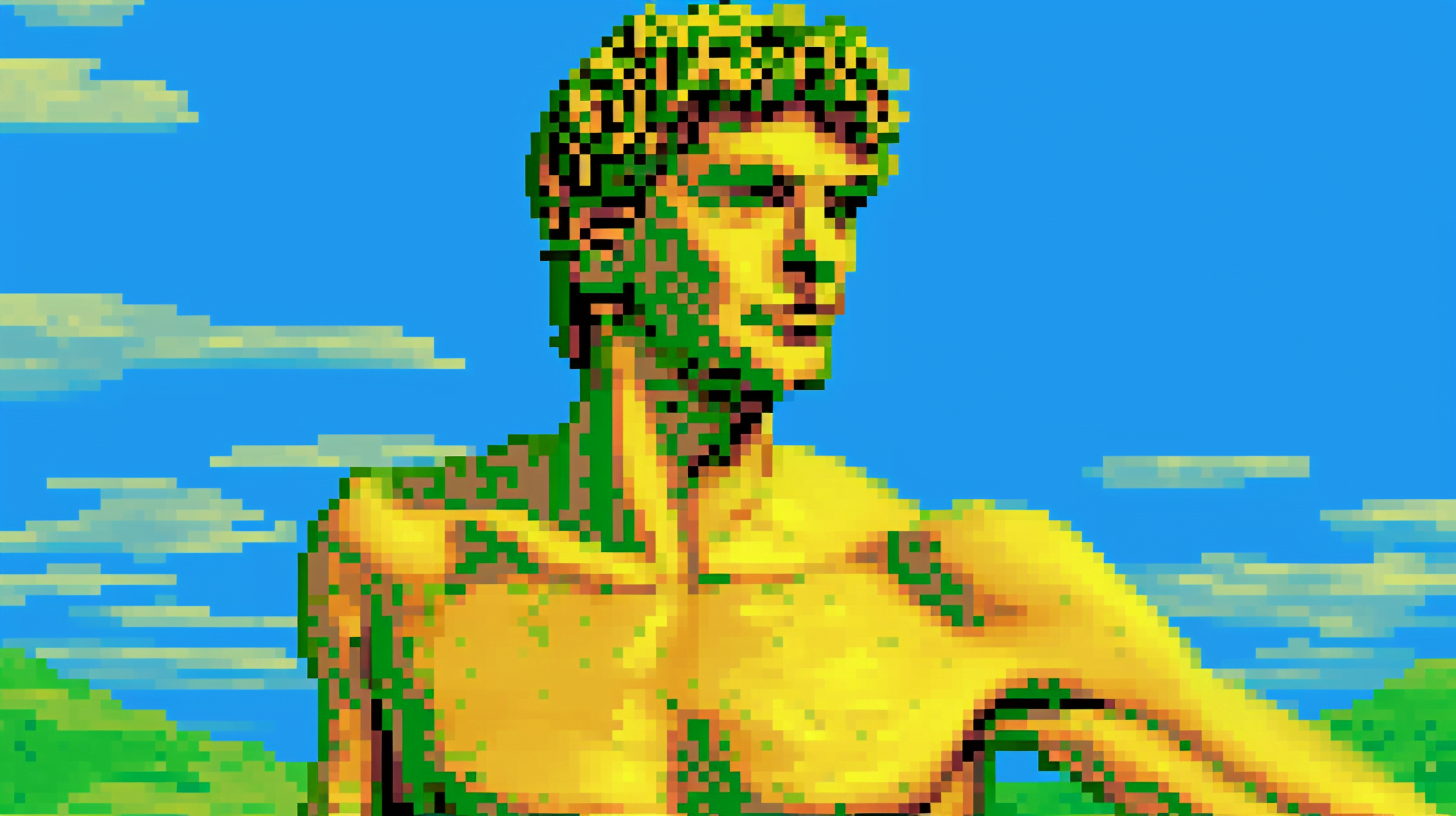
Nvidia's Neuralangelo sets a new standard for 3D reconstruction of 2D video clips using neural networks.
Neuralangelo is a new AI model from Nvidia and Johns Hopkins University that learns 3D reconstructions from video footage and can output and render them as 3D objects. Compared to previous methods, Neuralangelo captures far more surface detail and can render simple objects, house facades, or entire buildings with their surroundings.
According to Nvidia, the 3D structures generated by Neuralangelo can be imported into design applications and then further processed for art, video games, robotics, or industrial digital twins.
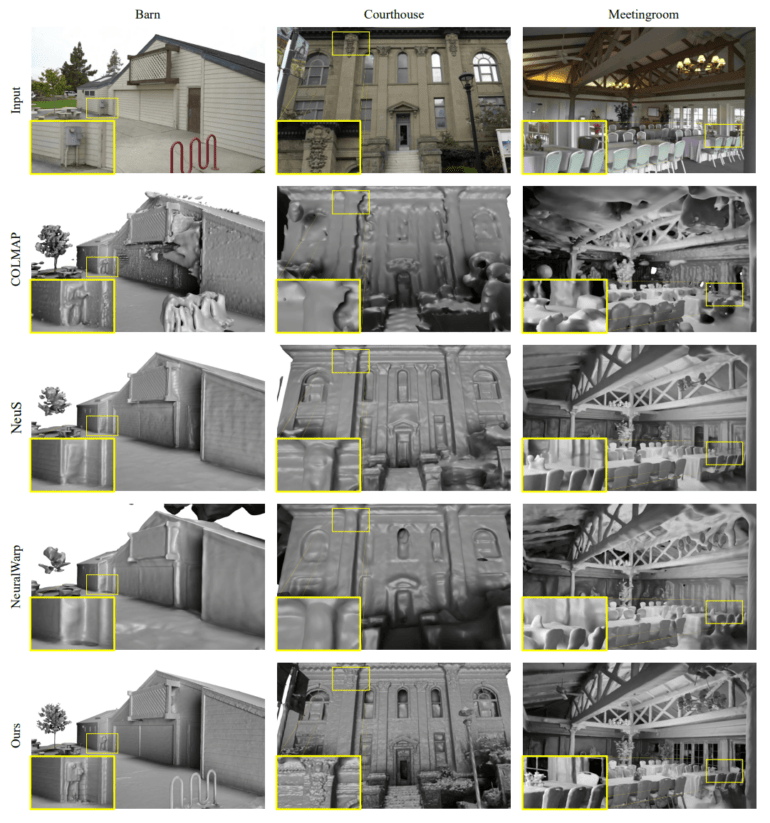
Neuralangelo captures more detail than other methods"
"Neuralangelo’s ability to translate the textures of complex materials — including roof shingles, panes of glass and smooth marble — from 2D videos to 3D assets significantly surpasses prior methods. The high fidelity makes its 3D reconstructions easier for developers and creative professionals to rapidly create usable virtual objects for their projects using footage captured by smartphones," the company said.

In footage released by Nvidia, the team shows how Neuralangelo can reconstruct everything from Michelangelo's marble statue to a fruit basket to the Nvidia Bay Area Campus park.
The AI model overcomes the limitations of previous approaches with some optimizations and uses Nvidia's Instant-NGP method to capture finer details. As a result, objects have a much higher resolution, and artifacts that occur with other methods, such as errors in smooth walls, do not appear.
Nvidia wants to further optimize Neuralangelo
The team ran all the experiments on an Nvidia V100 GPU and trained for 500,000 iterations. With this, it takes around 16 hours to train a scene.
Our method currently samples pixels from images randomly without tracking their statistics and errors. Therefore, we use long training iterations to reduce the stochastics and ensure sufficient sampling of details.
From the paper.
In the future, the team hopes to develop more efficient sampling strategies to speed up Neuralangelo's training process. Nvidia's InstantNeRF has already shown that this is possible.
More information is available on the Neuralangelo project page.