Nvidia rival Cerebras opens six data centers for rapid AI inference

Cerebras Systems plans to strengthen its AI inference capabilities by building new data centers across North America and Europe.
The company plans to concentrate 85 percent of its capacity in the United States, with three facilities already operational in Santa Clara, Stockton, and Dallas. Additional centers will open in Minneapolis (Q2 2025), Oklahoma City and Montreal (Q3), and Atlanta and France (Q4).
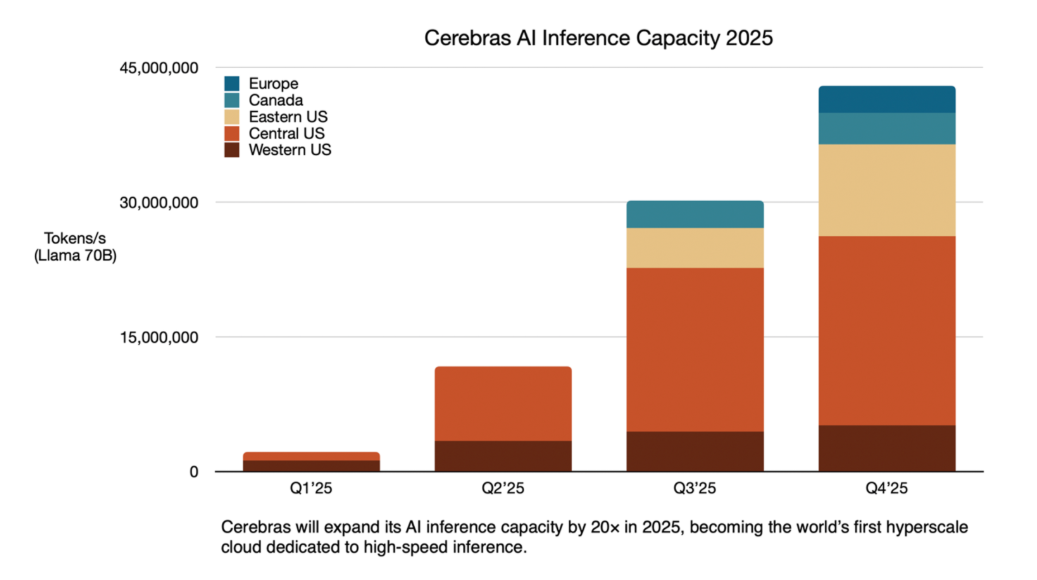
At the heart of these facilities are Cerebras' wafer-scale engines, a specialized chip architecture optimized for AI applications. The company says its CS-3 systems will process 40 million Llama-70B tokens per second for inference tasks.
The Oklahoma City facility will house more than 300 CS-3 systems. Built to Level 3+ standards, the center includes protection against tornadoes and earthquakes, plus triple redundant power supplies. Operations begin in June 2025.
Early adoption by industry leaders
Several prominent AI companies have already signed on to use Cerebras' infrastructure, including French startup Mistral with its Le Chat assistant and AI answer engine Perplexity. HuggingFace and AlphaSense have also committed to the platform.
The technology particularly benefits reasoning models like Deepseek-R1 and OpenAI o3, which typically require several minutes for calculations and generate numerous tokens during their thought processes.
The expansion represents part of Cerebras' broader 2025 scaling strategy, with some locations operated in partnership with Emirati company G42. In Montreal, Bit Digital subsidiary Enovum will manage the facility, which promises inference speeds ten times faster than current GPUs when it launches in July 2025.
Cerebras Systems, a U.S.-based company, specializes in developing AI chips with a unique approach: using entire wafers as single chips, called "Wafer Scale Engines." The WSE-3 represents their third generation of this technology.
The system is currently used at Argonne National Laboratory, Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center, and GlaxoSmithKline. However, it has limitations: it doesn't support native CUDA (Nvidia's standard) and offers less server compatibility than Nvidia solutions.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.