OpenAI releases its first open-weight language models since GPT-2 with GPT-oss
OpenAI has released two large language models with open weights for the first time since GPT-2: gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b.
Both are specialized reasoning models built with a Mixture-of-Experts architecture, designed for complex logical reasoning, step-by-step problem-solving, and working with external tools like web search or code interpreters. The models are distributed under the Apache-2.0 license.
OpenAI says gpt-oss-120b can run on a single 80 GB GPU, while gpt-oss-20b is aimed at systems with 16 GB of RAM. CEO Sam Altman described the move as part of building a "democratic" AI infrastructure. Both models are available through Hugging Face.
Strong performance in logic, coding, and health
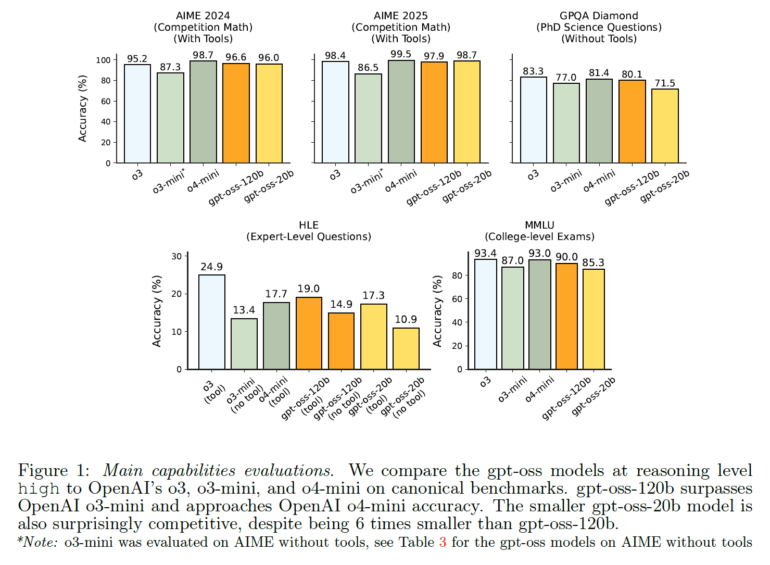
According to OpenAI, gpt-oss-120b delivers benchmark results close to the proprietary o4-mini model and outperforms GPT-4o in many scenarios. The models are particularly strong at tasks that require extended reasoning. On the AIME 2024 math competition, gpt-oss-120b scores 96.6% accuracy when using tools, just behind o4-mini at 98.7%.
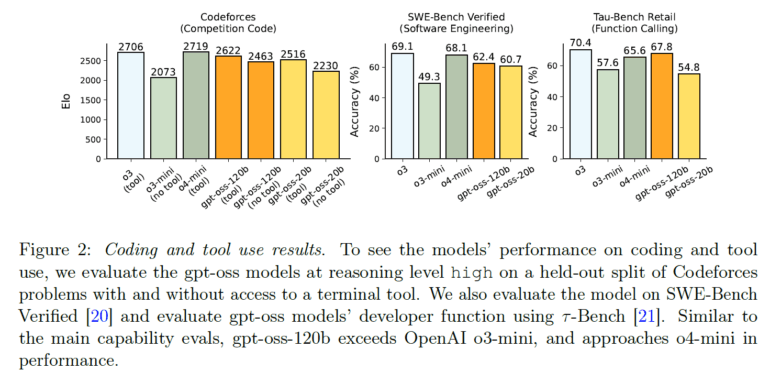
The models also perform well on programming challenges. On the Codeforces benchmark, gpt-oss-120b achieves an Elo rating of 2622, approaching o4-mini's 2719. On SWE-bench Verified, the scores are 60% and 62% for the open models (compared to 69% for o4-mini and 68% for o3).
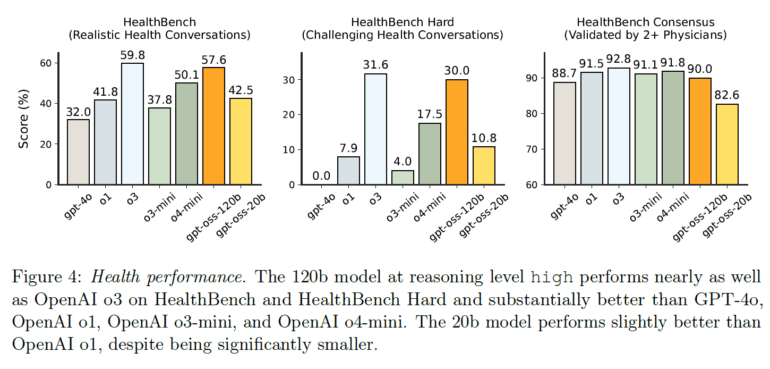
In healthcare, gpt-oss-120b surpasses many other models on the HealthBench benchmark and nearly matches o3, according to OpenAI.
It is important to note that these are text-only models. They cannot process or generate images, and their knowledge is current as of June 2024.
The gpt-oss models have some drawbacks when it comes to factual accuracy. According to OpenAI, they are more prone to hallucinations, which is expected for smaller models with less world knowledge.
A new safety protocol for open source AI
OpenAI is introducing a new safety protocol to address the risks posed by open-source models, which can be modified by malicious actors. The centerpiece is a "worst-case fine-tuning" process, where the model is deliberately trained on dangerous capabilities like planning cyberattacks or using biological knowledge.
According to OpenAI's safety paper, even after this process, the model did not reach a "high" risk threshold in the monitored categories. The results were reviewed by OpenAI's internal Safety Advisory Group and external experts. OpenAI concludes that releasing these models does not significantly increase the risk of open source models acquiring dangerous capabilities, since other models like Qwen 3 Thinking and Kimi K2 already offer similar performance.
Despite these safety measures, the Model Card highlights ongoing challenges. The gpt-oss models are less reliable at following instruction hierarchies than o4-mini, and their reasoning chains were intentionally not filtered for "bad thoughts," leaving moderation up to developers. As a result, they may contain unmoderated content.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.