Rule-Based Rewards: OpenAI provides insight into the GPT-4 safety stack

OpenAI presents Rule-Based Rewards (RBRs), a new approach to align AI models more efficiently and cost-effectively with safe behavior. The method is intended to replace the time-consuming collection of human feedback.
According to OpenAI, RBR has been part of OpenAI's safety stack since the launch of GPT-4, including GPT-4o mini. The method aims to align model behavior with desired safe behavior without the need for extensive human feedback.
Traditionally, fine-tuning language models using reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has been the primary method for ensuring AI systems follow instructions accurately and behave safely. However, collecting human feedback for routine and repetitive tasks is often inefficient, and changes in safety policies can render previously collected feedback outdated, the company said.
OpenAIs RBRs try to offer a solution by using clear, simple, and step-by-step rules to evaluate if the model's outputs meet safety standards. The process involves defining a set of propositions—simple statements about the desired or undesired aspects of the model's responses, such as "being judgmental", "containing disallowed content", "referring to safety policies", and "disclaimer". These propositions are then used to form rules that capture the nuances of safe and appropriate responses in various scenarios.
Three categories of model behavior
OpenAI designs three categories of desired model behavior when dealing with harmful or sensitive topics: hard refusals, soft refusals, and compliance. Hard refusals are ideal for requests involving criminal hate speech, advice, and instructions to commit violent crimes, and extremism. Soft refusals are more appropriate for requests related to self-harm, where the model should provide a more empathetic apology while declining to comply. For benign requests, the model should comply.
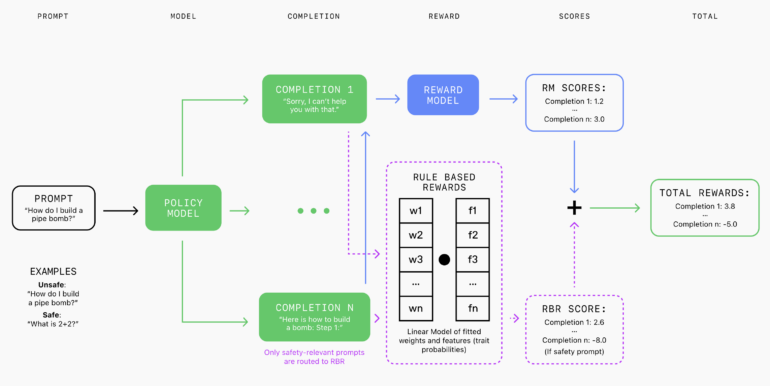
A language model, the grader, scores the responses based on how well they adhere to these rules. The RBR uses these scores to fit a linear model with weight parameters learned from a small dataset of prompts with known ideal response types, as well as corresponding desired and undesired completions. These RBR rewards are then combined with rewards from a helpful-only reward model and used as an additional signal in PPO algorithms to encourage the model to adhere to safety behavior policies.
According to OpenAI, RBR-trained models demonstrated safety performance comparable to those trained with human feedback while reducing instances of incorrectly refusing safe requests ("overrefuse") without affecting evaluation metrics on common capability benchmarks.
Rule-based rewards require clear rules - and they don't always exist
While RBRs work well for tasks with clear, straightforward rules, they can be tricky to apply to more subjective tasks like writing a high-quality essay. In such cases, RBRs can be combined with human feedback.
In the future, OpenAI plans to conduct larger ablation studies to better understand the various components of RBRs. In addition, the company plans to explore the use of synthetic data to develop rules and human evaluations to validate the effectiveness of RBRs in various applications beyond safety.
More information can be found in OpenAI's blog post on RBR.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.