Mistral releases three new LLMs for math, code and general tasks

Mistral AI this week introduced three new LLMs that set new benchmarks for general-purpose tasks and specialized areas such as mathematical reasoning and code generation.
Mathstral: 7 Billion Parameters for math tasks
Mathstral, a 7-billion-parameter model, was developed by the French startup in collaboration with Project Numina, a non-profit organization focused on advancing human and artificial intelligence in mathematics. It outperforms similarly sized models on mathematical benchmarks such as MATH (56.6%) and general benchmarks such as MMLU (63.47%).
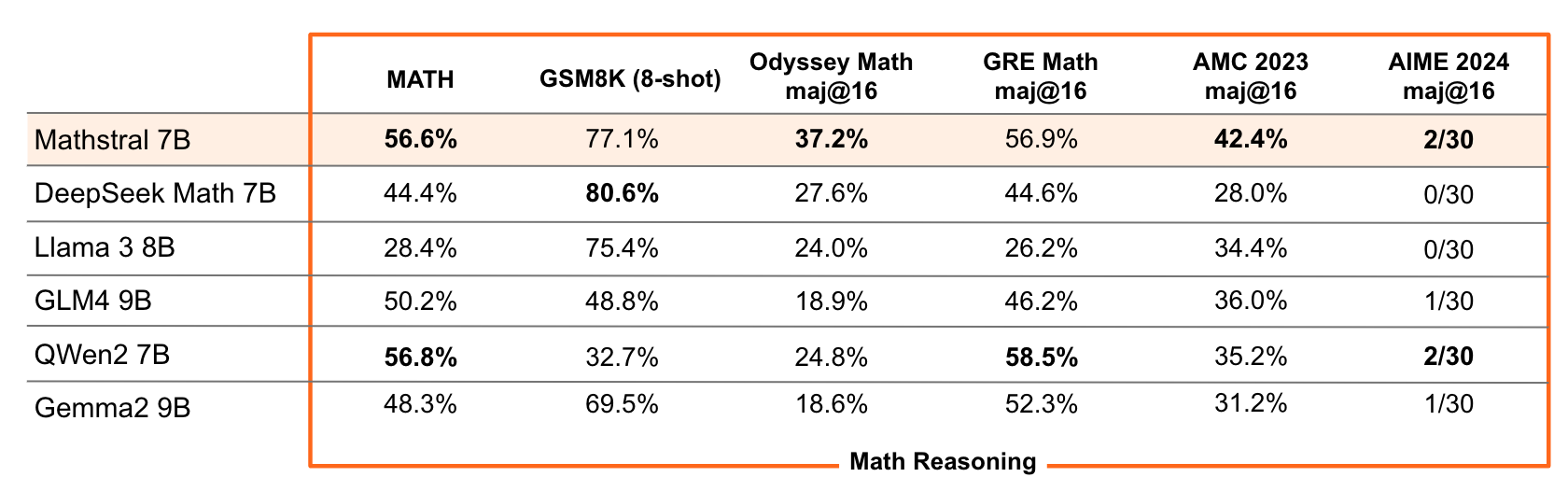
The Mistral team pointed to Mathstral as an example of their design philosophy of balancing performance and speed in purpose-built models.
Codestral Mamba: New architecture with larger context window
Following the May 2024 release of Codestral, a 22-billion-parameter code model, Mistral has now introduced Codestral Mamba. This new model uses the Mamba2 architecture, offering fast code generation with context windows up to 256,000 tokens.
This makes it ideal as a local code assistant, as you can feed your own codebase and documentation from programming frameworks into a single prompt. Codestral Mamba processes sequences in linear time, enabling quicker responses and theoretically infinite output lengths.
It often outperformed similarly sized models in benchmarks, though the larger Transformer-based Codestral still leads in most areas.
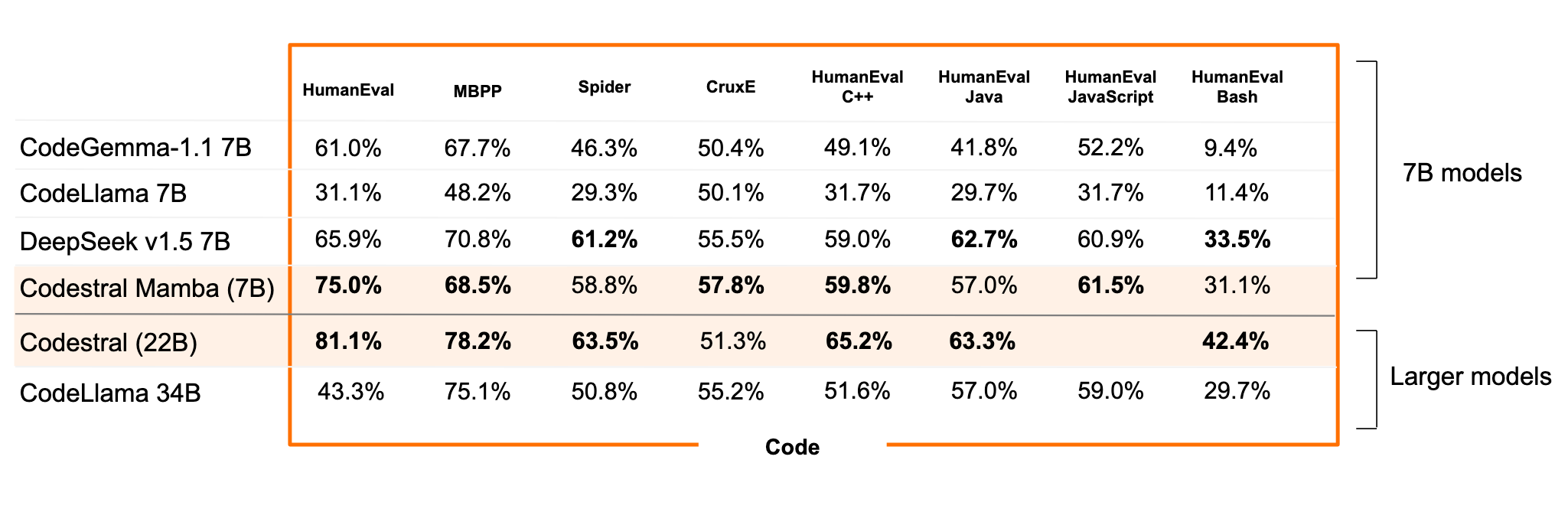
Mistral hasn't yet released technical documentation that provides more insight into the training data and model architectures. However, the weights are available on Hugging Face (Mathstral, Codestral Mamba).
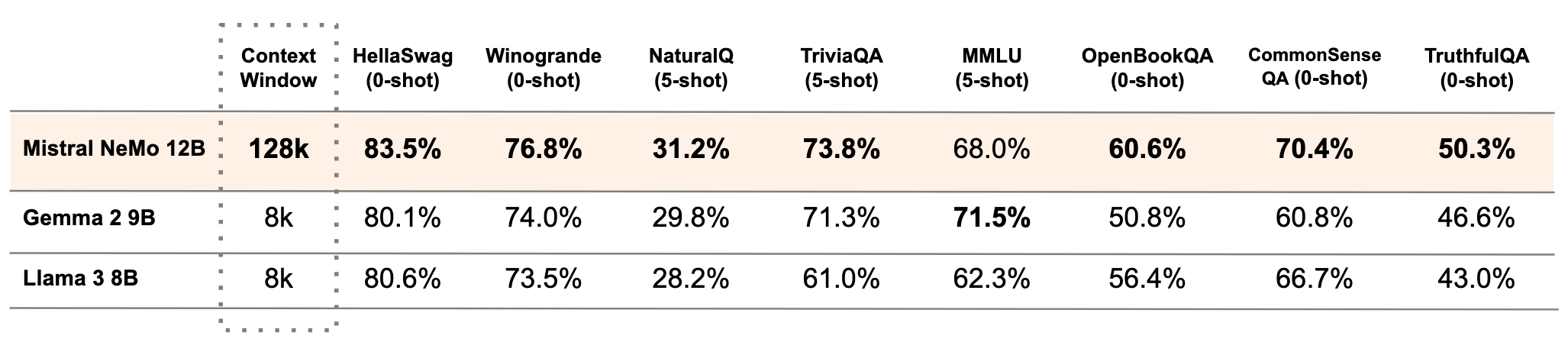
Mistral NeMo: A replacement for the Mistral-7B?
Developed with NVIDIA, Mistral NeMo features 12 billion parameters and a context window of up to 128,000 tokens. It excels in logic, world knowledge, and coding capabilities, making it suitable for global, multilingual applications.
Mistral NeMo is based on a standard architecture, allowing for easy integration into existing systems. Compared to other open-source models like Gemma-2-9B and LLaMA-3-8B, the NeMo base model shows similar or better results in benchmarks while supporting a context window 16 times larger.
The model was trained with a new tokenizer called Tekken, optimized for over 100 languages, enabling greater compression of natural text and source code than the previously used SentencePiece tokenizer.
Compared to the LLaMA 3 tokenizer, Tekken offers more efficient compression for 85 percent of languages. Mistral NeMo is particularly powerful in languages like English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic and Hindi.
Mistral has released the pre-trained base and instruction-optimized checkpoints under the Apache 2.0 license to encourage adoption by researchers and companies. NeMo seems to follow in the footsteps of Mistral-7B, which received an update in May.
Mistral remains Europe's top LLM startup
Mistral AI continues to lead as Europe's top LLM startup. Earlier this year, the company launched Mistral Large to compete with OpenAI's GPT-4. The company secured a multi-year partnership with Microsoft in February and raised $600 million in June.
Overall, Mistral AI is positioning itself as a leading European AI company, developing capable and specialized AI models that also take into account aspects such as transparency and data protection in line with European standards.
In Europe's LLM sector, there is also Aleph Alpha, which hasn't yet caught up with Mistral at the model level, DeepL, which wants to expand AI language solutions for enterprises with $300 million in backing, and Silo AI, which was recently acquired by AMD.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.