Algorithms from the 1980s power today's AI breakthroughs, earn Turing Award for researchers
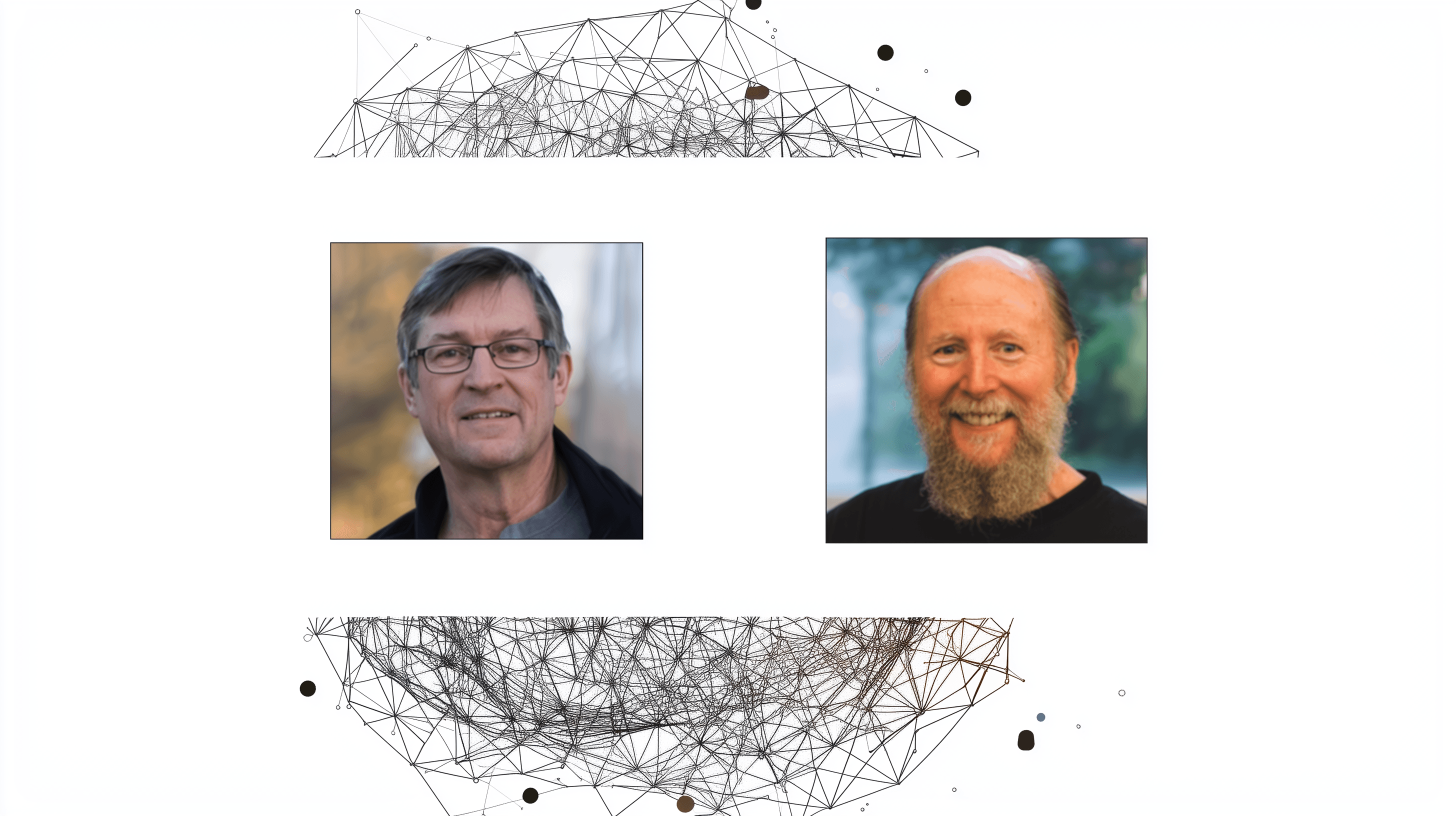
Andrew Barto and Richard Sutton have won the 2024 A.M. Turing Award for developing key technologies that power modern artificial intelligence, including recent breakthroughs in large reasoning models.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) selected Barto and Sutton for their groundbreaking work on reinforcement learning - technology that later enabled achievements like AlphaGo and today's large reasoning models (LRMs). The award, often called the "Nobel Prize in Computer Science," comes with a $1 million prize and recognizes their algorithms and concepts from the 1980s that allow machines to learn independently through reward signals.
From psychology principles to AI breakthroughs
The researchers took a simple concept from psychology - systems learning from feedback about their actions - and transformed it into a mathematical framework now used across AI applications. Their 1998 textbook "Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction" has become a cornerstone of the field, cited more than 75,000 times.
When combined with deep learning, their methods led to major advances: AlphaGo defeating world champion Lee Sedol, ChatGPT's training through human feedback, and new LRMs like OpenAI's o3 and Deepseek's R1. The technology now powers everything from advanced robotics to improvements in networking, chip design and online advertising.
Building on Turing's vision
Google Senior VP Jeff Dean sees their work as fulfilling Alan Turing's original goals: "In a 1947 lecture, Alan Turing stated ‘What we want is a machine that can learn from experience. Reinforcement learning, as pioneered by Barto and Sutton, directly answers Turing’s challenge."
The partnership began in 1978 at the University of Massachusetts, where Barto mentored Sutton during his doctoral studies. Their research has earned numerous accolades and sparked billions in AI investment. Today, Barto is professor emeritus at UMass Amherst, while Sutton works at both the University of Alberta and Keen Technologies. Sutton is also known for writing the influential essay The Bitter Lesson.
Barto and Sutton join an elite group of computer science innovators, including deep learning pioneers Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun, who received the award in 2019. Named for British mathematician Alan Turing, the prize has recognized transformative contributions to computer science since 1966.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.