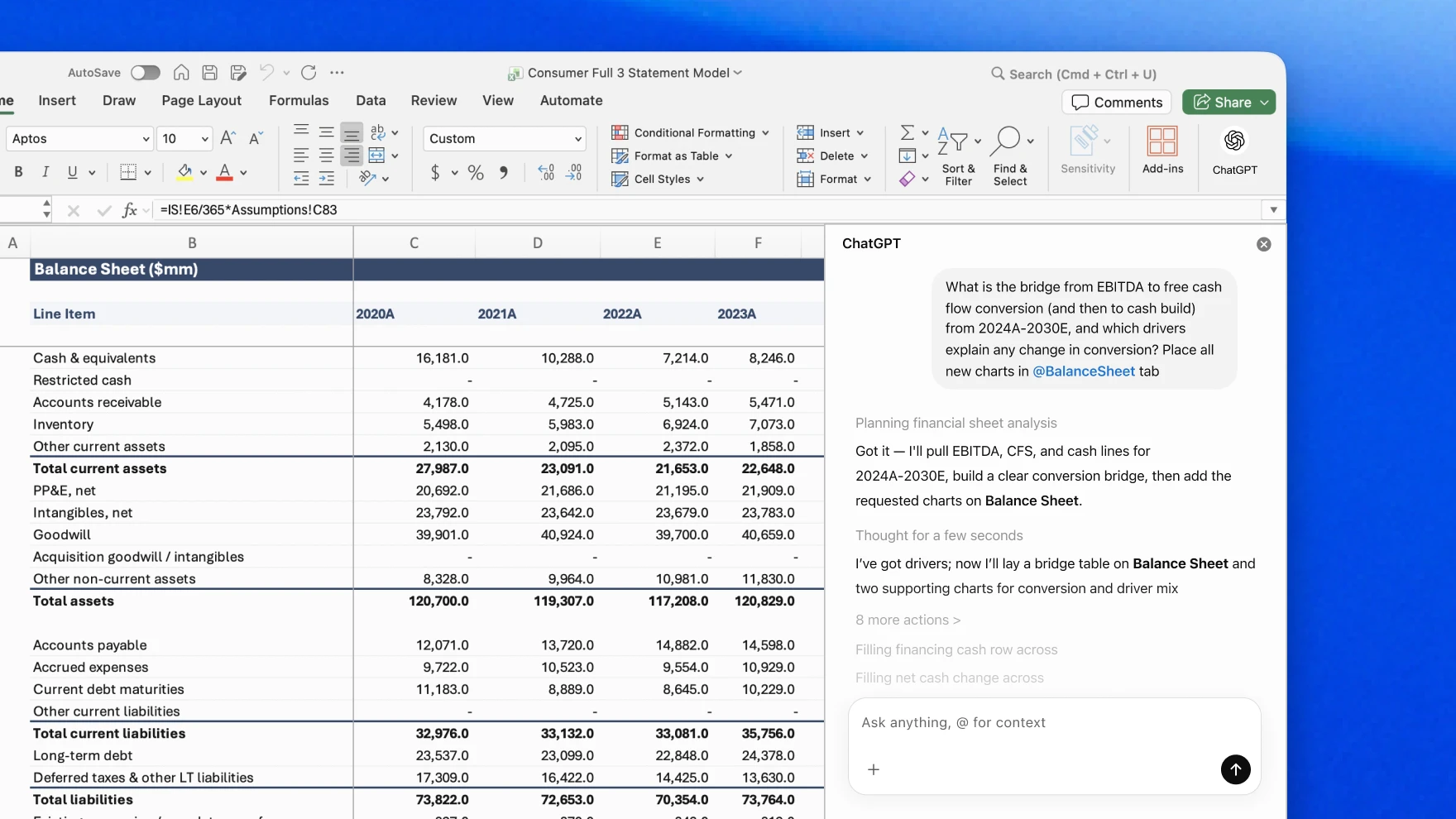
OpenAI and Oracle have decided not to expand their data center site in Abilene, Texas, beyond the planned 1.2 gigawatts. Oracle has leased eight buildings at the location for OpenAI, designed to house around 400,000 Nvidia Blackwell chips, but only two have been completed so far.
Oracle had pushed to get OpenAI into six more buildings, but both sides passed because the additional power supply wouldn't be available for at least a year. Instead of expanding the current Blackwell generation, OpenAI plans to buy Nvidia's next-generation Vera Rubin chips for a different data center. According to Bloomberg, Nvidia is now trying to get Meta to fill the vacant space, though those talks are still in the early stages.
OpenAI's compute manager Sachin Katti described the Stargate site as already one of the largest AI data center campuses in the country. "We considered expanding it further, but ultimately chose to put that additional capacity in other locations," Katti writes, adding that OpenAI is currently developing more than half a dozen sites across several US states.