Mozilla and Anthropic have teamed up to find more than 100 bugs in Firefox. Anthropic used its Claude AI model to scan the browser's codebase for security flaws, and the model found 14 serious vulnerabilities, 22 official security advisories (CVEs), and 90 additional bugs. All critical vulnerabilities have been patched in Firefox 148, Mozilla says.
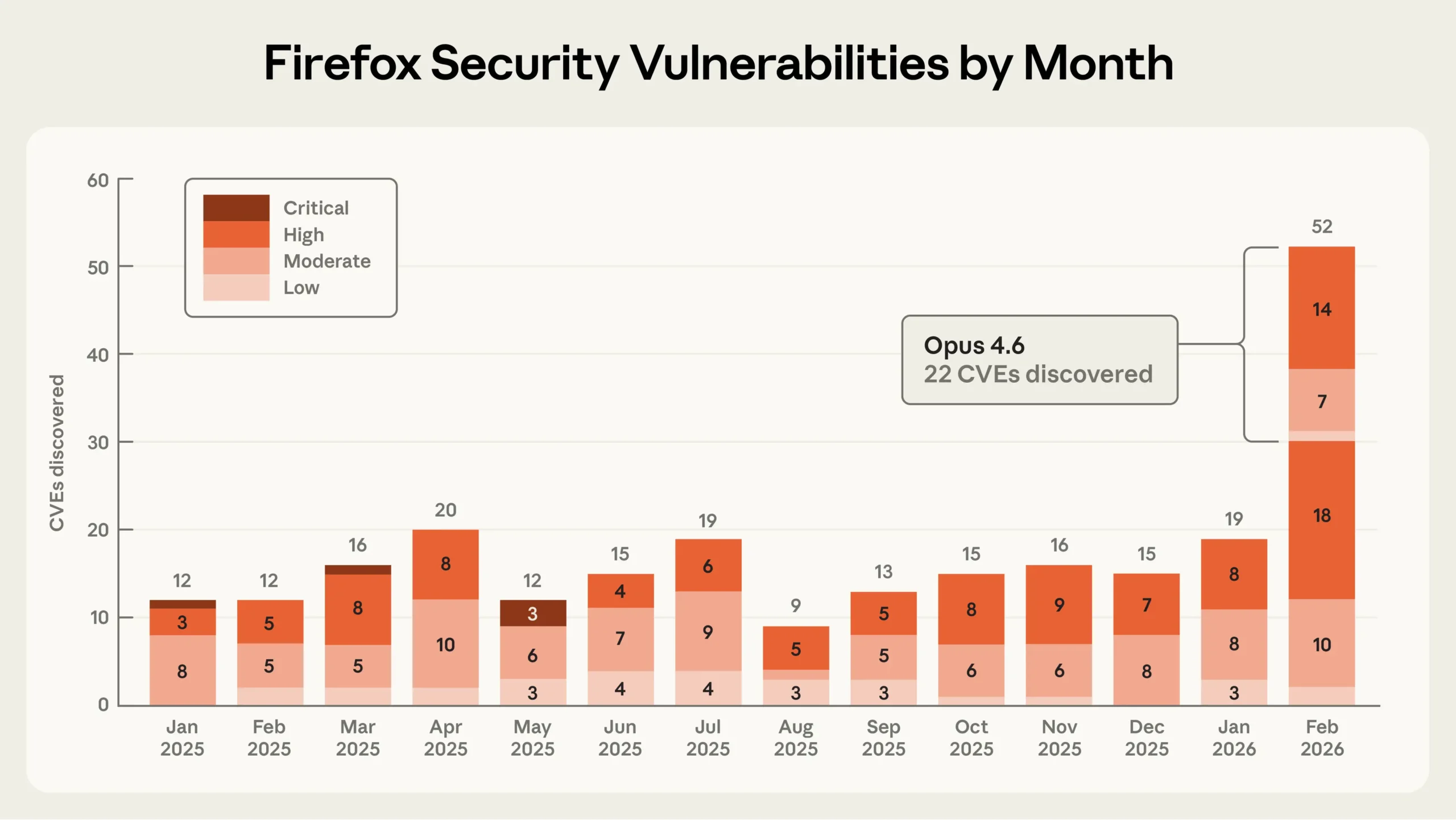
Claude identified entire classes of errors that conventional automated testing methods like fuzzing had missed despite decades of use, according to Mozilla. Anthropic delivered reproducible test cases alongside its findings, making the review process significantly easier. Going forward, Mozilla plans to integrate AI-powered code analysis into its internal security workflow.
Anthropic says it picked Firefox as a testing ground because it's one of the most heavily scrutinized open-source projects in the world. The company has published a detailed technical report on its findings. Anthropic also recently shipped a dedicated cybersecurity feature for its in-house AI tool, Claude Code.