Open-Sora 2.0 matches competitive AI video models at 90% lower training costs

HPC-AI Tech has developed a new video AI system that achieves commercial-grade quality at about one-tenth the typical training cost by using new compression methods.
While language models have become increasingly efficient, video AI still requires substantial GPU resources. Open-Sora 2.0 takes a different approach by trading some resolution for dramatically lower computing needs.
Prompt: "Two women sit on a beige couch in a cozy, warmly lit room with a brick wall backdrop. They engage in a cheerful conversation, smiling and toasting red wine in an intimate medium shot." | Video: HPC-AI Tech
Prompt: "A group of anthropomorphic mushrooms having a disco party in the middle of a dark enchanted forest, with glowing neon lights and exaggerated dance moves, their smooth textures and reflective surfaces emphasizing a comical 3D look." | Video: HPC-AI Tech
Prompt: "A tomato surfing on a piece of lettuce down a waterfall of ranch dressing, with exaggerated surfing moves and creamy wave effects to highlight the 3D animated fun." | Video: HPC-AI Tech
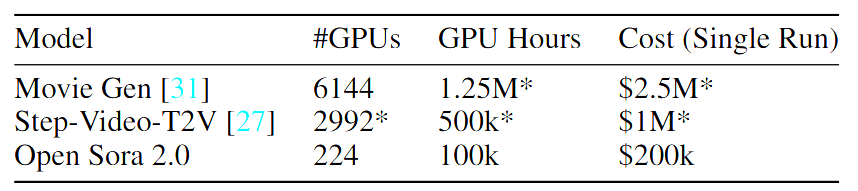
The research paper reveals training costs of approximately $200,000 - roughly one-tenth of what systems like Movie Gen or Step-Video-T2V require. Testing indicates quality comparable to commercial systems like Runway Gen-3 Alpha and HunyuanVideo. The team used 224 Nvidia H200 GPUs for training.
The system achieves its efficiency through three training phases: beginning with low-resolution videos, specializing in image-to-video conversion, and finally fine-tuning for higher resolution. The team further optimized resources by incorporating pre-trained image models like Flux.
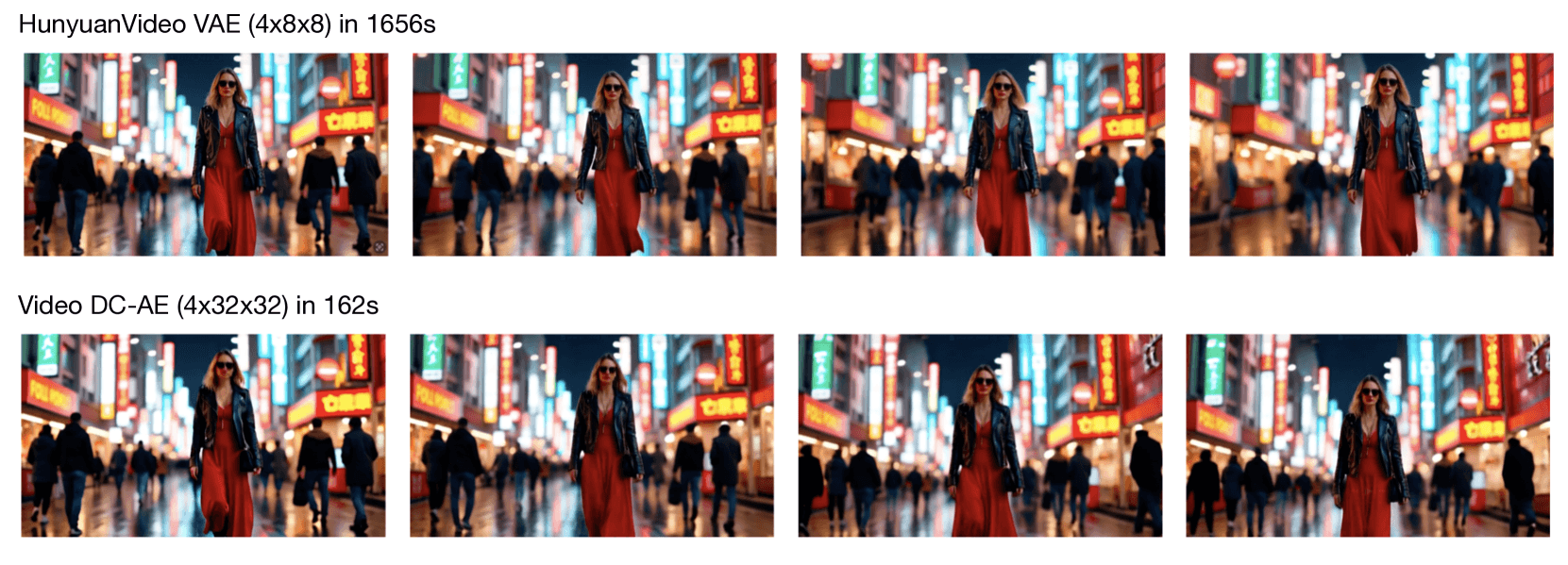
Central to the system is the Video DC-AE autoencoder, which delivers superior compression rates compared to existing methods. This innovation makes training 5.2 times faster while improving video generation speed by more than tenfold.

Open-source system challenges commercial video AI
Open-Sora 2.0 can generate videos from both text descriptions and single images. It includes a motion score feature that lets users control movement intensity in the generated clips.

The system has notable limitations. Videos can only reach 768x768 pixels in resolution and run for five seconds maximum (128 frames). For comparison, OpenAI's Sora - which shares only its name with this project - can generate 1080p videos lasting up to 20 seconds.
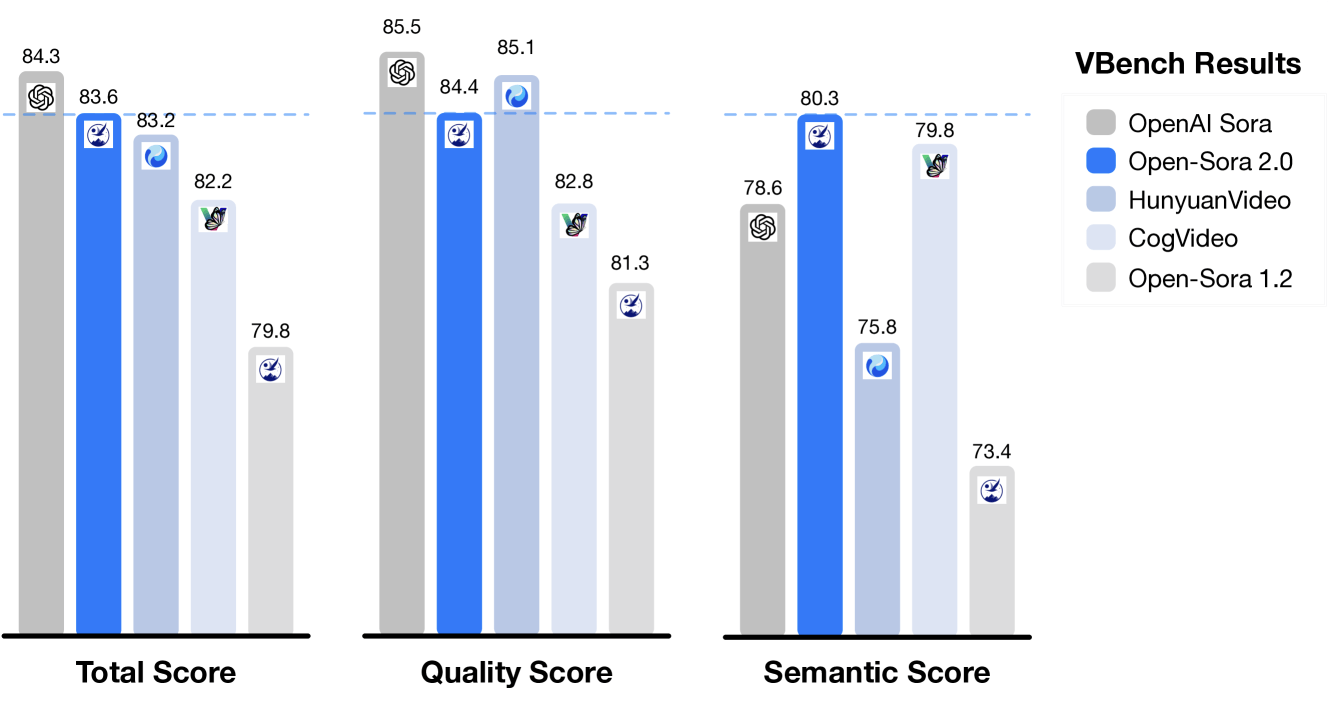
Testing shows the system performing at near-commercial levels across key metrics including visual quality, prompt accuracy, and motion handling. Most notably, Open-Sora 2.0's VBench score now sits just 0.69 percent behind OpenAI's Sora, substantially closing the 4.52 percent gap seen in the previous version.
Open-Sora is now available as open source on GitHub. Like other AI video models, it still faces challenges with occasional artifacts and physics-defying movements. You can watch more examples on the official project page.
AI video generation has become an increasingly competitive field, with Chinese companies leading much of the development. New systems launch almost weekly, including open-source projects like Genmo Mochi 1 and MiniMax Video-01. While these models often show modest benchmark improvements, none has achieved a major breakthrough in overall video quality.
The cost-efficiency strategies of Open-Sora 2.0 echo aspects of the "Deepseek moment" in language models, when improved training methods helped open-source systems achieve commercial-level performance at reduced costs. This could affect pricing throughout the video AI sector, where services like Google's latest model currently require 0.50 cents per second due to intensive computing needs.
However, the performance gap between open-source and commercial video AI remains more significant than in language models, as even industry leaders continue working to solve fundamental technical challenges.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.