OpenAI launches GPT-4.1: New model family to improve agents, long contexts and coding

OpenAI adds three new GPT-4.1 models to its API. The models are designed to outperform GPT-4o in most areas, while lowering costs and improving speed.
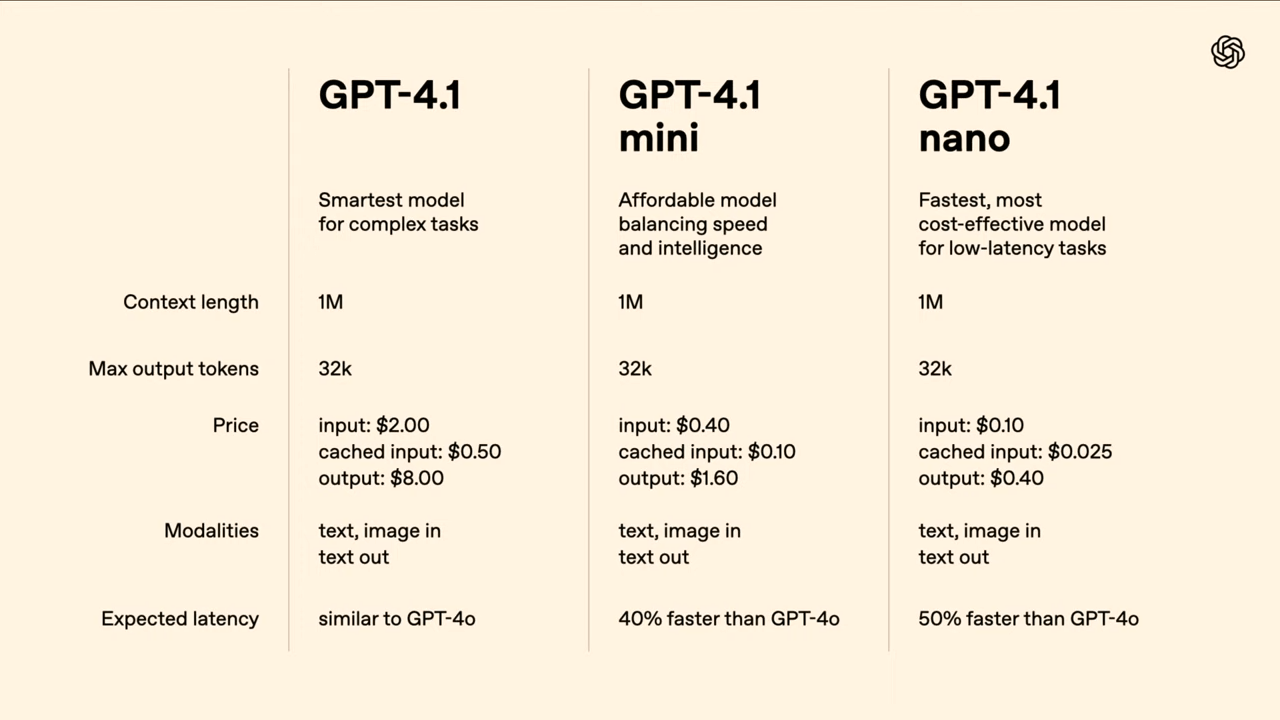
OpenAI has introduced a new family of language models—GPT-4.1, GPT-4.1 mini, and GPT-4.1 nano—exclusively for use via its API. According to the company, these models are targeted at professional developers and are intended to offer higher performance, faster output, and lower costs compared to previous offerings, including GPT-4o and the now-deprecated GPT-4.5 Preview.
Although GPT-4.1 is not currently available in ChatGPT, OpenAI says many of its improvements have already been incorporated into GPT-4o, with more updates planned.
Focusing on developer needs
OpenAI says the GPT-4.1 series was developed in direct response to feedback from the developer community. Key priorities include reliable formatting, structured outputs, more stable code generation—especially for frontend applications—and improved long-term memory for agent-based use cases.
One feature OpenAI highlights is the models’ ability to generate “code diffs,” enabling targeted modifications to existing codebases rather than rewriting entire files from scratch.
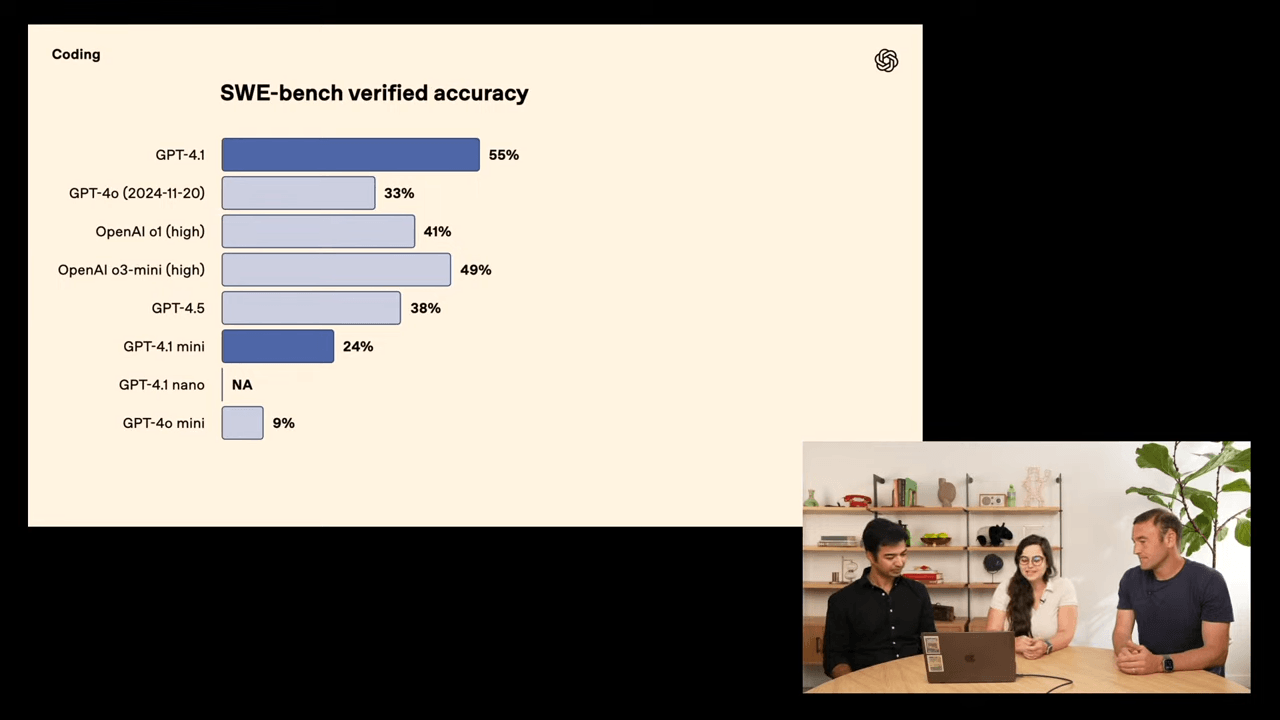
OpenAI says GPT-4.1 surpasses GPT-4o in several benchmarks. For instance, it scores 54.6% on the SWE-Bench Verified test for real-world software development tasks—over 21 percentage points higher than its predecessor. The company does not include a comparison with Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, which reportedly reaches 70% on the same test. GPT-4.1 also performs better on multi-step reasoning tasks.
Introducing GPT‑4.1 mini and nano
In addition to the main model, OpenAI has released two smaller variants: GPT-4.1 mini and GPT-4.1 nano. These models are designed for applications where speed and efficiency are critical. OpenAI claims that GPT-4.1 mini is 83% cheaper and twice as fast as GPT-4o, while delivering equal or better performance on benchmarks such as MMMU (Multimodal Understanding) and MathVista.
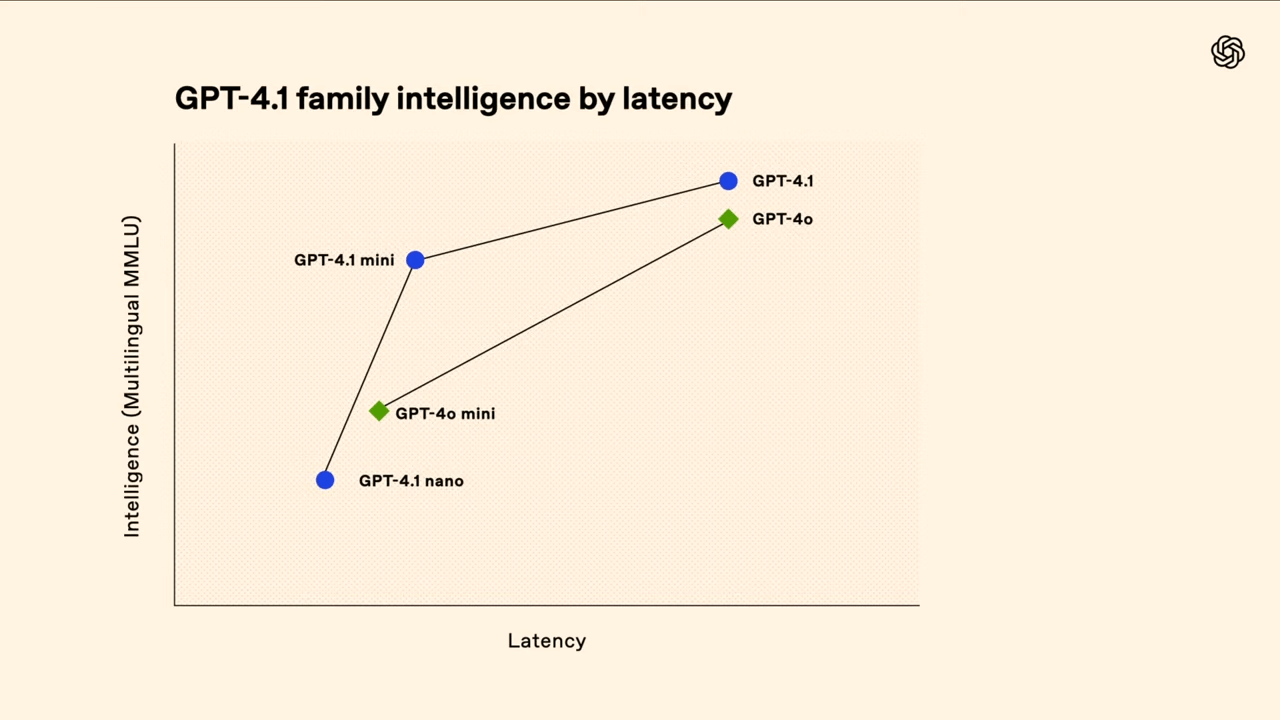
GPT-4.1 nano is the most compact model in the series and is optimized for latency-sensitive or cost-constrained tasks like classification, autocomplete, and information extraction.
New context window supports up to 1 million tokens
All three models introduce a significantly expanded context window of up to one million tokens—eight times the previous OpenAI limit of 128,000. In theory, this allows the analysis of eight complete React codebases in a single prompt.
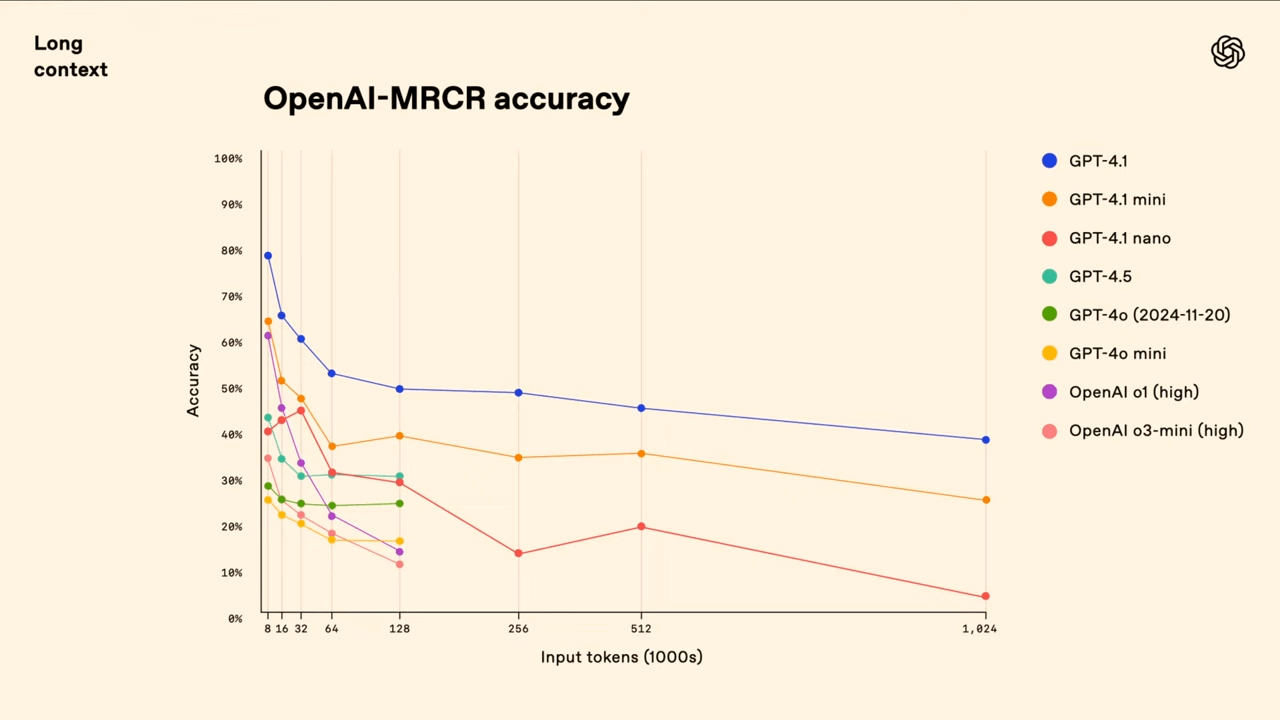
However, a larger context window does not guarantee consistent performance. OpenAI acknowledges the limitations of the widely used Needle-in-a-Haystack test, which it says all three models passed. The company introduces a new benchmark, MRCR (Multi-Round Coreference Resolution), intended to evaluate a model’s ability to distinguish between nearly identical user prompts spread across lengthy contexts.
In MRCR, multiple prompts like “Write a poem about tapirs” are embedded at different points in a long input. The model must then respond to a specific instance—for example, “Give me the third poem about tapirs.” Because these prompts are nearly identical and surrounded by distracting content, simple keyword searches are not effective.
Although GPT-4.1 leads in this benchmark, results show a sharp drop in accuracy—from 80% to around 50%—when the full context window is used. During a livestream demo, the model took over a minute to identify a single inserted line from a 450,000-token log file.
The Graphwalks benchmark, also introduced by OpenAI, tests the model’s ability to reason over large volumes of text by simulating graph-like structures. In this benchmark, the model must identify points a fixed number of “edges” away from a given node—similar to finding all locations two streets away on a city map. This requires the model to infer relationships rather than rely on surface-level reading.
GPT-4.1 achieves an accuracy of 61.7% in this benchmark with context lengths of less than 128,000 tokens, clearly beating GPT-4o (42%). GPT-4.1 also remains the leader for contexts over 128,000 tokens, although its accuracy drops to 19% there - a sign of how challenging these tasks remain. Smaller models such as GPT-4.1 mini or nano perform significantly worse here.
Early adoption and use cases
Several companies report measurable improvements using GPT-4.1. Legal-tech firm Blue J cites a 53% increase in accuracy on complex tax scenarios. At analytics platform Hex, success rates for SQL queries reportedly doubled. Thomson Reuters saw a 17% gain in legal document analysis accuracy, and Carlyle reports a 50% improvement in extracting information from lengthy financial texts.
Startup Windsurf, which had early access to GPT-4.1, also notes substantial gains. For the next seven days, users can try the model for free via the developer platform of the same name, after which it will be available at a discounted rate. This approach may serve as a competitive strategy in the increasingly crowded “vibe-coding” space, currently led by tools like Cursor.
Pricing and deprecation of GPT-4.5
OpenAI is positioning the GPT-4.1 series aggressively on price. GPT-4.1 is 26% cheaper than GPT-4o for medium-sized queries, with input costing $2 and output $8 per million tokens. GPT-4.1 nano is the most affordable, priced at $0.10 per million input tokens. Long-context capabilities are included at no extra cost, and prompt caching discounts reach up to 75%.
The previously released GPT-4.5 Preview will be retired on July 14, 2025. “We need those GPUs back,” joked the hosts during the livestream. OpenAI encourages developers to migrate to GPT-4.1 and has published an updated prompting guide available here.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.