The TravelPlanner benchmark is designed to test whether a language model can plan a trip. In the first tests, all models fail - including GPT-4.
Researchers from Fudan University, Ohio State University, Pennsylvania State University, and Meta AI have developed a new benchmark that tests the ability of AI-driven language agents to create complex travel plans while taking into account numerous constraints.
The ability to plan is considered an important characteristic of human intelligence, which includes the use of various tools to gather information and make decisions. Using travel planning as an example, TravelPlanner shows that despite advances in large language models, GPT-4 and other models have significant difficulties in performing such realistic planning.
TravelPlanner tests planning including finding flights
In TravelPlanner, models must generate detailed itineraries based on specific user requests. They must take into account user requirements such as budget and room type, as well as implicit "common sense" constraints, such as choosing different restaurants or sights along the way.
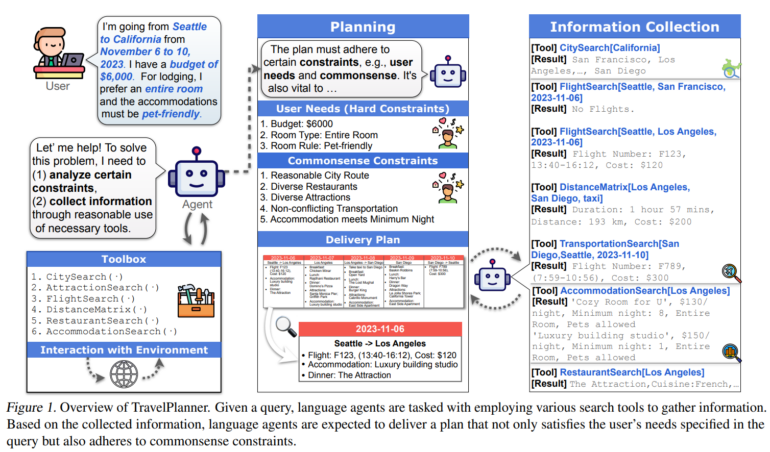
The challenges for the models are complex: they must make long-term and interdependent decisions, take into account explicit and implicit constraints, and proactively gather and evaluate information.
The team tested several large language models, including GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4-Turbo, and Gemini Pro, as well as the open-source models Mistral-7B-32K and Mixtral-8x7B-MoE.
Even GPT-4 fails the new benchmark
The results show that even the most advanced model, GPT-4-Turbo, only achieved a success rate of 0.6%. Other models were unable to complete a single task. The results clearly show that current AI models alone are not able to achieve human-level performance in complex, multi-faceted planning.

According to the team, models need to be better able to understand and integrate complex requirements, gather external information more efficiently, and make better use of tools. The researchers also suggest that performance could be improved by enhancing memory capabilities. In addition, the development of advanced planning strategies and training with realistic scenarios, supplemented by interactive learning, are important to enable continuous improvement, they say.
TravelPlanner therefore represents a significant challenge and opportunity for the development of future AI systems: An AI system that cracks the benchmark would bring AI research one step closer to human planning capabilities.