Chinese OpenAI o1 challenger Kimi k1.5 now available as free web version

Update: January 25, 2025
Moonshot AI's latest reasoning model, Kimi k1.5, is now available to everyone through Kimi.ai. The model now works in English too, though the company says it's still fine-tuning the language support.
According to a recent announcement from Moonshot AI, users can access k1.5's full feature set without any usage limits. The system can search the web in real time across more than 100 websites, process up to 50 files at once, and comes with improved reasoning and image understanding capabilities.
While the service is free, you'll need to sign up with a Chinese or US phone number to get started, though Google sign-in is coming soon.
Original article: January 21, 2025
Moonshot AI unveils Kimi k1.5, China's next o1 competitor
Following DeepSeek-R1's release, another reasoning model has emerged from China. Moonshot AI's new multimodal Kimi k1.5 is showing impressive results against established AI models in complex reasoning tasks.
Moonshot AI has developed two versions of Kimi k1.5 - one for detailed reasoning (long-CoT) and another for concise answers (short-CoT). According to the company's technical report, both versions match or exceed the performance of leading models like OpenAI's o1 and DeepSeek-R1. The long-CoT version walks through its thinking step by step, while the short-CoT version aims for brevity. In several benchmarks, it performs as well as or better than GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
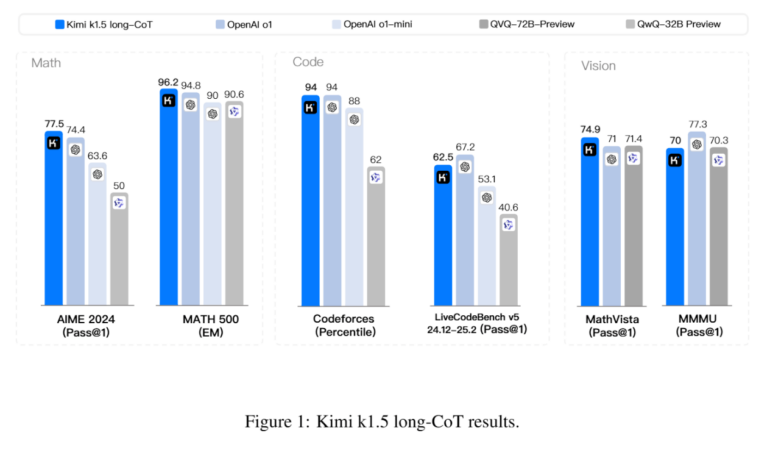
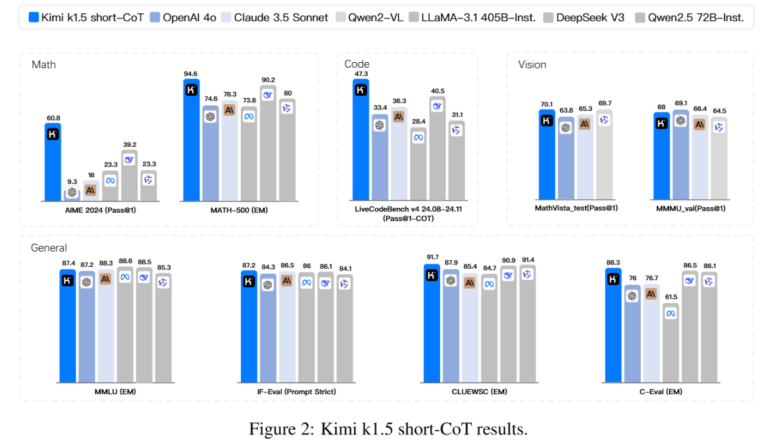
Unlike DeepSeek-R1, Kimi k1.5 can process both text and images, allowing it to draw conclusions across different types of input. The model scores particularly well on multimodal benchmarks like MathVista and MMMU. However, as with all AI models, real-world performance may differ from benchmark results.
As always, however, it remains to be seen how useful the model is in practice beyond benchmarks.
Kimi k1.5 relies on SFT and RL
The development process started with standard pre-training on a massive dataset of text and images to build basic language and visual understanding. The team then fine-tuned the model on a carefully selected smaller dataset (SFT). For tasks with clear right or wrong answers, like math problems, they used "rejection sampling" - generating multiple answers and keeping only the correct ones for training. They also created additional training data showing detailed step-by-step reasoning.
The final phase used reinforcement learning, but with a key difference from typical approaches. Instead of using value functions to evaluate intermediate steps, the team focused on the final outcome. They argue this gives the model more freedom to explore different paths to the correct answer. To keep responses efficient, they added a penalty for overly long answers.
This approach differs significantly from DeepSeek's R-1 and R-1-Zero models. While R-1 uses a simpler reinforcement learning process with rule-based feedback, R-1-Zero took an even more minimal approach, training exclusively with reinforcement learning and no additional data.
Making reasoning more efficient
Since detailed reasoning (long-CoT) produces good results but requires more computing power, the team developed ways to transfer this knowledge to models that give shorter answers. They combined several techniques, including model fusion and "Shortest Rejection Sampling," which picks the most concise correct answer from multiple attempts.
The team also found that increasing the context length (up to 128k tokens) consistently improved performance by allowing for more complex reasoning. Their research also showed that effective reasoning models don't need complicated components like Monte-Carlo Tree Search - similar to what DeepSeek-R1's developers discovered.
Their success in transferring knowledge from longer to shorter models mirrors a broader industry trend. Anthropic probably used similar knowledge distillation techniques for its smaller yet powerful latest Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
Moonshot AI's rapid growth mirrors the model's ambitions. Founded in 2023, the company secured over $1 billion in funding led by Alibaba in February 2024, reaching a $2.5 billion valuation. By August, that value grew to $3.3 billion after additional investment from Tencent and Gaorong Capital. While Kimi k1.5 will power the company's ChatGPT competitor, Moonshot AI hasn't yet made the models publicly available.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.