Here's how OpenAI's DALL-E 3 could leapfrog the competition

All generative AI models for images currently use diffusion models. OpenAI presents an alternative that is significantly faster and could power new models like DALL-E 3.
DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion, or Midjourney use diffusion models that gradually synthesize an image from noise during image generation. The same iterative process is used in audio or video models.
While diffusion models produce great results and can be controlled via text prompts, they are comparatively slow and require anywhere from 10 to 2,000 times more computing power than GANs. This hinders their use in real-time applications.
OpenAI is therefore developing a new variant of generative AI models called Consistency Models.
Consistency models are designed to combine the advantages of diffusion models and GANs
According to OpenAI, consistency models support fast, one-step image synthesis, but also allow for few-step sampling, "to trade compute for sample quality". Consistency models can therefore produce useful results even without an iterative process, and could soon be suitable for real-time applications.
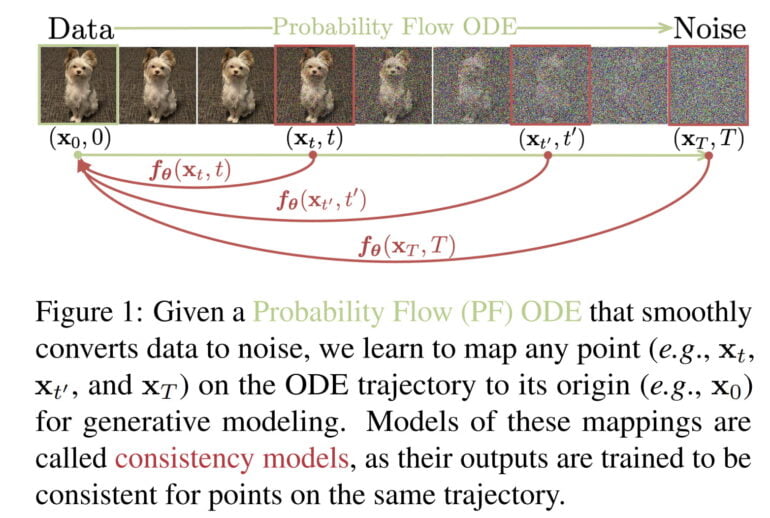
Like diffusion models, they also support zero-shot data editing, e.g. for inpainting, colorization, or super-resolution tasks. Consistency models can either distilled from a pre-trained diffusion model or be trained in isolation. According to OpenAI, consistency models are able to outperform many GANs in singe step generation and all other non-adversarial, single-step generative models.

The company conducted all testing on relatively small networks and image datasets, for example, training a neural network to synthesize cat images. All models were released by the company as open source for research purposes.
A new generative AI architecture for DALL-E 3 and video synthesis?
According to the authors, there are also striking similarities to other AI techniques used in other fields, such as deep Q-learning from reinforcement learning or momentum-based contrastive learning from semi-supervised learning. "This offers exciting prospects for cross-pollination of ideas and methods among these diverse fields.," the team says.
In the months leading up to the release of DALL-E 2, OpenAI had published several articles on diffusion models and finally presented GLIDE, a very impressive model at the time. So the research on consistency models could be an indication that OpenAI is looking for new and more effective generative AI architectures that could, for example, enable a much faster DALL-E 3 and be used for real-time video generation.
OpenAI's current work should therefore be seen as a feasibility study, with a larger AI model being the likely next step. The same architecture could eventually be used for other modalities or for 3D content synthesis.
AI News Without the Hype – Curated by Humans
As a THE DECODER subscriber, you get ad-free reading, our weekly AI newsletter, the exclusive "AI Radar" Frontier Report 6× per year, access to comments, and our complete archive.
Subscribe nowAI news without the hype
Curated by humans.
- Over 20 percent launch discount.
- Read without distractions – no Google ads.
- Access to comments and community discussions.
- Weekly AI newsletter.
- 6 times a year: “AI Radar” – deep dives on key AI topics.
- Up to 25 % off on KI Pro online events.
- Access to our full ten-year archive.
- Get the latest AI news from The Decoder.